 W
WIn the nineteenth century, the Oregon Country was a disputed region of the Pacific Northwest of North America. The region was occupied by British and French Canadian fur traders from before 1810, and American settlers from the mid-1830s, with its coastal areas north from the Columbia River frequented by ships from all nations engaged in the maritime fur trade, most of these from the 1790s through 1810s being Boston-based. The Oregon Treaty of 1846 ended disputed joint occupancy pursuant to the Treaty of 1818 and established the British-American boundary at the 49th parallel.
 W
WAdventure was built by the crew of Captain Robert Gray on his second voyage in the maritime fur trade to the Northwest Coast of North America. The 45-ton sloop was built to allow the trading venture to access smaller inlets the Columbia could not reach. At the end of his second voyage Gray sold the ship to the Spanish Navy. It was renamed Orcacitas and served the Naval Department of San Blas for some years.
 W
WSamuel Kimbrough Barlow was a pioneer in the area that became the U.S. state of Oregon, and was key in establishing the Barlow Road, the most widely chosen final segment to the Oregon Trail.
 W
WThe Battle of Woody Point was an incident in western Canada in June 1811 involving the Tla-o-qui-aht natives of the Pacific Northwest and the Tonquin, an American merchant ship of the Astor Expedition. The vessel had traveled to Clayoquot Sound off Vancouver Island to trade for furs. Following an argument begun during the bartering, the Tla-o-qui-aht captured the vessel and massacred most of the crew; one remaining sailor then scuttled her by detonating the powder magazine.
 W
WJames Biddle, of the Biddle family, brother of financier Nicholas Biddle and nephew of Capt. Nicholas Biddle, was an American commodore. His flagship was USS Columbus.
 W
WFrançois Norbert Blanchet was a French Canadian-born missionary priest and prelate of the Catholic Church who was instrumental in establishing the Catholic Church presence in the Pacific Northwest. He was one of the first Catholic priests to arrive in what was then known as the Oregon Country and subsequently became the first bishop and archbishop of the Archdiocese of Oregon City.
 W
WJean-Baptiste-Zacharie Bolduc was a Québécois Jesuit. His career started as a missionary in the Pacific Northwest, where he resided for eight years. Later he worked in the Catholic medical efforts in Québec.
 W
WWilliam Robert Broughton was a British naval officer in the late 18th century. As a lieutenant in the Royal Navy, he commanded HMS Chatham as part of the Vancouver Expedition, a voyage of exploration through the Pacific Ocean led by Captain George Vancouver in the early 1790s.
 W
WFort Clatsop was the encampment of the Lewis and Clark Expedition in the Oregon Country near the mouth of the Columbia River during the winter of 1805-1806. Located along the Lewis and Clark River at the north end of the Clatsop Plains approximately 5 miles (8.0 km) southwest of Astoria, the fort was the last encampment of the Corps of Discovery, before embarking on their return trip east to St. Louis.
 W
WThe Columbia District was a fur trading district in the Pacific Northwest region of British North America in the 19th century. Much of its territory overlapped with the disputed Oregon Country. It was explored by the North West Company between 1793 and 1811, and established as an operating fur district around 1810. The North West Company was absorbed into the Hudson's Bay Company in 1821 under which the Columbia District became known as the Columbia Department. The Oregon Treaty of 1846 marked the effective end of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department.
 W
WThomas Lamb Eliot was an Oregon pioneer, minister of one of the first churches on the west coast of the U.S., president of the Portland Children's Home, president of the Oregon Humane Society, a director of the Art Association, director of the Library Association, and founder of Reed College.
 W
WJohn Floyd was a Virginia politician and soldier. He represented Virginia in the United States House of Representatives and later served as the 25th Governor of Virginia.
 W
WFort Astoria was the primary fur trading post of John Jacob Astor's Pacific Fur Company (PFC). A maritime contingent of PFC staff was sent on board the Tonquin, while another party traveled overland from St. Louis. This land based group later became known as the Astor Expedition. Built at the entrance of the Columbia River in 1811, Fort Astoria was the first American-owned settlement on the Pacific coast of North America.
 W
WFort Boise is either of two different locations in the western United States, both in southwestern Idaho. The first was a Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) trading post near the Snake River on what is now the Oregon border, dating from the era when Idaho was included in the British fur company's Columbia District. After several rebuilds, the fort was ultimately abandoned in 1854, after it had become part of United States territory following settlement in 1846 of the northern boundary dispute.
 W
WThe trade center Fort Colvile was built by the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) at Kettle Falls on the Columbia River in 1825 and operated in the Columbia fur district of the company. Named for Andrew Colvile, a London governor of the HBC, the fort was a few miles west of the present site of Colville, Washington. It was an important stop on the York Factory Express trade route to London via the Hudson Bay. The HBC for some time considered Fort Colvile second in importance only to Fort Vancouver, near the mouth of the Columbia, until the foundation of Fort Victoria.
 W
WFort Hall was a fort that was built in 1834 as a fur trading post by Nathaniel Jarvis Wyeth. It was located on the Snake River in the eastern Oregon Country, now part of present-day Bannock County in southeastern Idaho, United States. Wyeth was an inventor and businessman from Boston, Massachusetts, who also founded a post at Fort William, in present-day Portland, Oregon, as part of a plan for a new trading and fisheries company. Unable to compete with the powerful British Hudson's Bay Company, based at Fort Vancouver, in 1837 Wyeth sold both posts to it. Great Britain and the United States both operated in the Oregon Country in these years.
 W
WFort Langley National Historic Site, commonly shortened to Fort Langley, is a former fur trading post of the Hudson's Bay Company in the community of Fort Langley of Langley, British Columbia, Canada. The national historic site sits above the banks of the Bedford Channel across McMillan Island. The national historic site contains a visitor centre and a largely reconstructed trading post that contains ten structures surrounded by wooden palisades.
 W
WFort Nez Percés, later known as (Old) Fort Walla Walla, was a fortified fur trading post on the Columbia River on the territory of modern-day Wallula, Washington. Despite being named after the Nez Perce people, the fort was in the traditional lands of the Walla Walla. Founded in 1818 by the North-West Company, after 1821 it was run by the Hudson's Bay Company until its closure in 1857.
 W
WFort Nisqually was an important fur trading and farming post of the Hudson's Bay Company in the Puget Sound area, part of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department. It was located in what is now DuPont, Washington. Today it is a living history museum located in Tacoma, Washington, USA, within the boundaries of Point Defiance Park. The Fort Nisqually Granary, moved along with the Factor's House from the original site of the second fort to this park, is a U.S. National Historic Landmark. Built in 1843, the granary is the oldest building in Washington state and one of the only surviving examples of a Hudson's Bay Company "post on sill" structure. The Factor's House and the granary are the only surviving Hudson's Bay Company buildings in the United States.
 W
WFort Umpqua was a trading post built by the Hudson's Bay Company in the company's Columbia District, in what is now the U.S. state of Oregon. It was first established in 1832 and moved and rebuilt in 1836.
 W
WFort Vancouver was a 19th-century fur trading post that was the headquarters of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department, located in the Pacific Northwest. Named for Captain George Vancouver, the fort was located on the northern bank of the Columbia River in present-day Vancouver, Washington. The fort was a major center of the regional fur trading. Every year trade goods and supplies from London arrived either via ships sailing to the Pacific Ocean or overland from Hudson Bay via the York Factory Express. Supplies and trade goods were exchanged with a plethora of Indigenous cultures for fur pelts. Furs from Fort Vancouver were often shipped to the Chinese port of Guangzhou where they were traded for Chinese manufactured goods for sale in the United Kingdom. At its pinnacle, Fort Vancouver watched over 34 outposts, 24 ports, six ships, and 600 employees. Today, a full-scale replica of the fort, with internal buildings, has been constructed and is open to the public as Fort Vancouver National Historic Site.
 W
WGabriel Franchère was a French Canadian author and explorer of the Pacific Northwest.
 W
WFrench Prairie is a prairie located in Marion County, Oregon, United States, in the Willamette Valley between the Willamette River and the Pudding River, north of Salem. It was named for some of the earliest settlers of that part of the Oregon Country, French Canadian/Métis people who were mostly former employees of the Hudson's Bay Company. French Prairie is also known as an early Métis settlement in the Pacific Northwest history.
 W
WPeter French was a rancher in the western United States in the late 19th century. The community of Frenchglen, Oregon was partially named for him.
 W
WRobert Gray was an American merchant sea captain who is known for his achievements in connection with two trading voyages to the northern Pacific coast of North America, between 1790 and 1793, which pioneered the American maritime fur trade in that region. In the course of those voyages, Gray explored portions of that coast and, in 1790, completed the first American circumnavigation of the world. He was noted for coming upon and naming the Columbia River in 1792, while on his second voyage.
 W
WAlexander Henry 'The Younger', was an early Canadian fur trader, explorer and diarist. From 1799 until his premature death in 1814 he kept an extensive diary which is the most complete record ever printed of the daily life of a fur trader in the north. His journals were an account of "personal doings", but cannot be considered a diary of inward thoughts. These journals cover everything that happened to him in a most matter-of-fact manner and have yielded much material for historians and other researchers of that time period in North American history. Henry married the daughter of Liard Ah-ne-him-ish Cottonwood Little Shell, the brother of the Great Pembina Chippewa Nation Grand Chief La Petite Coquille Little Shell I Corbeau and son of The Great Sioux Nation & The Great Pembina Chippewa Nation Wazhazha Mdewakanton Grand Chief Little Crow I Petit Corbeau Red Wing I.
 W
WThe history of British Columbia covers the period from the arrival of Paleo-Indians thousands of years ago to the present day. Prior to European colonization, the lands encompassing present-day British Columbia were inhabited for millennia by a number of First Nations.
 W
WThe Hudson's Bay Company is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada and the United States. It had been a member of the International Association of Department Stores from 2001 to 2005.
 W
WWilson Price Hunt was an early pioneer and explorer of the Oregon Country in the Pacific Northwest of North America. Employed as an agent in the fur trade under John Jacob Astor, Hunt organized and led the greater part of a group of about 60 men on an overland expedition to establish a fur trading outpost at the mouth of the Columbia river. The Astorians, as they have become known, were the first major party to cross to the Pacific after the Lewis and Clark expedition.
 W
WPaul Kane was an Irish-born Canadian painter, famous for his paintings of First Nations peoples in the Canadian West and other Native Americans in the Columbia District.
 W
WHall Jackson Kelley was an American settler and writer from New England known for his strong advocacy for settlement by the United States of the Oregon Country in the 1820s and 1830s. A native of New Hampshire, he was a school teacher in Maine and Massachusetts, and a longtime resident of the latter state after graduating from Harvard College.
 W
WJason Lee was a Canadian Methodist Episcopalian missionary and pioneer in the Pacific Northwest. He was born on a farm near Stanstead, Quebec.
 W
WDavid Leslie was an American missionary and pioneer in what became the state of Oregon. A native of New Hampshire, he joined Jason Lee as a missionary at the Methodist Mission in the Oregon Country in 1836. In that region he participated in the early movement to start a government and his home was used for some of these meetings. With the closing of the mission he became a founder of the city of Salem, Oregon, and board member of the Oregon Institute, which later became Willamette University.
 W
WThe maritime fur trade was a ship-based fur trade system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otters and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska. The furs were mostly sold in China in exchange for tea, silks, porcelain, and other Chinese goods, which were then sold in Europe and the United States. The maritime fur trade was pioneered by Russians, working east from Kamchatka along the Aleutian Islands to the southern coast of Alaska. British and Americans entered during the 1780s, focusing on what is now the coast of British Columbia. The trade boomed around the beginning of the 19th century. A long period of decline began in the 1810s. As the sea otter population was depleted, the maritime fur trade diversified and transformed, tapping new markets and commodities, while continuing to focus on the Northwest Coast and China. It lasted until the middle to late 19th century.
 W
WJohn Minto IV was an American pioneer born in Wylam, England. He was a prominent sheep farmer in the U.S. state of Oregon and a four-time Republican representative in the state legislature. Minto also volunteered for the militia during the Cayuse War and years later helped locate Minto and Santiam passes through the Cascade Mountains east of Salem, Oregon.
 W
WThe North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great wealth at stake, tensions between the companies increased to the point where several minor armed skirmishes broke out, and the two companies were forced by the British government to merge.
 W
WThe Oregon boundary dispute or the Oregon Question was a 19th-century territorial dispute over the political division of the Pacific Northwest of North America between several nations that had competing territorial and commercial aspirations over the region.
 W
WThe Oregon Institute was an American school located in the Willamette Valley of the Oregon Country during the 19th century. Begun in 1842, it was the first school built for European Americans west of Missouri. Founded by members of the Methodist Mission, it was located in what is now Salem, Oregon. The school began as a pre-college institution, but by 1853 was developed as Willamette University. The school's three-story building was a prominent feature in the early days of Oregon; it served as a meeting place for the Oregon Territorial Legislature when it first moved to Salem.
 W
WOregon pioneer history (1806–1890) is the period in the history of Oregon Country and Oregon Territory, in the present day state of Oregon and Northwestern United States.
 W
WThe Oregon Trail was a 2,170-mile (3,490 km) east-west, large-wheeled wagon route and emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what is now the state of Kansas and nearly all of what are now the states of Nebraska and Wyoming. The western half of the trail spanned most of the current states of Idaho and Oregon.
 W
WThe Oregon Treaty is a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to the Oregon Country; the area had been jointly occupied by both Britain and the U.S. since the Treaty of 1818.
 W
WThe Pacific Fur Company (PFC) was an American fur trade venture wholly owned and funded by John Jacob Astor that functioned from 1810 to 1813. It was based in the Pacific Northwest, an area contested over the decades between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, the Spanish Empire, the United States of America and the Russian Empire.
 W
WGeneral Joel Palmer was an American pioneer of the Oregon Territory in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. He was born in Canada, and spent his early years in New York and Pennsylvania before serving as a member of the Indiana House of Representatives.
 W
WSamuel Parker (1779–1866) was an American missionary in the Pacific Northwest, He was the first Presbyterian minister in the region. He scouted locations for potential missions with Marcus Whitman among the Liksiyu and Niimíipu nations in 1835.
 W
WRobert Gray's Columbia River expedition was conducted in 1792 in the Pacific Northwest. In May of that year, American merchant sea captain Robert Gray sailed into the Columbia River, becoming the first recorded European to navigate into it. The voyage, conducted on the privately owned Columbia Rediviva, was eventually used as a basis for the United States' claim on the Pacific Northwest, although its relevance to the claim was disputed by the British. As a result of the outcome the river was afterwards named after the ship. Gray spent nine days on the river trading fur pelts before sailing out of the river.
 W
WThe Sager orphans were the children of Henry and Naomi Sager. In April 1844 the Sager family took part in the great westward migration and started their journey along the Oregon Trail. During it, both Henry and Naomi died and left their seven children orphaned. Later adopted by Marcus and Narcissa Whitman, missionaries in what is now Washington, they were orphaned a second time, when both their new parents, as well as brothers John and Francis Sager, were killed during the Whitman massacre in November 1847. About 1860 Catherine, the oldest daughter, wrote a first-hand account of their journey across the plains and their life with the Whitmans. Today it is regarded as one of the most authentic accounts of the American westward migration.
 W
WJames Sinclair was a trader and explorer with the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC). He twice led large parties of settlers from the Red River Colony to the Columbia River valley. These were both authorized by the HBC as a part of grandiose plans to strengthen British claims in the Oregon boundary dispute.
 W
WThe Star of Oregon was a schooner sailing vessel of the mid-19th century used on the west coast of North America. It was the first American sailing ship built in what is now the U.S. state of Oregon. Pioneer settlers built the ship from 1840 to 1842 in order to sail it to California and exchange it for livestock. During World War II a Liberty ship was named the SS Star of Oregon in honor of the 19th century sailing vessel.
 W
WRobert Stuart was a Scottish-born, Canadian and American fur trader, best known as a member of the first European-American party to cross South Pass during an overland expedition from Fort Astoria to Saint Louis in 1811. He was a member of the North West Company (NWC) until recruited by John Jacob Astor to develop the new Pacific Fur Company, which was based at Fort Astoria, on the coast of present-day Oregon. Astor intended the venture to develop a continent-wide commercial empire in fur trading.
 W
WJackson Sundown, born Waaya-Tonah-Toesits-Kahn, was a Native American rodeo rider who has become a folk-hero for his mythic performance in the 1916 Pendleton Round-Up, largely popularized by Ken Kesey's novel The Last Go 'Round.
 W
WThe Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, is an international treaty signed in 1818 between the United States and the United Kingdom. This treaty resolved standing boundary issues between the two nations. The treaty allowed for joint occupation and settlement of the Oregon Country, known to the British and in Canadian history as the Columbia District of the Hudson's Bay Company, and including the southern portion of its sister district New Caledonia.
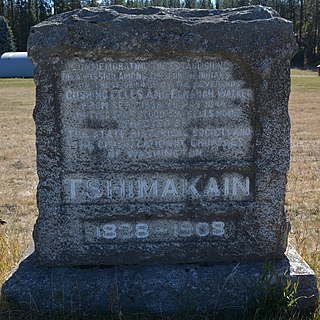 W
WThe Tshimakain Mission started in September 1838, with the arrival of Congregationalist missionaries Cushing and Myra Fairbanks Eells and Elkanah and Mary Richardson Walker to the area along Chamokane Creek at the community of Ford, Washington. Fort Colvile Chief Factor Archibald McDonald recommended the area to Eells and Walker on their first visit to the area.
 W
WThe Whitman massacre was the murder of Washington missionaries Marcus Whitman and his wife Narcissa, along with eleven others, on November 29, 1847. They were killed by members of the Cayuse tribe who accused Whitman of having poisoned 200 Cayuse in his medical care. The incident began the Cayuse War. It took place in southeastern Washington state near the town of Walla Walla, Washington and was one of the most notorious episodes in the U.S. settlement of the Pacific Northwest. Whitman had helped lead the first wagon train to cross Oregon's Blue Mountains and reach the Columbia River via the Oregon Trail, and this incident was the climax of several years of complex interaction between him and the local Native Americans. The story of the massacre shocked the United States Congress into action concerning the future territorial status of the Oregon Country. The Oregon Territory was established on August 14, 1848.
 W
WWhitman Mission National Historic Site is a United States National Historic Site located just west of Walla Walla, Washington, at the site of the former Whitman Mission at Waiilatpu. On November 29, 1847, Dr. Marcus Whitman, his wife Narcissa Whitman, and 11 others were slain by Native Americans of the Cayuse. The site commemorates the Whitmans, their role in establishing the Oregon Trail, and the challenges encountered when two cultures meet.
 W
WMarcus Whitman was an American physician and missionary.
 W
WNarcissa Prentiss Whitman was an American missionary in the Oregon Country of what would become the state of Washington. On their way to found the Protestant Whitman Mission in 1836 with her husband, Marcus, near modern-day Walla Walla, Washington, she and Eliza Hart Spalding became the first documented European-American women to cross the Rocky Mountains.
 W
WJohn Work was a Chief Factor of the Hudson's Bay Company and head of one of the original founding families in Victoria, British Columbia. Work joined the Hudson's Bay Company in 1814 and served in many capacities until his death in 1861, ultimately becoming a member of the company's Board of Management for its Western Department. He also served on Vancouver Island’s Legislative Council. At the time of his death, Work was the largest private land owner of Vancouver Island. Work left an important legacy in the form of sixteen journals which chronicle his trading expeditions from 1823 to 1851. His journals provide a detailed record of Pacific Northwest land features, native peoples, and the Hudson’s Bay Company’s fur trading business in the early 19th century.
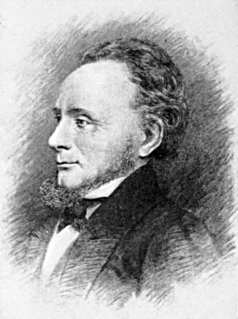 W
WNathaniel Jarvis Wyeth was an American inventor and businessman in Boston, Massachusetts who contributed greatly to its ice industry. Due to his inventions, Boston could harvest and ship ice internationally. In the 1830s, he was also a mountain man who led two expeditions to the Northwest and set up two trading posts, one in present-day Idaho and one in present-day Oregon.