 W
WDan is a Mande language spoken primarily in Ivory Coast and Liberia. There is also a population of about 800 speakers in Guinea. Dan is a tonal language, with around 9-11 contour and register tones depending on the dialect.
 W
WDyula is a language of the Mande language family spoken in Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast and Mali. It is one of the Manding languages and is most closely related to Bambara, being mutually intelligible with Bambara as well as Malinke. It is a trade language in West Africa and is spoken by millions of people, either as a first or second language. Like the other Mande languages, it uses tones. It may be written in the Latin, Arabic or N'Ko scripts.
 W
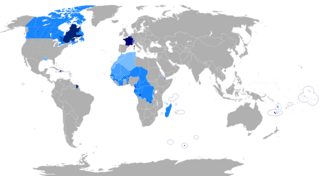
WFrench is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French.
 W
WFula, also known as Fulani or Fulah, is a Senegambian language spoken by more than 65 million people as a set of various dialects in a continuum that stretches across some 20 countries in West and Central Africa. Along with other related languages such as Serer and Wolof, it belongs to the Senegambian branch within the Niger–Congo family, which does not have tones, unlike most other Niger–Congo languages. More broadly, it belongs to the Atlantic geographic grouping within Niger–Congo. It is spoken as a first language by the Fula people from the Senegambia region and Guinea to Cameroon, Nigeria, and Sudan and by related groups such as the Toucouleur people in the Senegal River Valley. It is also spoken as a second language by various peoples in the region, such as the Kirdi of northern Cameroon and northeastern Nigeria.
 W
WPular is a Fula language spoken primarily by the Fula people of Fouta Djallon, Guinea. It is also spoken in parts of Guinea-Bissau, Sierra Leone, and Senegal. There are a small number of speakers in Mali. Pular is spoken by 8.5 million Guineans, about 55% of the national population. This makes Pular the most widely spoken indigenous language in the country. Substantial numbers of Pular speakers have migrated to other countries in West Africa, notably Senegal.
 W
WThe Kpelle language is spoken by the Kpelle people and is part of the Mande family of languages. Guinean Kpelle, spoken by half a million people, concentrated primarily, but not exclusively, in the forest regions of Guinea, whose capital, Nzérékoré, is the third largest city in Guinea and the largest city in the Guinée forestière region of south-eastern Guinea bordering Liberia, Ivory Coast, and Sierra Leone. Liberian Kpelle, spoken by half again as many, is currently taught in schools in Liberia.
 W
WLoma is a Mande language spoken by the Loma people of Liberia and Guinea.
 W
WThe Mano language, also known as Maa, Mah, and Mawe, is a significant Mande language of Liberia and Guinea. It is spoken primarily in Nimba County in north-central Liberia and in Nzérékoré, Lola and Yomou Prefectures in Guinea.
 W
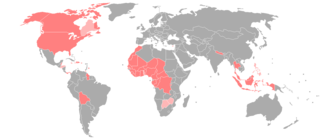
WAmerican Sign Language (ASL) developed in the United States and Canada, but has spread around the world. Local varieties have developed in many countries, but there is little research on which should be considered dialects of ASL and which have diverged to the point of being distinct languages.