 W
WAircraft dope is a plasticised lacquer that is applied to fabric-covered aircraft. It tightens and stiffens fabric stretched over airframes, which renders them airtight and weatherproof, increasing their durability and lifespan. The technique has been commonly applied to both full-size and flying models of aircraft.
 W
WAn alkyd is a polyester resin modified by the addition of fatty acids and other components. Alkyds are derived from polyols and organic acids including dicarboxylic acids or carboxylic acid anhydride and triglyceride oils. The term alkyd is a modification of the original name "alcid", reflecting the fact that they are derived from alcohol and organic acids. The inclusion of a fatty acid confers a tendency to form flexible coatings. Alkyds are used in paints, varnishes and in moulds for casting. They are the dominant resin or binder in most commercial oil-based coatings. Approximately 200,000 tons of alkyd resins are produced each year. The original alkyds were compounds of glycerol and phthalic acid sold under the name Glyptal. These were sold as substitutes for the darker-colored copal resins, thus creating alkyd varnishes that were much paler in colour. From these, the alkyds that are known today were developed.
 W
WAnodizing is an electrolytic passivation process used to increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the surface of metal parts.
 W
WAnti-climb paint is a class of paint consisting of a thick oily coating that is applied with a stiff brush, trowel or by hand using a protective glove. In appearance it is similar to smooth gloss paint when applied but it remains slippery indefinitely thereby preventing any intruder from gaining a foothold.
 W
WThe Bresle method is used to determine concentration of soluble salts on metal surfaces prior to coating application, such as painting. These salts can cause serious adhesion problems after time.
 W
WCarbonyl metallurgy is used to manufacture products of iron, nickel, steel, and other metals. Coatings are produced by vapor plating using metal carbonyl vapors. These are metal-ligand complexes where carbon monoxide is bonded to individual atoms of metals.
 W
WChalk paint is a water-based, decorative paint invented by Annie Sloan which may be applied over almost any surface. It requires very little preparation and needs a topcoat to avoid flaking.
 W
WChemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
 W
WChromate conversion coating or alodine coating is a type of conversion coating used to passivate steel, aluminium, zinc, cadmium, copper, silver, titanium, magnesium, and tin alloys. The coating serves as a corrosion inhibitor, as a primer to improve the adherence of paints and adhesives, as a decorative finish, or to preserve electrical conductivity. It also provides some resistance to abrasion and light chemical attack on soft metals.
 W
WGas dynamic cold spraying or cold spraying (CS) is a coating deposition method. Solid powders are accelerated in a supersonic gas jet to velocities up to ca. 1200 m/s. During impact with the substrate, particles undergo plastic deformation and adhere to the surface. To achieve a uniform thickness the spraying nozzle is scanned along the substrate. Metals, polymers, ceramics, composite materials and nanocrystalline powders can be deposited using cold spraying. The kinetic energy of the particles, supplied by the expansion of the gas, is converted to plastic deformation energy during bonding. Unlike thermal spraying techniques, e.g., plasma spraying, arc spraying, flame spraying, or high velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF), the powders are not melted during the spraying process.
 W
WDetonation spraying is one of the many forms of thermal spraying techniques that are used to apply a protective coating at supersonic velocities to a material in order to change its surface characteristics. This is primarily to improve the durability of a component. It was first invented in 1955 by H.B. Sargent, R.M. Poorman and H. Lamprey and is applied to a component using a specifically designed detonation gun (D-gun). The component being sprayed must be prepared correctly by removing all surface oils, greases, debris and roughing up the surface in order to achieve a strongly bonded detonation spray coating. This process involves the highest velocities and temperatures (≈4000 °C) of coating materials compared to all other forms of thermal spraying techniques. Which means detonation spraying is able to apply low porous and low oxygen content protective coatings that protect against corrosion, abrasion and adhesion under low load.
 W
WDiamond-like carbon (DLC) is a class of amorphous carbon material that displays some of the typical properties of diamond. DLC is usually applied as coatings to other materials that could benefit from such properties.
 W
WDimethylol propionic acid -DMPA is a chemical compound that has the full IUPAC name of 2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)propionic acid and is an organic compound with one carboxyl and two hydroxy groups. It has the CAS Registry Number of 4767-03-7.
 W
WDip coating is an industrial coating process which is used, for example, to manufacture bulk products such as coated fabrics and condoms and specialised coatings for example in the biomedical field. Dip coating is also commonly used in academic research, where many chemical and nano material engineering research projects use the dip coating technique to create thin-film coatings.
 W
WElectroless nickel-boron coating is a metal plating process that can create a layer of a nickel-boron alloy on the surface of a solid substrate, like metal or plastic. The process involves dipping the substrate in a water solution containing nickel salt and a boron-containing reducing agent, such as an alkylamineborane or sodium borohydride. It is a type of electroless nickel plating. A similar process, that uses a hypophosphite as a reducing agent, yields a nickel-phosphorus coating instead.
 W
WEnamel paint is paint that air-dries to a hard, usually glossy, finish, used for coating surfaces that are outdoors or otherwise subject to hard wear or variations in temperature; it should not be confused with decorated objects in "painted enamel", where vitreous enamel is applied with brushes and fired in a kiln. The name is something of a misnomer, as in reality, most commercially available enamel paints are significantly softer than either vitreous enamel or stoved synthetic resins, and are totally different in composition; vitreous enamel is applied as a powder or paste and then fired at high temperature. There is no generally accepted definition or standard for use of the term "enamel paint", and not all enamel-type paints may use it.
 W
WEnamelled glass or painted glass is glass which has been decorated with vitreous enamel and then fired to fuse the glasses. It can produce brilliant and long-lasting colours, and be translucent or opaque. Unlike most methods of decorating glass, it allows painting using several colours, and along with glass engraving, has historically been the main technique used to create the full range of image types on glass.
 W
WThe environmental effects of paint can vary depending on the type of paint used and mitigation measures. Traditional painting materials and processes can have harmful effects on the environment, including those from the use of lead and other additives. Measures can be taken to reduce its environmental effects, including accurately estimating paint quantities so waste is minimized, and use of environmentally preferred paints, coating, painting accessories, and techniques.
 W
WThe European Coatings Journal is an English-language trade magazine for the coatings industry. It is published by Vincentz Network. It was established in 1986. According to the Informationsgemeinschaft zur Feststellung der Verbreitung von Werbeträgern, it reached about 33.000 readers per issue in 2010. The European Coatings Journal is an official partner of the Conseil Européen de l'Industrie des Peintures, des Encres d'Imprimerie et des Couleurs d'Arts, the European coatings association.
 W
WCoating is an industrial process that consists of applying a liquid or a powder into the surface of an edible product to convey new properties. Coating designates an operation as much as the result of it: the application of a layer and the layer itself. Coating takes different meanings depending on the industry concerned.
 W
WGold plating is a method of depositing a thin layer of gold onto the surface of another metal, most often copper or silver, by chemical or electrochemical plating. This article covers plating methods used in the modern electronics industry; for more traditional methods, often used for much larger objects, see gilding.
 W
WHerbol is one of the oldest German brands for professional coatings. It has its origins in the Lackfabrik Herbig-Haarhaus that was founded in Cologne in 1844. The product range contains façade paints, interior wall paints, lacquers and glazing, crack reinforcement as well as concrete and floor system. The coatings systems are used for renovation, maintenance and new constructions. Since 1999 the brand Herbol is part of the Akzo Nobel Deco GmbH, an affiliate of the Dutch concern AkzoNobel, the world's biggest coatings manufacturer.
 W
WHot-dip galvanization is a form of galvanization. It is the process of coating iron and steel with zinc, which alloys with the surface of the base metal when immersing the metal in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of around 450 °C (842 °F). When exposed to the atmosphere, the pure zinc (Zn) reacts with oxygen (O2) to form zinc oxide (ZnO), which further reacts with carbon dioxide (CO2) to form zinc carbonate (ZnCO3), a usually dull grey, fairly strong material that protects the steel underneath from further corrosion in many circumstances. Galvanized steel is widely used in applications where corrosion resistance is needed without the cost of stainless steel, and is considered superior in terms of cost and life-cycle. It can be identified by the crystallization patterning on the surface (often called a "spangle").
 W
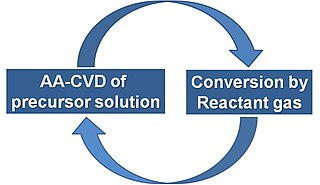
WHybrid physical–chemical vapor deposition (HPCVD) is a thin-film deposition technique, that combines physical vapor deposition (PVD) with chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
 W
WIon layer gas reaction (ILGAR®) is a non-vacuum, thin-film deposition technique developed and patented by the group of Professor Dr. Christian-Herbert Fischer at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin for materials and energy in Berlin, Germany. It is a sequential and cyclic process that enables the deposition of semiconductor thin films, mainly for photovoltaic applications, specially chalcopyrite absorber layers and buffer layers. The ILGAR technique was awarded as German High Tech Champion 2011 by the Fraunhofer Society.
 W
WLacquer is a type of hard and potentially shiny coating or finish applied to materials such as wood or metal. The term originates from the Sanskrit word lākshā (लाक्षा), representing the number one hundred thousand (100,000), which was used for both the lac insect and the scarlet resinous secretion, rich in shellac that it produces, used as wood finish in ancient India and neighbouring areas.
 W
WMadapollam is a soft cotton fabric manufactured from fine yarns with a dense pick laid out in linen weave. Madapollam is used as an embroidery and handkerchief fabric and as a base for fabric printing. The equal warp and weft mean that the tensile strength and shrinkage is the same in any two directions at right angles and that the fabric absorbs liquids such as ink, paint and aircraft dope equally along its X and Y axes.
 W
WMetallizing is the general name for the technique of coating metal on the surface of objects. Metallic coatings may be decorative, protective or functional.
 W
WNanoparticle deposition refers to the process of attaching nanoparticles to solid surfaces called substrates to create coatings of nanoparticles. The coatings can have a monolayer or a multilayer and organized or unorganized structure based on the coating method used. Nanoparticles are typically difficult to deposit due to their physical properties.
 W
WOptically active additive (OAA) is an organic or inorganic material which, when added to a coating, makes that coating react to ultra violet light. This effect enables quick, non-invasive inspection of very large coated areas during the application process allowing the coating inspector to identify and concentrate on defective areas, thus reducing inspection time while assuring the probability of good application and coverage. It works by highlighting holidays and pin-holes, areas of over and under application as well as giving the opportunity for crack detection and identification of early coating deterioration through life. The use of optically active additives or fluorescing additives is specified in US Military Specification MIL-SPEC-23236C. The use of and the inspection technique is described in the SSPC document Technology Up-date 11.
 W
WPaint is any pigmented liquid, liquefiable, or solid mastic composition that, after application to a substrate in a thin layer, converts to a solid film. It is most commonly used to protect, color, or provide texture to objects. Paint can be made or purchased in many colors—and in many different types, such as watercolor or synthetic. Paint is typically stored, sold, and applied as a liquid, but most types dry into a solid. Most paints are either oil-based or water-based and each have distinct characteristics. For one, it is illegal in most municipalities to discard oil-based paint down household drains or sewers. Clean up solvents are also different for water-based paint than they are for oil-based paint. Water-based paints and oil-based paints will cure differently based on the outside ambient temperature of the object being painted Usually the object being painted must be over 10 °C (50 °F), although some manufacturers of external paints/primers claim they can be applied when temperatures are as low as 2 °C (35 °F).
 W
WIn the paint and coating industries, paint adhesion testing is often used to determine if the paint or coating will adhere properly to the substrates to which they are applied. There are several different tests to measure the resistance of paints and coatings from substrates: cross-cut test, scrape adhesion, pull-off test, and others.
 W
WParkerizing is a method of protecting a steel surface from corrosion and increasing its resistance to wear through the application of a chemical phosphate conversion coating. Parkerizing is usually considered to be an improved zinc or manganese phosphating process, and not to be an improved iron phosphating process, although some use the term parkerizing as a generic term for applying phosphating coatings that does include the iron phosphating process. Bonderizing, phosphating, and phosphatizing are other terms associated with the Parkerizing process. It has also been known as pickling in the context of wrought iron and steel.
 W
WA Persoz pendulum is a device used for measuring hardness of materials. The instrument consists of a pendulum which is free to swing on two balls resting on a coated test panel. The pendulum hardness test is based on the principle that the amplitude of the pendulum's oscillation will decrease more quickly when supported on a softer surface. The hardness of any given coating is given by the number of oscillations made by the pendulum within the specified limits of amplitude determined by accurately positioned photo sensors. An electronic counter records the number of swings made by the pendulum
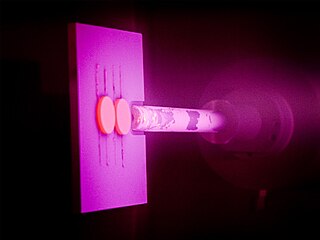 W
WPhysical vapor deposition (PVD), sometimes called physical vapor transport (PVT), describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods which can be used to produce thin films and coatings. PVD is characterized by a process in which the material goes from a condensed phase to a vapor phase and then back to a thin film condensed phase. The most common PVD processes are sputtering and evaporation. PVD is used in the manufacture of items which require thin films for mechanical, optical, chemical or electronic functions. Examples include semiconductor devices such as thin film solar panels, aluminized PET film for food packaging and balloons, and titanium nitride coated cutting tools for metalworking. Besides PVD tools for fabrication, special smaller tools have been developed.
 W
WPolyurethane is a commonly encountered polymer composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from a wide range of starting materials (monomers) and is therefore a class of polymers, rather than a distinct compound. This chemical variety allows for polyurethanes with very different physical properties, leading to an equally wide range of different applications including: rigid and flexible foams, varnishes and coatings, adhesives, electrical potting compounds, and fibres such as spandex and PUL. Of these, foams are the largest single application, accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016.
 W
WSlot-die coating is a coating technique for the application of solution, slurry, or extruded thin films onto typically flat substrates such as glass, metal, paper, fabric or plastic foils. The process was first developed for the industrial production of photographic papers in the 1950's. It has since become relevant in numerous commercial processes and nanomaterials related research fields.
 W
WIn physics, sputtering is a phenomenon in which microscopic particles of a solid material are ejected from its surface, after the material is itself bombarded by energetic particles of a plasma or gas. It occurs naturally in outer space, and can be an unwelcome source of wear in precision components. However, the fact that it can be made to act on extremely fine layers of material is utilised in science and industry—there, it is used to perform precise etching, carry out analytical techniques, and deposit thin film layers in the manufacture of optical coatings, semiconductor devices and nanotechnology products. It is a physical vapor deposition technique.
 W
WTetramethyl bisphenol F (TMBPF) is a new coating intended as a safer replacement for bisphenol A and bisphenol F to use in epoxy linings of aluminium cans and steel cans. It was previously suggested as an insulator in electronic circuit boards.
 W
WThermal spraying techniques are coating processes in which melted materials are sprayed onto a surface. The "feedstock" is heated by electrical or chemical means.
 W
WTinning is the process of thinly coating sheets of wrought iron or steel with tin, and the resulting product is known as tinplate. The term is also widely used for the different process of coating a metal with solder before soldering.
 W
WIn French interior design, vernis Martin is a type of japanning or imitation lacquer named after the 18th century French Martin brothers: Guillaume, Etienne-Simon, Robert and Julien. They ran a leading factory from between about 1730 and 1770, and were vernisseurs du roi. But they did not invent the process, nor were they the only producers, nor does the term cover a single formula or technique. It imitated Chinese lacquer and European subjects, and was applied to a wide variety of items, from furniture to coaches. It is said to have been made by heating oil and copal and then adding Venetian turpentine.
 W
WVitreous enamel, also called porcelain enamel, is a material made by fusing powdered glass to a substrate by firing, usually between 750 and 850 °C. The powder melts, flows, and then hardens to a smooth, durable vitreous coating. The word comes from the Latin vitreum, meaning "glass".
 W
WWhitewash, or calcimine, kalsomine, calsomine, or lime paint is a type of paint made from slaked lime (calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2) or chalk calcium carbonate, (CaCO3), sometimes known as "whiting". Various other additives are sometimes used.
 W
WZimmerit was a paste-like coating used on mid- and late-war German armored fighting vehicles during World War II. It was used to produce a hard layer covering the metal armor of the vehicle, providing enough separation that magnetically attached anti-tank mines would fail to stick to the vehicle, although Germany was the only country to use magnetic anti-tank mines in numbers. Zimmerit was often left off late-war vehicles due to the unfounded concern that it could catch fire when hit. It was developed by the German company Chemische Werke Zimmer & Co (Berlin).