 W
WAn airplane or aeroplane is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spectrum of uses for airplanes includes recreation, transportation of goods and people, military, and research. Worldwide, commercial aviation transports more than four billion passengers annually on airliners and transports more than 200 billion tonne-kilometers of cargo annually, which is less than 1% of the world's cargo movement. Most airplanes are flown by a pilot on board the aircraft, but some are designed to be remotely or computer-controlled such as drones.
 W
WAn autogyro, also known as a gyroplane or gyrocopter, is a type of rotorcraft that uses an unpowered rotor in free autorotation to develop lift. Forward thrust is provided independently, by an engine-driven propeller. While similar to a helicopter rotor in appearance, the autogyro's rotor must have air flowing across the rotor disc to generate rotation, and the air flows upwards through the rotor disc rather than down.
 W
WA backpack helicopter is a helicopter motor and rotor and controls assembly that can be strapped to a person's back, so they can walk about on the ground wearing it, and can use it to fly. It uses a harness like a parachute harness and should have a strap between the legs. Some designs may use a ducted fan design to increase upward thrust. Several inventors have tried to make backpack helicopters, with mixed results.
 W
WA blended wing body (BWB), also known as blended body or hybrid wing body (HWB), is a fixed-wing aircraft having no clear dividing line between the wings and the main body of the craft. The aircraft has distinct wing and body structures, which are smoothly blended together with no clear dividing line. This contrasts with a flying wing, which has no distinct fuselage, and a lifting body, which has no distinct wings. A BWB design may or may not be tailless.
 W
WThe X-53 Active Aeroelastic Wing (AAW) development program is a completed American research project that was undertaken jointly by the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), Boeing Phantom Works and NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, where the technology was flight tested on a modified McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet. Active Aeroelastic Wing Technology is a technology that integrates wing aerodynamics, controls, and structure to harness and control wing aeroelastic twist at high speeds and dynamic pressures. By using multiple leading and trailing edge controls like "aerodynamic tabs", subtle amounts of aeroelastic twist can be controlled to provide large amounts of wing control power, while minimizing maneuver air loads at high wing strain conditions or aerodynamic drag at low wing strain conditions. This program was the first full-scale proof of AAW technology.
 W
WIn aircraft design, a chine is a longitudinal line of sharp change in the cross-section profile of the fuselage or similar body. The term chine originates in boatbuilding, where it applies to a sharp profile change in the hull of a boat. In a flying boat hull or floatplane float, the longitudinal line of sharp change in cross-section where the bottom plane meets the sidewall, is an example of a chine.
 W
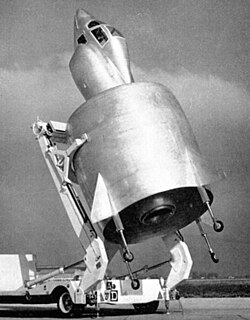
WA coleopter is a type of VTOL aircraft design that uses a ducted fan as the primary fuselage of the entire aircraft. Generally they appear to be a large barrel-like extension at the rear, with a small cockpit area suspended above it. Coleopters are generally designed as tail-sitters. The term is an anglicisation of the French coléoptère "beetle" after the first actual implementation of this design, the SNECMA Coléoptère of the mid-1950s.
 W
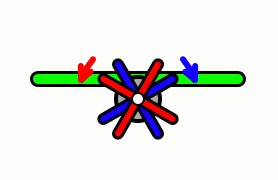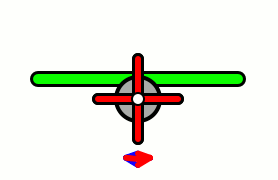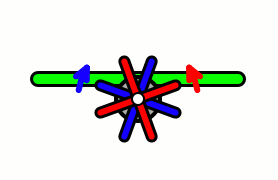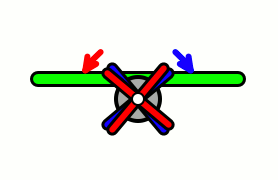
WAircraft equipped with contra-rotating propellers, also referred to as CRP, coaxial contra-rotating propellers, or high-speed propellers, apply the maximum power of usually a single piston or turboprop engine to drive two coaxial propellers in contra-rotation. Two propellers are arranged one behind the other, and power is transferred from the engine via a planetary gear or spur gear transmission. Contra-rotating propellers are also known as counter-rotating propellers, although counter-rotating propellers is much more widely used when referring to airscrews on separate non-coaxial shafts turning in opposite directions.
 W
WConventional landing gear, or tailwheel-type landing gear, is an aircraft undercarriage consisting of two main wheels forward of the center of gravity and a small wheel or skid to support the tail. The term taildragger is also used, although some argue it should apply only to those aircraft with a tailskid rather than a wheel.
 W
WIn aeronautics, dihedral is the angle between the left and right wings of an aircraft. "Dihedral" is also used to describe the effect of sideslip on the rolling of the aircraft.
 W
WA double-deck aircraft has two decks for passengers; the second deck may be only a partial deck, and may be above or below the main deck. Most commercial aircraft have one passenger deck and one cargo deck for luggage and ULD containers, but only a few have two decks for passengers, typically above or below a third deck for cargo. Most of them are disappearing.
 W
WThe FanWing is an aircraft configuration in which a horizontal-axis cross-flow fan is used in close conjunction with a fixed wing. The fan forces airflow over the fixed surface to provide both lift and forward thrust.
 W
WA fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct from rotary-wing aircraft, and ornithopters. The wings of a fixed-wing aircraft are not necessarily rigid; kites, hang gliders, variable-sweep wing aircraft and airplanes that use wing morphing are all examples of fixed-wing aircraft.
 W
WA Flettner airplane is a type of rotor airplane which uses a Flettner rotor to provide lift. The rotor comprises a spinning cylinder with circular end plates and, in an aircraft, spins about a spanwise horizontal axis. When the aircraft moves forward, the Magnus effect creates lift.
 W
WA flying boat is a fixed-winged seaplane with a hull, allowing it to land on water, that usually has no type of landing gear to allow operation on land. It differs from a floatplane as it uses a purpose-designed fuselage which can float, granting the aircraft buoyancy. Flying boats may be stabilized by under-wing floats or by wing-like projections from the fuselage.
 W
WA four-engined jet, sometimes called a quadjet, is a jet aircraft powered by four engines. The presence of four engines offers increased power, allowing such aircraft to be used as airliners, freighters, and military aircraft. Many of the first purpose-built jet airliners had four engines, among which stands the De Havilland Comet, the world's first commercial jetliner. In the decades following their introduction, their use has gradually declined due to a variety of factors, including the approval of twin-engine jets to fly farther from diversion airports and an increased emphasis on fuel efficiency.
 W
WA ground-effect vehicle (GEV), also called a wing-in-ground-effect (WIG), ground-effect craft, wingship, flarecraft or ekranoplan, is a vehicle that is able to move over the surface by gaining support from the reactions of the air against the surface of the earth or water. Typically, it is designed to glide over a level surface by making use of ground effect, the aerodynamic interaction between the moving wing and the surface below. Some models can operate over any flat area such as frozen lakes or flat plains similar to a hovercraft.
 W
WA gyrodyne is a type of VTOL aircraft with a helicopter rotor-like system that is driven by its engine for takeoff and landing only, and includes one or more conventional propeller or jet engines to provide forward thrust during cruising flight. During forward flight the rotor is unpowered and free-spinning, like an autogyro, and lift is provided by a combination of the rotor and conventional wings. The gyrodyne is one of a number of similar concepts which attempt to combine helicopter-like low-speed performance with conventional fixed-wing high-speeds, including tiltrotors and tiltwings.
 W
WHang gliding is an air sport or recreational activity in which a pilot flies a light, non-motorised foot-launched heavier-than-air aircraft called a hang glider. Most modern hang gliders are made of an aluminium alloy or composite frame covered with synthetic sailcloth to form a wing. Typically the pilot is in a harness suspended from the airframe, and controls the aircraft by shifting body weight in opposition to a control frame.
 W
WA helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally-spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of VTOL aircraft cannot perform.
 W
WA human-powered helicopter (HPH) is a helicopter powered solely by one or more humans carried on board. As in other human-powered aircraft, the power is usually generated by pedalling. It remains a considerable engineering challenge to obtain both the power-to-weight ratio and rotor efficiency required to sustain a helicopter in flight.
 W
WA hydrogen-powered aircraft is an aeroplane that uses hydrogen fuel as a power source. Hydrogen can either be burned in a jet engine or another kind of internal combustion engine, or can be used to power a fuel cell to generate electricity to power a propeller. Unlike most aircraft, which store fuel in the wings, hydrogen-powered aircraft are usually designed with the hydrogen fuel tanks inside the fuselage.
 W
WA jet pack, rocket belt, or rocket pack is a device worn on the back which uses jets of gas or liquid to propel the wearer through the air. The concept has been present in science fiction for almost a century and became widespread in the 1960s. Real jet packs have been developed using a variety of mechanisms, but their uses are much more limited than their fictional counterparts because of the challenges of the Earth's atmosphere, gravity, the low energy density of utilisable fuels, and the human body not being suited to flight, and they are principally used for stunts. A practical use for the jet pack has been in extra-vehicular activities for astronauts because of the apparent weightlessness and lack of friction-creating atmosphere in orbit. The term jet suit is used for a system incorporating a jet pack and associated jets attached to the arms to increase manoeuvrability.
 W
WA kite is a tethered heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create lift and drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. Kites often have a bridle and tail to guide the face of the kite so the wind can lift it. Some kite designs don’t need a bridle; box kites can have a single attachment point. A kite may have fixed or moving anchors that can balance the kite. One technical definition is that a kite is “a collection of tether-coupled wing sets“. The name derives from its resemblance to a hovering bird.
 W
WLift fan is an aircraft configuration in which lifting fans are located in large holes in an otherwise conventional fixed wing or fuselage. It is used for V/STOL operation.
 W
WA lifting body is a fixed-wing aircraft or spacecraft configuration in which the body itself produces lift. In contrast to a flying wing, which is a wing with minimal or no conventional fuselage, a lifting body can be thought of as a fuselage with little or no conventional wing. Whereas a flying wing seeks to maximize cruise efficiency at subsonic speeds by eliminating non-lifting surfaces, lifting bodies generally minimize the drag and structure of a wing for subsonic, supersonic and hypersonic flight, or spacecraft re-entry. All of these flight regimes pose challenges for proper flight safety.
 W
WA monocopter or gyropter is a rotorcraft that uses a single rotating blade. The concept is similar to the whirling helicopter seeds that fall from some trees. The name gyropter is sometimes applied to monocopters in which the entire aircraft rotates about its center of mass as it flies. The name "monocopter" has also been applied to the personal jet pack constructed by Andreas Petzoldt.
 W
WA narrow-body aircraft or single-aisle aircraft is an airliner arranged along a single aisle, permitting up to 6-abreast seating in a cabin below 4 metres (13 ft) of width. In contrast, a wide-body aircraft is a larger airliner usually configured with multiple aisles and a fuselage diameter of more than 5 metres (16 ft), allowing at least seven-abreast seating and often more travel classes.
 W
WAn oblique wing is a variable geometry wing concept. On an aircraft so equipped, the wing is designed to rotate on center pivot, so that one tip is swept forward while the opposite tip is swept aft. By changing its sweep angle in this way, drag can be reduced at high speed without sacrificing low speed performance. This is a variation on the classic swing-wing design, intended to simplify construction and retain the center of gravity as the sweep angle is changed.
 W
WAn ornithopter is an aircraft that flies by flapping its wings. Designers seek to imitate the flapping-wing flight of birds, bats, and insects. Though machines may differ in form, they are usually built on the same scale as these flying creatures. Manned ornithopters have also been built, and some have been successful. The machines are of two general types: those with engines, and those powered by the muscles of the pilot.
 W
WParagliding is the recreational and competitive adventure sport of flying paragliders: lightweight, free-flying, foot-launched glider aircraft with no rigid primary structure. The pilot sits in a harness or lies supine in a cocoon-like 'speed bag' suspended below a fabric wing. Wing shape is maintained by the suspension lines, the pressure of air entering vents in the front of the wing, and the aerodynamic forces of the air flowing over the outside.
 W
WA podded engine is a jet engine that has been built up and integrated in its nacelle. This may be done in a podding facility as part of an aircraft assembly process. The nacelle contains the engine, engine mounts and parts which are required to run the engine in the aircraft, known as the EBU. The nacelle consists of an inlet, an exhaust nozzle and a cowling which opens for access to the engine accessories and external tubing. The exhaust nozzle may include a thrust reverser. The podded engine is a complete powerplant, or propulsion system, and is usually attached below the wing on large aircraft like commercial airliners or to the rear fuselage on smaller aircraft such as business jets.
 W
WA proprotor is a spinning airfoil that function as both an airplane-style propeller and a helicopter-style rotor. Several proprotor-equipped convertiplanes, such as the Bell Boeing V-22 Osprey tiltrotor, are capable of switching back and forth between flying akin to both helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft. Accordingly this type of airfoil has been predominantly applied to vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft.
 W
WAn aircraft constructed with a push-pull configuration has a combination of forward-mounted tractor (pull) propellers, and backward-mounted (pusher) propellers.
 W
WIn an aircraft with a pusher configuration, the propeller(s) are mounted behind their respective engine(s). According to British aviation author Bill Gunston, a "pusher propeller" is one mounted behind the engine, so that the drive shaft is in compression in normal operation.
 W
WA rocket-powered aircraft or rocket plane is an aircraft that uses a rocket engine for propulsion, sometimes in addition to airbreathing jet engines. Rocket planes can achieve much higher speeds than similarly sized jet aircraft, but typically for at most a few minutes of powered operation, followed by a gliding flight. Unhindered by the need for oxygen from the atmosphere, they are suitable for very high-altitude flight. They are also capable of delivering much higher acceleration and shorter takeoffs. Many rocket aircraft may be drop launched from transport planes, as take-off from ground may leave them with insufficient time to reach high altitudes.
 W
WA rotorcraft or rotary-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft with rotary wings or rotor blades, which generate lift by rotating around a vertical mast. Several rotor blades mounted on a single mast are referred to as a rotor. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) defines a rotorcraft as "supported in flight by the reactions of the air on one or more rotors".
 W
WAn S-duct is a type of jet engine intake duct used in several types of trijet aircraft. In this configuration, the intake is in the upper rear center of the aircraft, above or below the stabilizer, while the exhaust and engine is at the rear of the aircraft. The S-duct is located in the tail, or empennage, of the aircraft. The shape of the S-duct is distinctive and easily recognized, and was used in several aircraft, beginning in 1962 with the Hawker Siddeley Trident. Currently, the Dassault Falcon 8X and Dassault Falcon 900 business jets are the only aircraft in production that use the S-duct design.
 W
WIn aircraft design, a stepless cockpit means that the nose of the aircraft has no separate "windscreen" panels directly in front of the pilot's or co-pilot's seating positions, and generally has no "breaks" in the nose contour — curved or otherwise — from their absence. In the conventional design, the pilot's cabin is a different part of the aircraft than the nose. The stepless design is believed to help make the plane more aerodynamic thus aiding speed and fuel efficiency. The stepless design did, however, present serious challenges to the inclusion of a nose-mount turreted gun position, in eras where manned or remotely-aimed gun turrets were still important for a bomber's defensive needs.
 W
WA tail-sitter, or tailsitter, is a type of VTOL aircraft that takes off and lands on its tail, then tilts horizontally for forward flight.
 W
WA tethered, moored or captive balloon is a balloon that is restrained by one or more tethers attached to the ground and so it cannot float freely. The base of the tether is wound around the drum of a winch, which may be fixed or mounted on a vehicle, and is used to raise and lower the balloon.
 W
WA three-surface aircraft or sometimes three-lifting-surface aircraft has a foreplane, a central wing and a tailplane. The central wing surface always provides lift and is usually the largest, while the functions of the fore and aft planes may vary between types and may include lift, control and/or stability.
 W
WA tiltjet is an aircraft propulsion configuration that was historically tested for proposed Vertical Take-off and Landing (VTOL)-capable fighters.
 W
WA tiltrotor is an aircraft which generates lift and propulsion by way of one or more powered rotors mounted on rotating shafts or nacelles usually at the ends of a fixed wing. Almost all tiltrotors use a transverse rotor design, with a few exceptions that use other multirotor layouts.
 W
WA tiltwing aircraft features a wing that is horizontal for conventional forward flight and rotates up for vertical takeoff and landing. It is similar to the tiltrotor design where only the propeller and engine rotate. Tiltwing aircraft are typically fully capable of VTOL operations.
 W
WIn aviation, the term tractor configuration refers to an aircraft constructed in the standard configuration with its engine mounted with the propeller in front of it so that the aircraft is "pulled" through the air. Oppositely, the pusher configuration places the airscrew behind and propels the aircraft forward. Through common usage, the word "propeller" has come to mean any airscrew, whether it actually propels or pulls the plane.
 W
WTricycle gear is a type of aircraft undercarriage, or landing gear, arranged in a tricycle fashion. The tricycle arrangement has a single nose wheel in the front, and two or more main wheels slightly aft of the center of gravity. Tricycle gear aircraft are the easiest for takeoff, landing and taxiing, and consequently the configuration is the most widely used on aircraft.
 W
WA trijet is a jet aircraft powered by three jet engines. In general, passenger airline trijets are considered to be second-generation jet airliners, due to their innovative engine locations, in addition to the advancement of turbofan technology. Trijets are more efficient than quadjets, but not as efficient as twinjets, which replaced trijets as larger and more reliable turbofan engines became available.
 W
WA wide-body aircraft, also known as a twin-aisle aircraft, is an airliner with a fuselage wide enough to accommodate two passenger aisles with seven or more seats abreast. The typical fuselage diameter is 5 to 6 m. In the typical wide-body economy cabin, passengers are seated seven to ten abreast, allowing a total capacity of 200 to 850 passengers. The largest wide-body aircraft are over 6 m (20 ft) wide, and can accommodate up to eleven passengers abreast in high-density configurations.
 W
WA twin-boom aircraft is characterised by two longitudinal booms. The booms may contain ancillary items such as fuel tanks and/or provide a supporting structure for other items. Typically, twin tailbooms support the tail surfaces, although on some types such as the Rutan Model 72 Grizzly the booms run forward of the wing. The twin-boom configuration is distinct from twin-fuselage designs in that it retains a central fuselage.
 W
WA twin-fuselage aircraft has two main fuselages. It is distinct from the twin-boom configuration which has a single main fuselage with two subsidiary boom structures.
 W
WA twinjet or twin-engine jet is a jet aircraft powered by two engines. A twinjet is able to fly well enough to land with a single working engine, making it safer than a single-engine aircraft in the event of failure of an engine. Fuel efficiency of a twinjet is better than that of aircraft with more engines. These considerations have led to the widespread use of aircraft of all types with twin engines, including airliners, fixed-wing military aircraft, and others.
 W
WA variable-incidence wing has an adjustable angle of incidence relative to its fuselage. This allows the wing to operate at a high angle of attack for take-off and landing while allowing the fuselage to remain close to horizontal.
 W
WA waverider is a hypersonic aircraft design that improves its supersonic lift-to-drag ratio by using the shock waves being generated by its own flight as a lifting surface, a phenomenon known as compression lift.
 W
WA wide-body aircraft, also known as a twin-aisle aircraft, is an airliner with a fuselage wide enough to accommodate two passenger aisles with seven or more seats abreast. The typical fuselage diameter is 5 to 6 m. In the typical wide-body economy cabin, passengers are seated seven to ten abreast, allowing a total capacity of 200 to 850 passengers. The largest wide-body aircraft are over 6 m (20 ft) wide, and can accommodate up to eleven passengers abreast in high-density configurations.
 W
WThe wing configuration of a fixed-wing aircraft is its arrangement of lifting and related surfaces.
 W
WIn aerodynamics, wing loading is the total mass of an aircraft or flying animal divided by the area of its wing. The stalling speed of an aircraft in straight, level flight is partly determined by its wing loading. An aircraft or animal with a low wing loading has a larger wing area relative to its mass, as compared to one with a high wing loading.
 W
WWingtip devices are intended to improve the efficiency of fixed-wing aircraft by reducing drag. Although there are several types of wing tip devices which function in different manners, their intended effect is always to reduce an aircraft's drag by partial recovery of the tip vortex energy. Wingtip devices can also improve aircraft handling characteristics and enhance safety for following aircraft. Such devices increase the effective aspect ratio of a wing without greatly increasing the wingspan. Extending the span would lower lift-induced drag, but would increase parasitic drag and would require boosting the strength and weight of the wing. At some point, there is no net benefit from further increased span. There may also be operational considerations that limit the allowable wingspan.