 W
WIn ice hockey, an assist is attributed to up to two players of the scoring team who shot, passed or deflected the puck towards the scoring teammate, or touched it in any other way which enabled the goal, meaning that they were "assisting" in the goal. There can be a maximum of two assists per goal. The assists will be awarded in the order of play, with the last player to pass the puck to the goal scorer getting the primary assist and the player who passed it to the primary assister getting the secondary assist. Players who gain an assist will get one point added to their player statistics.
 W
WA bench-clearing brawl is a form of ritualistic fighting that occurs in sports, most notably baseball and ice hockey, in which every player on both teams leaves their dugouts, bullpens, or benches, and charges the playing area in order to fight one another or try to break up a fight. Penalties for leaving the bench can range from nothing to severe.
 W
WA breakaway is a situation in ice hockey in which a player with the puck has no defending players, except for the goaltender, between himself and the opposing goal, leaving him free to skate in and shoot at will. A breakaway is considered a lapse on the part of the defending team. If a player's progress is illegally impeded by an opposing player or if the goalie throws his stick at the oncoming player, the breakaway player is awarded a penalty shot. If a player faces an empty net and is illegally impeded by an opposing player, he is automatically awarded a goal for his team instead of taking a penalty shot.
 W
WIn ice hockey, butterfly style is a technique of goaltending distinguished by the goaltender guarding the lower part of the net by dropping to the knees to block attempts to score. The butterfly style derives its name from the resemblance of the spread goal pads and hands to a butterfly's wings. The butterfly style is contrasted with stand-up style, where most shots on a goal are stopped with the goaltender on his feet.
 W
WIn basketball and other such timed sports, a buzzer beater is a shot that is taken before the game clock of a quarter, a half, or an overtime period expires but does not go in the basket until after the clock expires and the buzzer sounds hence the name "buzzer beater". The concept normally applies to baskets that beat an end-of-quarter/half/overtime buzzer but is sometimes applied to shots that beat the shot clock buzzer.
 W
WIn ice hockey, the captain is the player designated by a team as the only person authorized to speak with the game officials regarding rule interpretations when the captain is on the ice. At most levels of play each team must designate one captain and a number of alternate captains who speak to the officials when the captain is on the bench. Captains wear a "C" on their sweaters, while alternate captains wear an "A".
 W
WA "cup of coffee" is a North American sports idiom for a short time spent by a minor league player at the major league level. The idea behind the term is that the player was only in the big leagues long enough to have a cup of coffee before being returned to the minors. The term originated in baseball and is extensively used in ice hockey, both of whose professional leagues utilize extensive farm systems; it is rarely used in basketball or American football since neither the NBA nor NFL have implemented a true farm system.
 W
WA deke feint or fake is an ice hockey technique whereby a player draws an opposing player out of position or is used to skate by an opponent while maintaining possession and control of the puck. The term is a Canadianism formed by abbreviating the word decoy.
 W
WA diamond formation is a formation of four or more aircraft, soldiers on horseback, players in a team sport, etc., wherein the elements of the group adopt a diamond, or kite, shape.
 W
WAn empty net goal, abbreviated as EN or ENG and colloquially called an empty netter, occurs in several team sports when a team scores a goal into a net with no goaltender (goalie) present.
 W
WEnforcer is an unofficial role in ice hockey. The term is sometimes used synonymously with "fighter", "tough guy", or "goon". An enforcer's job is to deter and respond to dirty or violent play by the opposition. When such play occurs, the enforcer is expected to respond aggressively, by fighting or checking the offender. Enforcers are expected to react particularly harshly to violence against star players or goalies.
 W
WA face-off is the method used to begin and restart play after goals in some sports using sticks, primarily ice hockey, bandy and lacrosse. The two teams line up in opposition to each other, and the opposing players attempt to gain control of the puck or ball after it is dropped or otherwise placed between their sticks by an official.
 W
WIn sports, a false start is a disallowed start, usually due to a movement by a participant before being signaled or otherwise permitted by the rules to start. Depending on the sport and the event, a false start can result in a penalty against the athlete's or team's field position, a warning that a subsequent false start will result in disqualification, or immediate disqualification of the athlete from further competition.
 W
WIn sports, a farm team, farm system, feeder team, or nursery club is generally a team or club whose role is to provide experience and training for young players, with an agreement that any successful players can move on to a higher level at a given point, usually in an association with a major-level parent team. This system can be implemented in many ways, both formally and informally. It is not to be confused with a practice squad, which fulfills a similar developmental purpose but the players on the practice squad are members of the parent team.
 W
WThe five-hole is an ice hockey term for the space between a goaltender's legs. The name is attributed to David Neal, and its first recorded usage was in 1980. The phrases through the five-hole and gone five-hole are used when a player scores by shooting the puck into the goal between the goaltender's legs. The term is also be used in basketball, association football, and field hockey.
 W
WA game seven is the final game of a best of seven series. This game can occur in the postseasons for Major League Baseball (MLB), the National Basketball Association (NBA), and the National Hockey League (NHL).
 W
WIn ice hockey, a goal is scored when the puck entirely crosses the goal line between the two goal posts and below the goal crossbar. A goal awards one point to the team attacking the goal scored upon, regardless of which team the player who actually deflected the puck into the goal belongs to. Typically, a player on the team attempting to score shoots the puck with their stick towards the goal net opening, and a player on the opposing team called a goaltender tries to block the shot to prevent a goal from being scored against their team.
 W
WIn sport, a goal may refer to either an instance of scoring, or to the physical structure or area where an attacking team must send the ball or puck in order to score points. The structure of a goal varies from sport to sport, and one is placed at or near each end of the playing field for each team to defend. For many sports, each goal structure usually consists of two vertical posts, called goal posts, supporting a horizontal crossbar. A goal line marked on the playing surface between the goal posts demarcates the goal area. Thus, the objective is to send the ball or puck between the goal posts, under or over the crossbar, and across the goal line. Other sports may have other types of structures or areas where the ball or puck must pass through, such as the basketball hoop.
 W
WGoal difference, goal differential or points difference is a form of tiebreaker used to rank sport teams which finish on equal points in a league competition. Either "goal difference" or "points difference" is used, depending on whether matches are scored by goals or by points.
 W
WIn ice hockey, a grinder is a player better known for his hard work and checking than his scoring. A grinder is often a player who has limited offensive skills, but is valuable to a hockey team due to physical forechecking skills especially along the boards; for "grinding along the boards". The grinder is not in the spotlight as would be the offensively skilled scoring stars, but they are often fan favorites due to their work effort in games. A grinder is often the player who, by their willingness to endure the physical abuse of going into the corners to dig out the puck, often sets up the goals by getting the puck to the team's offensive stars. It is common belief in hockey that a good team needs a balance of scoring stars and grinders.
 W
WA Gordie Howe hat trick is a variation on ice hockey's hat-trick. It is accomplished when a player collects a goal, an assist, and a fight in the same game. It is named after Hall of Famer Gordie Howe.
 W
WHigh-sticking is the name of two infractions in the sport of ice hockey that may occur when a player intentionally or inadvertently plays the puck with their stick above the height of the shoulders or above the cross bar of a hockey goal. This can result in a penalty or a stoppage of play. In the rules of the National Hockey League, high-sticking is defined as a penalty in Rule 60 and as a non-penalty foul in Rule 80.A penalty is assessed if a player strikes another player with a high stick. The player is given a minor penalty unless their high stick caused an injury, in which case the referee has the option to assess a double-minor, major, game misconduct or match penalty. It is the referee's discretion which penalty to assess: the rule calls for a double minor for an accidental injury, or a match penalty for a deliberate attempt to injure. Injury is usually decided by the high stick causing bleeding, but the presence of blood does not automatically mean an extra penalty is awarded. Some referees have been known to award an extra penalty without the presence of blood if the referee determines that the injury sustained was sufficient to warrant a double-minor penalty. A stoppage in play results if a high stick comes in contact with the puck and the team who touched it regains control of the puck. However, play usually continues if a player touches the puck with a high stick and the opposing team gains control of the puck. If the puck goes into the opposing net after coming into contact with a high stick, the goal is disallowed. The level at which a stick is considered too high for a goal is the crossbar of the net. However, if a player knocks the puck into their own net with a high stick, the goal is allowed.
 W
WIn ice hockey, icing is an infraction when a player shoots the puck over the center red line and the opposing team's red goal line, in that order, and the puck remains untouched without scoring a goal.
 W
WThe left wing lock is a defensive ice hockey strategy similar to the neutral zone trap.
 W
WThe neutral zone trap is a defensive strategy used in ice hockey to prevent an opposing team from proceeding through the neutral zone and to force turnovers. The strategy is generally used to level the playing field for teams that are not as offensively talented as their opponents, although the trap can also be used by teams simply looking to protect a lead late in the game. The trap was innovated by the Toronto Maple Leafs in the 1920s and 1930s but became the defensive scheme for most coaches during the late 90s and early 2000s—known as the "Dead Puck era"—as a direct result of the success seen by the New Jersey Devils under the coaching of Jacques Lemaire; the Devils won three Stanley Cup championships during this era. Lemaire used the trap that was employed by the Montreal Canadiens under his coach Scotty Bowman.
 W
WIn ice hockey, a one timer is a shot that occurs when a player meets a teammate's pass with an immediate slapshot, without any attempt to control the puck on their stick. An effective one timer requires precise timing on the part of both players involved, especially the shooter. This play often results in a good chance at a goal. A wrist shot can also be done on a one-timer, though the puck is released far slower than a slapshot one-timer.
 W
WThe Original Six are the teams that comprised the National Hockey League (NHL) between 1942 and 1967. The six teams are the Boston Bruins, Chicago Black Hawks, Detroit Red Wings, Montreal Canadiens, New York Rangers, and Toronto Maple Leafs. After serving as the league's only teams for 25 seasons, they were joined by six new franchises in the 1967 NHL expansion.
 W
WA penalty in ice hockey is a punishment for an infringement of the rules. Most penalties are enforced by sending the offending player to a penalty box for a set number of minutes. During the penalty the player may not participate in play. Penalties are called and enforced by the referee, or in some cases, the linesman. The offending team may not replace the player on the ice, leaving them short-handed as opposed to full strength. When the opposing team is said to be on a power play, they will have one more player on the ice than the short-handed team. The short-handed team is said to be "on the penalty kill" until the penalty expires and the penalized player returns to play. While standards vary somewhat between leagues, most leagues recognize several common varieties of penalties, as well as common infractions.
 W
WThe penalty box or sin bin is the area in ice hockey, rugby union, rugby league, roller derby and some other sports where a player sits to serve the time of a given penalty, for an offence not severe enough to merit outright expulsion from the contest. Teams are generally not allowed to replace players who have been sent to the penalty box.
 W
WA pest in ice hockey is a player who attempts to antagonize opponent players either by physical play or verbal incitation. Pests employ legal, illegal, or borderline tactics to accomplish their goals. Some common tactics include trash talk or slashing and hooking while referees are not looking. They may employ the tactic of goading opponents into a fight but then backing off in order to draw a penalty against them. Some pests may not only use these tactics against opposing skaters, but opposing goaltenders as well. Pest and agitator are sometimes used synonymously, as both are usually characterized by short bursts of intensity and speed with the intention of creating havoc. The pest characterization has been used derogatorily, as a player who incites anger in the opposition but is unwilling to directly confront the result of their actions by engaging in fighting, as would an enforcer. George McPhee, former general manager of the Washington Capitals and president of the Vegas Golden Knights, said, "Pests are really the guys who have no courage. They start stuff and don't back it up."
 W
WA playoff beard is the superstitious practice of male athletes not shaving their beards during the playoffs. Playoff beards were introduced by ice hockey players participating in the Stanley Cup playoffs, and are now a tradition in many sports leagues. Many fans of professional sports teams also grow playoff beards. The player stops shaving when his team enters the playoffs and does not shave until his team is eliminated or wins the Stanley Cup.
 W
WIn ice hockey, power forward (PWF) is a loosely applied characterization of a forward who is big and strong, equally capable of playing physically or scoring goals and would most likely have high totals in both points and penalties. It is usually used in reference to a forward who is physically large, with the toughness to dig the puck out of the corners, possesses offensive instincts, has mobility, puck-handling skills, may be difficult to knock off the puck or to push away from the front of the goal and willingly engage in fights when he feels it is required. Possessing both physical size and offensive ability, power forwards are also often referred to as the 'complete' hockey player.
 W
WA puck bunny is a female ice hockey fan whose interest in the sport is primarily motivated by sexual attraction to the players rather than enjoyment of the game itself. Primarily a Canadian term, it gained popular currency in the 21st century, and in 2004 was added to the second edition of the Canadian Oxford Dictionary which defines it as follows:Puck bunny: a young female hockey fan, especially one motivated more by a desire to meet the players than by an interest in hockey.
 W
W'Rebound' is a term used in sports to describe the ball becoming available for possession by either opponent after an attempt to put the ball or puck into the goal has been unsuccessful. Rebounds are generally considered to be a major part of the game, as they often lead either to a possession change or to a second opportunity to score by the side whose initial attempt failed.
 W
WAn ice hockey rink is an ice rink that is specifically designed for ice hockey, a competitive team sport. Alternatively it is used for other sports such as broomball, ringette and rink bandy. It is a rectangle with rounded corners and surrounded by walls approximately 1.22 metres (48 in) high called the boards.
 W
WIn ice hockey, a goaltender is credited with a save when they prevent a shot by the opponent from entering the net. A goaltender's efficiency in stopping shots, the save percentage, is calculated as a percentage of shots stopped divided by the total number of shots on goal. If a goaltender makes all the saves within a game it is called a shutout. In association football this is called a clean sheet.
 W
WIn ice hockey, a screen is obstruction by a player of the goaltender's view of the puck. The word can also be used as a verb, commonly "don't screen the goaltender", or "the goalie was screened". Screens can be both planned, as when an attacking forward positions himself in front of the net, or accidental, like when a defensemen accidentally blocks the goaltender's view. Attacking players may attempt to take advantage of a screen by taking a shot, which is more difficult for the opposing goaltender to save if he is being screened.
 W
WIn ice hockey, a shot on goal is a shot that directs the puck towards the net and either goes into the net for a goal or is stopped by the goaltender for a save.
 W
WA slapshot in ice hockey is the hardest shot one can perform. It has four stages which are executed in one fluid motion to make the puck fly into the net:The player winds up his hockey stick to shoulder height or higher. Next the player violently "slaps" the ice slightly behind the puck and uses his weight to bend the stick, storing energy in it like a spring. This bending of the stick gives the slapshot its speed. Just like a bow and arrow, the stick's tendency to return to being straight is transferred to the puck, giving it much more speed than just hitting it alone could. When the face of the stick blade strikes the puck, the player rolls his wrists and shifts his weight so that the energy stored in the stick is released through the puck. Finally, the player follows through, ending up with the stick pointed towards the desired target.
 W
WIn hockey, the slot is the area on the hockey rink directly in front of the goaltender between the faceoff circles and extending to the blue line. It is sometimes referred to as the "scoring area".
 W
WThe teddy bear toss is a popular Christmas season promotion most common at junior ice hockey and minor league hockey games. Fans are encouraged to bring teddy bears or other stuffed toys to the game, and to throw them onto the ice when the home team scores its first goal. The toys are gathered up to be donated as presents to hospitals and charities. In many cases, the players themselves personally donate some of the bears to children at area hospitals. The Hershey Bears claim a world record of 45,650 stuffed toys in a single game.
 W
WThe three stars in ice hockey are the three best players in a game as chosen by a third party, with the first star considered the best of the three players, akin to the Player of the match in other sports. Usually, the top point scorers or outstanding goaltenders are designated as the three best players of the game, but other players may be considered by affecting the game by other means.
 W
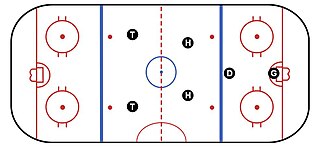
WThe torpedo system is an ice hockey on-ice system first used by the Swedish team Djurgårdens IF. The coach of Djurgårdens IF, Hardy Nilsson, took the system with him and it was used extensively by the Swedish national hockey team in international competition. The system converts the traditional hockey layout of three forwards and two defensemen, into two torpedoes up front, two halfbacks, and one lone defenceman. The torpedoes are responsible for forechecking in the corners when the puck is in the offensive zone, and stay around the neutral zone to be sprung into a scoring position. The halfbacks are all-purpose players that run the offense from the faceoff circles in the offensive zone, and defend against the other team's torpedoes. The libero protects the rear of the ice.
 W
WTowel Power is a term used by the Vancouver Canucks of the National Hockey League (NHL) to describe the waving of rally towels by their fans. The tradition started in the 1982 Campbell Conference Finals when Vancouver played the Chicago Blackhawks. During game two of the series, head coach Roger Neilson waved a white towel on the end of a hockey stick in a mock surrender after being upset with the officiating. Neilson was ejected and the Canucks lost 4–1. When Vancouver returned home from Chicago for the following game fans supported both Neilson and the Canucks by waving towels first at the airport when the team arrived and then during the next game. The Canucks won the next three games and advanced to the Stanley Cup Finals where they were defeated by the New York Islanders. As part of the tradition, the Canucks hand out towels prior to playoff games for fans to help support the team.
 W
WIn ice hockey, a two-way forward is a forward who handles the defensive aspects of the game as well as the offensive aspects. Typically, a player's frame is not an issue in whether he can be a two-way forward. Perseverance is key to being a two-way forward, as it is an attribute that gives rise to battling in the corners or preventing odd man rushes by the opposing team. A two-way forward can contribute for the team both offensively and defensively, scoring important game-winning goals or making big plays from which his team receives a significant advantage over the opponent team. As such, good two-way forwards are often capable playmakers.
 W
WWinger, in the game of ice hockey, is a forward position of a player whose primary zone of play on the ice is along the outer playing area. They typically work by flanking the centre forward. Originally the name was given to forward players who went up and down the sides of the rink. Nowadays, there are different types of wingers in the game — out-and-out goal scorers, checkers who disrupt the opponents, and forwards who work along the boards and in the corners. Often a winger's precise role on a line depends upon what type of role the other winger plays; usually lines will have one more goal-scoring oriented winger and one winger more focused on playing the boards, checking and passing the puck to others to take shots. They tend to be bigger than centreman and smaller than defenseman.