 W
WKava or kava kava is a crop of the Pacific Islands. The name kava is from Tongan and Marquesan, meaning 'bitter'; other names for kava include ʻawa (Hawaiʻi), ʻava (Samoa), yaqona or yagona (Fiji), sakau (Pohnpei), seka (Kosrae), and malok or malogu. Kava is consumed for its sedating effects throughout the Pacific Ocean cultures of Polynesia, including Hawaii, Vanuatu, Melanesia, and some parts of Micronesia, such as [Pohnpei & Kosrae]. Kava can be used for medicinal purposes to treat anxiety.
 W
WFlavokavains are a class of chalconoids found in the kava plant. Currently identified types include flavokavain A, flavokavain B, and flavokavain C.
 W
WFlavokavain A is a flavokavain found in the kava plant. It induces apoptosis in bladder cancer cells via a Bax protein-dependent and mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway.
 W
WFlavokavain B is a flavokavain found in the kava plant. In 2010 a paper was published identifying it as a glutathione-depleting hepatotoxin.
 W
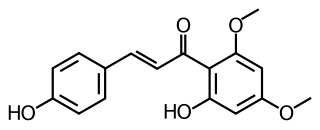
WFlavokavain C is a flavokavain found in the kava plant.
 W
WA nakamal is a traditional meeting place in Vanuatu. It is used for gatherings, ceremonies and the drinking of kava.
 W
WPipermethystine is a toxic alkaloid present in the aerial (aboveground) portions of the kava plant. It is not a kavalactone, containing no lactone structure. Correctly prepared kava root products will contain almost no pipermethystine.