 W
WThe construction of Gothic cathedrals was an ambitious, expensive, and technically demanding aspect of life in the Late Middle Ages.
 W
WGothic architecture is an architectural style that was popular in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France region of northern France as a development of Norman architecture. The style at the time was sometimes known as opus Francigenum ; the term Gothic was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the architecture of classical antiquity.
 W
WThe Gothic style of architecture was strongly influenced by the Romanesque architecture which preceded it; by the growing population and wealth of European cities, and by the desire to express national grandeur. It was also influenced by theological doctrines which called for more interior light as a symbol of divinity, and by the practical necessity of many churches to accommodate large numbers of pilgrims. It was especially by technical improvements in vaulting and buttresses which allowed much greater height and larger windows.
 W
WInternational Gothic is a period of Gothic art which began in Burgundy, France, and northern Italy in the late 14th and early 15th century. It then spread very widely across north-western and central regions of Europe, hence the name for the period, which was introduced by the French art historian Louis Courajod at the end of the 19th century.
 W
WBrick Gothic is a specific style of Gothic architecture common in Northeast and Central Europe especially in the regions in and around the Baltic Sea, which do not have resources of standing rock, but in many places many glacial boulders. The buildings are essentially built using bricks. Buildings classified as Brick Gothic are found in Belgium, Netherlands, Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Kaliningrad, Denmark, Sweden and Finland.
 W
WThis is a list of buildings which are representatives of Gothic architecture.
 W
WThe list of medieval bridges in France comprises all bridges built between 500 and 1500 AD in what is today France, that is including regions which were not part of the country in the Middle Ages, such as Burgundy, Alsace, Lorraine and Savoie. Along with those Roman bridges which remained in service throughout the period, there are in total over 700 structures known.
 W
WThe Romano-Gothic is term sometimes used for the architectural style, also called Early Gothic, which evolved in Europe in the 12th century from the Romanesque style, and was an early style in Gothic architecture. In England "Early English Gothic" remains the usual term. The style is characterized by rounded and pointed arches on a vertical plane. Flying buttresses were used, but are mainly undecorated. Romanesque buttresses were also used. Romano-Gothic began to use the decorative elements of Gothic architecture, but not the constructional principles of more fully Gothic buildings. Especially in Germany, the term is used of relatively late buildings in a cautious provincial version of Gothic.
 W
WThe term Brick Gothic is used for what more specifically is called Baltic Brick Gothic or North German Brick Gothic. That part of Gothic architecture, widespread in Northern Germany, Denmark, Poland and the Baltic states, is commonly identified with the sphere of influence of the Hanseatic League. But there is a continuous mega-region of Gothic brick architecture, or Brick Gothic in a sense based on the facts, from the Strait of Dover to Finland and Lake Peipus and to the Sub-Carpathian region of southeastern Poland and southwestern Ukraine.
 W
WThe Cathedral of Santa María la Menor in the Colonial City of Santo Domingo is dedicated to St. Mary of the Incarnation. It is the oldest still standing cathedral in the Americas, begun in 1514 and completed in 1541. It is the Cathedral of the Archbishop of Santo Domingo who has the honorary title of Primate of the Indies because this cathedral was the first Catholic diocese and the oldest cathedral established in the New World.
 W
WBelarusian Gothic is the architectural style of ecclesiastical buildings and fortified structures of the 15th and 16th centuries in modern Belarus, Lithuania, eastern Poland and western Ukraine.
 W
WBrabantine Gothic, occasionally called Brabantian Gothic, is a significant variant of Gothic architecture that is typical for the Low Countries. It surfaced in the first half of the 14th century at St. Rumbold's Cathedral in the City of Mechelen.
 W
WThe Castle Chapel in Lubin is located on Mikołaj Pruzio Street on the Castle Hill in Lubin, Poland. The chapel is the only element left from the medieval castle buildings. The date in the tympanum - 1349 - determines the time of construction. It had 3 altars in the 14th century. The chapel was destroyed during the Thirty Years' War, rebuilt in 18th century and fell into ruins again. After reconstruction in the middle of the 19th century it served Catholics until 1908, then it housed a diocesan library. In 1945 it was set on fire. For many years after the war the building remained devastated. In the end of the 1970s the sanctuary was renovated. The chapel was initially managed by the Office of Artistic Exhibitions in Legnica. After the renovation the building was adapted as the Castle Gallery in 1990. In 2005-2009 further renovation works were carried out.
 W
WCistercian architecture is a style of architecture associated with the churches, monasteries and abbeys of the Roman Catholic Cistercian Order. It was heavily influenced by Abbot Bernard of Clairvaux, who believed that churches should avoid superfluous ornamentation so as not to distract from prayer. Cistercian architecture was simple and utilitarian. Although a few images of religious subjects were allowed, such as the crucifix, elaborate figures common in medieval churches were prohibited. Bernard noted their capacity for distracting monks in a famous letter. Early Cistercian architecture shows a transition between Romanesque and Gothic architecture. Later abbeys were constructed in Renaissance and Baroque styles, which were more ornate by nature.
 W
WCompound pier or cluster pier is the architectural term given to a clustered column or pier which consists of a centre mass or newel, to which engaged or semi-detached shafts have been attached, in order to perform certain definite structural objects, such as to carry arches of additional orders, or to support the transverse or diagonal ribs of a vault, or the tie-beam of an important roof. In these cases, though performing different functions, the drums of the pier are often cut out of one stone. There are, however, cases where the shafts are detached from the pier and coupled to it by annulets at regular heights, as in the Early English period.
 W
WA diamond vault is a form of vault church architecture used in the Late Gothic and Renaissance style, which is based on an elaborate system of cavernous vaults in a manner resembling diamonds. It was widely used especially in Central European countries.
 W
WThe Doorway from Moutiers-Saint-Jean is a portal dating from c 1250, originally for the monastery of Moutiers-Saint-Jean, near Dijon, Burgundy, France, and installed at The Cloisters, New York City, since 1932. It was designed in the Gothic style and carved from white oolitic limestone. The abbey was founded in the 5th century, and became a major center of influence. The abbey was patronised by a line of kings and nobles over the centuries; at one time it was financed by the dukes of Burgundy.
 W
WEarly Gothic is the style of architecture that appeared in northern France, Normandy and then England between about 1130 and the mid-13th century. It combined and developed several key elements from earlier styles, particularly from Romanesque architecture, including the rib vault, flying buttress, and the pointed arch, and used them in innovative ways to create structures, particularly Gothic cathedrals and churches, of exceptional height and grandeur, filled with light from stained glass windows. Notable examples of early Gothic architecture in France include the ambulatory and facade of Saint-Denis Basilica; Sens Cathedral (1140); Laon Cathedral; Senlis Cathedral; (1160) and most famously Notre-Dame de Paris.
 W
WEncaustic tiles are ceramic tiles in which the pattern or figure on the surface is not a product of the glaze but of different colors of clay. They are usually of two colours but a tile may be composed of as many as six. The pattern appears inlaid into the body of the tile, so that the design remains as the tile is worn down. Encaustic tiles may be glazed or unglazed and the inlay may be as shallow as 1⁄8 inch (3 mm), as is often the case with "printed" encaustic tile from the later medieval period, or as deep as a quarter inch.
 W
WEnglish Gothic is an architectural style that flourished from the late 12th until the mid-17th century. The style was most prominently used in the construction of cathedrals and churches. Gothic architecture's defining features are pointed arches, rib vaults, buttresses, and extensive use of stained glass. Combined, these features allowed the creation of buildings of unprecedented height and grandeur, filled with light from large stained glass windows. Important examples include Westminster Abbey, Canterbury Cathedral and Salisbury Cathedral. The Gothic style endured in England much longer than in Continental Europe.
 W
WEnglish Gothic stained glass windows were an important feature of English Gothic architecture, which appeared between the late 12th and late 16th centuries. They evolved from narrow windows filled with a mosaic of deeply-coloured pieces of glass into gigantic windows that filled entire walls, with a full range of colours and more naturalistic figures. In later windows, the figures were often coloured with silver stain, enamel paints and flashed glass. Later windows used large areas of white glass, or grisaille, to bring more light into the interiors.
 W
WA fieldstone church is a type of church, built using fieldstone of glacial erratics and glacial rubble. Such cathedrals and monasteries occur mostly in areas where the ice ages have deposited such rock material on the one hand, and where on the other hand there is little or no access to natural rock for quarrying and fashioning. In Europe, the primary areas with fieldstone churches are Saxony-Anhalt, Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Brandenburg in Germany, as well as Poland, Finland, parts of Scandinavia and the Baltic states. The stones used are often granite, gneiss or quartzite; they can be used both hewn and unshaped. Since some of the churches are painted, the stones are not always visible. Especially in later examples, the fieldstones are often combined with other materials, such as brick or half-timbered parts.
 W
WFlamboyant is a form of late Gothic architecture that developed in Europe in the Late Middle Ages and Renaissance, from around 1375 to the mid-16th century. It is characterized by double curves forming flame-like shapes in the bar-tracery, which give the style its name; by the multiplication of ornamental ribs in the vaults; and by the use of the arch in accolade. Ribs in Flamboyant tracery are recognizable by their flowing forms, which are influenced by the earlier curvilinear tracery of the Second Gothic styles. Very tall and narrow pointed arches and gables, particularly double-curved ogee arches, are common in buildings of the Flamboyant style. In most regions of Europe, Late Gothic styles like Flamboyant replaced the earlier Rayonnant style and other early variations.
 W
WIn architecture, flushwork is the decorative combination on the same flat plane of flint and ashlar stone. If the stone projects from a flat flint wall then the term is proudwork, as the stone stands "proud" rather than being "flush" with the wall.
 W
WThe flying buttress is a specific form of buttress composed of an arch that extends from the upper portion of a wall to a pier of great mass, in order to convey to the ground the lateral forces that push a wall outwards, which are forces that arise from vaulted ceilings of stone and from wind-loading on roofs.
 W
WGaiety Theatre or Gaiety Heritage Cultural Complex is a significant tourist hot spot of Shimla. It is located on The Ridge, Shimla. It is the hub of cultural events of the state. It also very popular among Bollywood as many music videos and movies are often filmed here, including one for the 2019 song "Pachtaoge" by Arijit Singh.
 W
WIn architecture, and specifically in Gothic architecture, a gargoyle is a carved or formed grotesque with a spout designed to convey water from a roof and away from the side of a building, thereby preventing rainwater from running down masonry walls and eroding the mortar between. Architects often used multiple gargoyles on a building to divide the flow of rainwater off the roof to minimize the potential damage from a rainstorm. A trough is cut in the back of the gargoyle and rainwater typically exits through the open mouth. Gargoyles are usually an elongated fantastical animal because the length of the gargoyle determines how far water is directed from the wall. When Gothic flying buttresses were used, aqueducts were sometimes cut into the buttress to divert water over the aisle walls.
 W
WThe Głogów Tower is a Gothic building from the mid-14th century in Lubin, located in the northwestern part of the market square.
 W
WGothic cathedrals and churches are religious buildings created in Europe between the mid-12th century and the beginning of the 16th century. The cathedrals are notable particularly for their great height and their extensive use of stained glass to fill the interiors with light. They were the tallest and largest buildings of their time and the most prominent examples of Gothic architecture. The appearance of the Gothic cathedral was not only a revolution in architecture; it also introduced new forms in decoration, sculpture, and art.
 W
WGothic architecture is a style of architecture that flourished during the high and late medieval period. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture.
 W
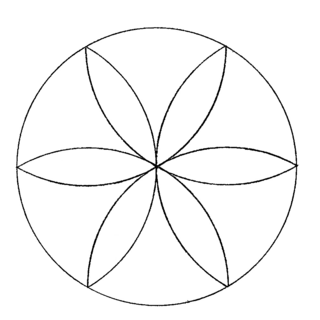
WA hexafoil is a geometric design that is used as a traditional element of Gothic architecture, created by overlapping six circular arcs to form a flower-like image. The hexafoil design is modeled after the six petal lily, for its symbolism of purity and relation to the Trinity. The hexafoil form is created from a series of compound units, and exists as a more complex variation of the same extruded figure. Other forms similar to the hexafoil include the trefoil, quatrefoil, and cinquefoil.
 W
WHigh Gothic is a particularly refined and imposing style of Gothic architecture that appeared in northern France from about 1195 until 1250. Notable examples include Chartres Cathedral, Reims Cathedral, Amiens Cathedral, Beauvais Cathedral, and Bourges Cathedral. It is characterized by great height, harmony, subtle and refined tracery and realistic sculpture, and by large stained glass windows, particularly rose windows and larger windows on the upper levels, which filled the interiors with light. It followed Early Gothic architecture and was succeeded by the Rayonnant style. It is often described as the high point of the Gothic style.
 W
WThe Isabelline style, also called the Isabelline Gothic, or Castilian late Gothic, was the dominant architectural style of the Crown of Castile during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs, Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon in the late-15th century to early-16th century. The Frenchman Émile Bertaux named the style after Queen Isabella.
 W
WThe Jubilee Clock Tower, striking clock, and drinking fountain, is a Grade II listed building in the village of Churchill in North Somerset, built to commemorate Queen Victoria's Diamond Jubilee in 1897. It stands on a plot between Dinghurst Road and Front Street, and is a prominent landmark at the entrance to the village. Designed by Joseph Foster Wood of Foster & Wood, Bristol, the tower is made of local stone and is of perpendicular Gothic style.
 W
WA lancet window is a tall, narrow window with a pointed arch at its top. It acquired the "lancet" name from its resemblance to a lance. Instances of this architectural element are typical of Gothic church edifices of the earliest period. Lancet windows may occur singly, or paired under a single moulding, or grouped in an odd number with the tallest window at the centre.
 W
WA Lombard band is a decorative blind arcade, usually located on the exterior of building. It was frequently used during the Romanesque and Gothic periods of Western architecture.
 W
WThe Milan Cathedral, or Metropolitan Cathedral-Basilica of the Nativity of Saint Mary, is the cathedral church of Milan, Lombardy, Italy. Dedicated to the Nativity of St Mary, it is the seat of the Archbishop of Milan, currently Archbishop Mario Delpini.
 W
WThe Northern Master was an anonymous artist in the late 13th century who worked in the Upper Church of the Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi. Although his precise origin is unknown, he is thought to be of French, German, or English origin. He and his assistants played a critical role in painting by merging northern Gothic and Italian influences in the frescoes. Also attributed to him are the designs for some of the stained glass windows.
 W
WNotre-Dame Cathedral is the Roman Catholic Cathedral of Luxembourg City, in southern Luxembourg. It was originally a Jesuit church, and its cornerstone was laid in 1613. It is the only cathedral in Luxembourg.
 W
WPerpendicular Gothic architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-centred arches, straight vertical and horizontal lines in the tracery, and regular arch-topped rectangular panelling. Perpendicular was the prevailing style of Late Gothic architecture in England from the 14th century to the 17th century. Perpendicular was unique to the country: no equivalent arose in Continental Europe or elsewhere in the British Isles. Of all the Gothic architectural styles, Perpendicular was the first to experience a second wave of popularity from the 18th century on in Gothic Revival architecture.
 W
WA pointed arch, ogival arch, or Gothic arch is an arch with a pointed crown, whose two curving sides meet at a relatively sharp angle at the top of the arch. This architectural element was particularly important in Gothic architecture. It first appeared in Indian and Islamic architecture as a way of making more decorative windows and doorways, but in the 12th century it began to be used in France and England as an important structural element, in combination with other elements, such as the rib vault and later the flying buttress. These allowed the construction of cathedrals, palaces and other buildings with dramatically greater height and larger windows which filled them with light.
 W
WThe pulpitum is a common feature in medieval cathedral and monastic church architecture in Europe. It is a massive screen, most often constructed of stone, or occasionally timber, that divides the choir from the nave and ambulatory. Typically the pulpitum is lavishly carved and decorated, and those of York Minster and Canterbury Cathedral preserve complete medieval sets of statues of the Kings of England.
 W
WIn French Gothic architecture, Rayonnant is the period from about the mid-13th century to mid-14th century. It was characterized by a shift away from the High Gothic search for increasingly large size toward more spatial unity, refined decoration, and additional and larger windows, which filled the space with light. Prominent features of Rayonnant include the large rose window, more windows in the upper-level clerestory; the reduction of the importance of the transept; and larger openings on the ground floor to establish greater communication between the central vessel and the side aisles. Interior decoration increased, and the decorative motifs spread to the outside, to the facade and the buttresses. utilizing great scale and spatial rationalism towards a greater concern for two-dimensional surfaces and the repetition of decorative motifs at different scales. The use of tracery gradually spread from the stained glass windows to areas of stonework, and to architectural features such as gables.
 W
WSondergotik is the style of Late Gothic architecture prevalent in Austria, Bavaria, Swabia, Saxony and Bohemia between 1350 and 1550. The term was invented by art historian Kurt Gerstenberg in his 1913 work Deutsche Sondergotik, in which he argued that the Late Gothic had a special expression in Germany marked by the use of the hall church or Hallenkirche. At the same time the style forms part of the International Gothic style in its origins.
 W
WSouthern French Gothic is a specific and militant style of Gothic architecture developed in the South of France, especially in the Toulouse region. It arose in the early 13th century following the victory of the Catholic church over the Cathars, as the church sought to re-establish its authority in the region. As a result, church buildings typically present features drawn from military architecture. Taking into account the Cathars' criticism of the Catholic Church, Southern French Gothic is simpler and less ornate than northern French Gothic, and further differs in that the construction material is typically brick rather than stone. Over time, the style came to influence secular buildings as well as churches and spread beyond the area where Catharism had flourished.
 W
WSt Leonard's Hospital is a grade II* listed timber-framed building in Tickhill, South Yorkshire, in England. It was originally constructed in the 15th century as a monastic building.
 W
WTracery is an architectural device by which windows are divided into sections of various proportions by stone bars or ribs of moulding. Most commonly, it refers to the stonework elements that support the glass in a window. The term probably derives from the tracing floors on which the complex patterns of windows were laid out in late Gothic architecture. Tracery can also be found on the interior of buildings and the exterior.
 W
WA transept is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the edifice. In churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform ("cross-shaped") building within the Romanesque and Gothic Christian church architectural traditions. Each half of a transept is known as a semitransept.