 W
WPre-Columbian art refers to the visual arts of indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, North, Central, and South Americas from at least 13,000 BCE to the European conquests starting in the late 15th and early 16th centuries. The Pre-Columbian era continued for a time after these in many places, or had a transitional phase afterwards. Unfortunately, many types of perishable artifacts that were no doubt once very common, such as woven textiles, typically have not been preserved, but Precolumbian monumental sculpture, metalwork in gold, pottery, and painting on ceramics, walls, and rocks have survived more frequently.
 W
WAmate is a type of bark paper that has been manufactured in Mexico since the precontact times. It was used primarily to create codices.
 W
WThe Andean textile tradition once spanned from the Pre-Columbian to the Colonial era throughout the western coast of South America, but was mainly concentrated in Peru. The arid desert conditions along the coast of Peru have allowed for the preservation of these dyed textiles, which can date to 6000 years old. Many of the surviving textile samples were from funerary bundles, however, these textiles also encompassed a variety of functions. These functions included the use of woven textiles for ceremonial clothing or cloth armor as well as knotted fibers for record-keeping. The textile arts were instrumental in political negotiations, and were used as diplomatic tools that were exchanged between groups. Textiles were also used to communicate wealth, social status, and regional affiliation with others. The cultural emphasis on the textile arts was often based on the believed spiritual and metaphysical qualities of the origins of materials used, as well as cosmological and symbolic messages within the visual appearance of the textiles. Traditionally, the thread used for textiles was spun from indigenous cotton plants, as well as alpaca and llama wool.
 W
WThis is a chronological list of significant or pivotal moments in the development of Native American art or the visual arts of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas. Earlier dates, especially before the 18th century, are mostly approximate.
 W
WBannerstones are artifacts usually found in the Eastern United States that are characterized by a centered hole in a symmetrically shaped carved or ground stone. The holes are typically 1⁄4" to 3⁄4" in diameter and extend through a raised portion centered in the stone. They usually are bored all the way through but some have been found with holes that extend only part of the way through. Many are made from banded slate or other colored hard stone. They often have a geometric "wing nut" or "butterfly" shape but are not limited to these. More than just functional artifacts, bannerstones are a form of art that appear in varying shapes, designs, and colors, symbolizing their ceremonial and spiritual importance.
 W
WBird stones are prehistoric, abstract stone carvings made by Native Americans. The artifacts were a common inclusion in graves and thought to have ceremonial importance. They are noted for their distinctive simplicity and beauty. They first appeared in the middle Archaic period around 5,000 years ago and continued into the early Woodland period to about 2,500 years before present.
 W
WCueva de las Manos is a cave and complex of rock art sites in the province of Santa Cruz, Argentina, 163 km (101 mi) south of the town of Perito Moreno. It is named for the hundreds of paintings of hands stenciled, in multiple collages, on the rock walls. The art in the cave dates to between 11,000 to 7,500 BC, during the Archaic period of Pre-Columbian South America, or the late Pleistocene to early Holocene geological periods. Several waves of people occupied the cave over time, as evidenced by some of the early artwork that has been radiocarbon dated to about 7300 BC. The age of the paintings was calculated from the remains of bone-made pipes used for spraying the paint on the wall of the cave to create the artwork. The site is considered by some scholars to be the best material evidence of South American early hunter-gatherer groups.
 W
WCave paintings are a type of parietal art, found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin, and the oldest known are more than 44,000 years old, found in both the Franco-Cantabrian region in western Europe, and in the caves in the district of Maros. The oldest are often constructed from hand stencils and simple geometric shapes. However, more recently, in 2021, cave art of a pig found in an Indonesian island, and dated to over 45,500 years, has been reported.
 W
WCeremonial Stone Landscapes is the term used by USET, United Southern and Eastern Tribes, Inc., a non-profit, intertribal organization of American Indians, for certain stone work sites in eastern North America. Elements often found at these sites include dry stone walls, rock piles, stone chambers, unusually-shaped boulders, split boulders with stones inserted in the split, and boulders propped up off the ground with smaller rocks. While neither the age of these sites nor the idea of their creation by indigenous peoples has been accepted generally, interest in the sites is increasing. This interest is generated in part by USET's Resolution #2007:037, entitled Sacred Ceremonial Stone Landscapes Found in the Ancestral Territories of United Southern and Eastern Tribes, Inc. Member Tribes.
 W
WCibola White Ware is a ceramic tradition of Arizona and New Mexico, dating from 1225-1325 CE.
 W
WThe double spout and bridge vessel was a form of usually ceramic drinking container developed sometime before 500 BC by indigenous groups on the Peruvian coast. True to its name, this type of bottle is distinguished by two spouts with a handle bridging them. First used by the Paracas culture, it was later adopted by the Nazca. While at first the Paracas tended to incise designs derived from the art of the Chavin culture on the surface of the vessels, later on they began to treat the vessel as a sculptural form, an advance facilitated by developments in ceramic technology that allowed them construct vessels with thinner walls. This tradition was continued by the Nazca, whose vessels were elaborately figurative, decorated with polychrome glazes, or both.
 W
WThe Dumbarton Oaks birthing figure is a possibly Aztec scapolite figurine of a woman giving childbirth in a squatting position. Housed in the Dumbarton Oaks collection, United States, the figurine is considered by several scholars to be a pre-Columbian artwork, while others believe it was made in modern times, possibly in the 19th century. The figurine measures 20.2 cm in height.
 W
WThe Fresno Art Museum is an art museum in Fresno, California. The museum's collection includes contemporary art, modern art, Mexican and Mexican-American art, and Pre-Columbian sculpture.
 W
WThe Museum of Gold is a museum located in Bogotá, Colombia. It is one of the most visited touristic highlights in the country. The museum receives around 500,000 tourists per year.
 W
WThe use of jade in Mesoamerica for symbolic and ideological ritual was highly influenced by its rarity and value among pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures, such as the Olmec, the Maya, and the various groups in the Valley of Mexico. Although jade artifacts have been created and prized by many Mesoamerican peoples, the Motagua River valley in Guatemala was previously thought to be the sole source of jadeite in the region.
 W
WThe Lanzón is a granite stela that is associated with the Chavín culture. It is located in the Old Temple of Chavin de Huantar which rests in the central highlands of Peru. The Chavín religion was the first major religious and cultural movement in the Andes mountains, flourishing between 900 and 200 BCE. The Lanzón itself was erected during the Early Horizon period of Andean art circa 500 BCE and takes its name from the Spanish word for "lance," an allusion to the shape of the sculpture. The name is deceiving, as its form more closely resembles a highland plow which would have been used for agricultural purposes at the time. It is suspected because of this that the deity depicted is linked to agrarian worship.
 W
WHarry Männil, also known as Harry Mannil Laul, was an Estonian businessman, art collector, and cultural benefactor in several countries, as well as an alleged war criminal.
 W
WOne of the best-known arts of the Mapuche is their textiles. The tradition of Mapuche textile production dates back to pre-Hispanic times and continues up to this day. Prior to the 20th century Mapuche textiles and ponchos in particular were important trade items.
 W
WAncient Mayan art is the visual arts of the Mayan civilization, an eastern and south-eastern Mesoamerican culture made up of a great number of small kingdoms in present-day Mexico, Guatemala, Belize and Honduras. Many regional artistic traditions existed side by side, usually coinciding with the changing boundaries of Maya polities. This civilization took shape in the course of the later Preclassic Period, when the first cities and monumental architecture started to develop and the hieroglyphic script came into being. Its greatest artistic flowering occurred during the seven centuries of the Classic Period.
 W
WMaya blue is a unique bright azure blue pigment manufactured by cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica, such as the Maya and Aztec.
 W
WMaya ceramics are ceramics produced in the Pre-Columbian Maya culture of Mesoamerica. The vessels used different colors, sizes, and had varied purposes. Vessels for the elite could be painted with very detailed scenes, while utilitarian vessels were undecorated or much simpler. Elite pottery, usually in the form of straight-sided beakers called "vases", used for drinking, was placed in burials, giving a number of survivals in good condition. Individual examples include the Princeton Vase and the Fenton Vase.
 W
WThis article describes the art produced by the Muisca. The Muisca established one of the four grand civilisations of the pre-Columbian Americas on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense in present-day central Colombia. Their various forms of art have been described in detail and include pottery, textiles, body art, hieroglyphs and rock art. While their architecture was modest compared to the Inca, Aztec and Maya civilisations, the Muisca are best known for their skilled goldworking. The Museo del Oro in the Colombian capital Bogotá houses the biggest collection of golden objects in the world, from various Colombian cultures including the Muisca.
 W
WPainting in the Americas before European colonization is the Precolumbian painting traditions of the Americas. Painting was a relatively widespread, popular and diverse means of communication and expression for both religious and utilitarian purpose throughout the regions of the Western Hemisphere. During the period before and after European exploration and settlement of the Americas; including North America, Central America, South America and the islands of the Caribbean, the Bahamas, the West Indies, the Antilles, the Lesser Antilles and other island groups, indigenous native cultures produced a wide variety of visual arts, including painting on textiles, hides, rock and cave surfaces, bodies especially faces, ceramics, architectural features including interior murals, wood panels, and other available surfaces. Many of the perishable surfaces, such as woven textiles, typically have not been preserved, but Precolumbian painting on ceramics, walls, and rocks have survived more frequently.
 W
WThe Paracas textiles were found at a necropolis in Peru in the 1920s. The necropolis held 420 bodies who had been mummified and wrapped in embroidered textiles of the Paracas culture in 200–300 BCE. The examples in the British Museum show flying shamans who hold severed heads by their hair.
 W
WA pictogram, also called a pictogramme, pictograph, or simply picto, and in computer usage an icon, is a graphic symbol that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object. Pictographs are often used in writing and graphic systems in which the characters are to a considerable extent pictorial in appearance. A pictogram may also be used in subjects such as leisure, tourism, and geography.
 W
WThe Raimondi Stele is a sacred object and significant piece of art of the Chavín culture of the central Andes in present-day Peru. The Chavín were named after Chavín de Huantar, the main structure found in ruin at this archaeological site. The Chavín are believed to have occupied this space from 1500 BCE to 300 BCE, which places them in the Early Horizon period of Andean cultures. The Early Horizon came to rise after the spread and domination of Chavín art styles, namely the hanging pendant eye and anthropomorphism/zoomorphism of feline, serpent, and crocodilian creatures. The stele is seven feet high, made of highly polished granite, with a lightly incised design featuring these key artistic choices shown in the depiction of the Staff God. After not being found in situ, the stele now is housed in the courtyard of the Museo Nacional de Arqueología Antropología e Historia del Perú in Lima.
 W
WRio Grande Glaze Ware is a late prehistoric and historic pottery tradition of the Puebloan peoples of New Mexico. The tradition involved painting pots with black paint made with lead ore; as the pots were fired the black paint fused and sometimes ran. The tradition lasted from AD 1315 to 1700. Rio Grande Glaze Ware was made or used in a number of villages from the Santa Fe area to the north end of Elephant Butte Reservoir, and from the valley of the Rio Puerco east to the upper Pecos River Valley.
 W
WRoosevelt Red Ware, also known as Salado Red Ware and Salado Polychrome, is a late prehistoric pottery tradition found across large portions of Arizona and New Mexico. The tradition involves the combination of red, white, and black paint in varying configurations along with compositional and morphological characteristics. This ceramic tradition begins about AD 1280-1290 and lasts until at least AD 1450 based on tree-ring dating.
 W
WThe Southeastern Ceremonial Complex, aka S.E.C.C., is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography, ceremonies, and mythology of the Mississippian culture. It coincided with their adoption of maize agriculture and chiefdom-level complex social organization from 1200 to 1650 CE. Due to some similarities between S.E.C.C. and contemporary Mesoamerican cultures, scholars from the late 1800s to mid-1900s suspected there was a connection between the two locations. But, later research indicates the two cultures have no direct links and that their civilizations developed independently.
 W
WThe stone spheres of Costa Rica are an assortment of over 300 petrospheres in Costa Rica, on the Diquís Delta and on Isla del Caño. Locally, they are also known as bolas de piedra. The spheres are commonly attributed to the extinct Diquís culture, and they are sometimes referred to as the Diquís Spheres. They are the best-known stone sculptures of the Isthmo-Colombian area.
 W
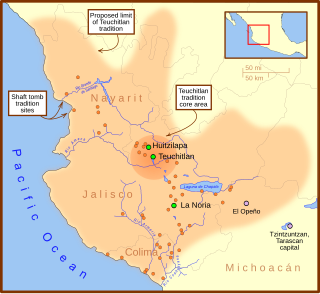
WThe Teuchitlán culture was one of several related cultures in West Mexico during the Late Formative to Classic period. Situated in the Tequila Valleys of Jalisco, the Teuchitlán culture shared in the tradition of burying some of their dead in shaft and chamber tombs. Archaeological work from the past few decades have demonstrated that West Mexico was not occupied by one homogeneous culture, historically referred to as the shaft tomb tradition, that stretched from Nayarit, Jalisco, and Colima. Instead, West Mexico was composed of multiple cultures with several distinct commonalities.
 W
WVisual arts by indigenous peoples of the Americas encompasses the visual artistic practices of the indigenous peoples of the Americas from ancient times to the present. These include works from South America and North America, which includes Central America and Greenland. The Siberian Yupiit, who have great cultural overlap with Native Alaskan Yupiit, are also included.
 W
WThe Western Mexico shaft tomb tradition refers to a set of interlocked cultural traits found in the western Mexican states of Jalisco, Nayarit, and, to a lesser extent, Colima to its south, roughly dating to the period between 300 BCE and 400 CE, although there is not wide agreement on this end date. Nearly all of the artifacts associated with this shaft tomb tradition have been discovered by looters and are without provenance, making dating problematic.
 W
WXicalcoliuhqui is a common motif in Mesoamerican art. It is composed of three or more steps connected to a hook or spiral, reminiscent of a "greek-key" meander. Pre-Columbian examples may be found on everything from jewelry, masks, ceramics, sculpture, textiles and featherwork to painted murals, codices and architectural elements of buildings. The motif has been in continual use from the pre-Columbian era to the present.
 W
W W
W W
W W
W