 W
WAbenaki, or Abnaki, is an endangered Algonquian language of Quebec and the northern states of New England. The language has Eastern and Western forms which differ in vocabulary and phonology and are sometimes considered distinct languages.
 W
WArikara is a Caddoan language spoken by the Arikara Native Americans who reside primarily at Fort Berthold Reservation in North Dakota. Arikara is close to the Pawnee language, but they are not mutually intelligible.
 W
WArutani–Sape, also known as Awake–Kaliana or Kalianan, is a proposed language family that includes two of the most poorly documented languages in South America, both of which are now extinct. They are at best only distantly related. Kaufman (1990) found a connection convincing, but Migliazza & Campbell (1988) maintained that there is no evidence for linking them. The two languages are,Arutani Sape
 W
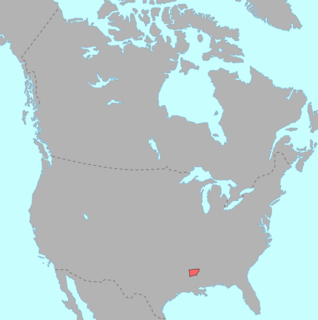
WCaddo is a Native American language, the traditional language of the Caddo Nation. It is critically endangered, with no exclusively Caddo-speaking community and only 25 speakers as of 2009 who acquired the language as children outside school instruction. Caddo has several mutually intelligible dialects. The most commonly used dialects are Hasinai and Hainai; others include Kadohadacho, Natchitoches and Yatasi.
 W
WThe Chickasaw language is a Native American language of the Muskogean family. It is agglutinative and follows the word order pattern of subject–object–verb (SOV). The language is closely related to, though perhaps not entirely mutually intelligible with, Choctaw. It is spoken by the Chickasaw tribe, now residing in Southeast Oklahoma, centered on Ada.
 W
WThe Chinookan languages were a small family of languages spoken in Oregon and Washington along the Columbia River by Chinook peoples. Although the last known native speaker of any Chinookan language died in 2012, the 2009-2013 American Community Survey found 270 self-identified speakers of Upper Chinook.
 W
WColorado River Numic, of the Numic branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family, is a dialect chain that stretches from southeastern California to Colorado. Individual dialects are Chemehuevi, which is in danger of extinction, Southern Paiute, and Ute. According to the Ethnologue, there were a little less than two thousand speakers of Colorado River Numic Language in 1990, or around 40% out of an ethnic population of 5,000.
 W
WComanche is a Uto-Aztecan language spoken by the Comanche people, who split from the Shoshone people soon after the Comanche had acquired horses around 1705. The Comanche language and the Shoshoni language are therefore quite similar, but certain consonant changes in Comanche have inhibited mutual intelligibility.
 W
WCrow is a Missouri Valley Siouan language spoken primarily by the Crow Nation in present-day southeastern Montana. The word, Apsáalooke, translates to "children of the large beaked bird." It is one of the larger populations of American Indian languages with 2,480 speakers according to the 1990 US Census.
 W
WFox is an Algonquian language, spoken by a thousand Meskwaki, Sauk, and Kickapoo in various locations in the Midwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
 W
WAtsina, or Gros Ventre, was the ancestral language of the Gros Ventre people of Montana. The last fluent speaker died in 2007, though revitalization efforts are underway.
 W
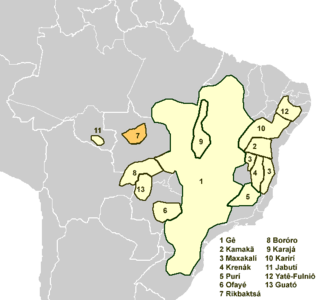
WGuató is a possible language isolate spoken by 1% of the Guató people of Brazil.
 W
WInuttitut, or Inuttut is a dialect of Inuktitut. It is spoken across northern Labrador by Inuit people, whose traditional lands are known as Nunatsiavut.
 W
WKiowa or Cáuijògà/Cáuijò:gyà is a Tanoan language spoken by the Kiowa Tribe of Oklahoma in primarily Caddo, Kiowa, and Comanche counties. The Kiowa tribal center is located in Carnegie. Like most North American indigenous languages, Kiowa is an endangered language.
 W
WKoasati is a Native American language of Muskogean origin. The language is spoken by the Coushatta people, most of whom live in Allen Parish north of the town of Elton, Louisiana, though a smaller number share a reservation near Livingston, Texas, with the Alabama people. In 1991, linguist Geoffrey Kimball estimated the number of speakers of the language at around 400 people, of whom approximately 350 live in Louisiana. The exact number of current speakers is unclear, but Coushatta Tribe officials claim that most tribe members over 20 speak Koasati. In 2007, the Coushatta Tribe of Louisiana, in collaboration with McNeese State University and the College of William and Mary, began the Koasati (Coushatta) Language Project as a part of broader language revitalization efforts with National Science Foundation grant money under the Documenting Endangered Languages program.
 W
WThe Kutenai language, also Kootenai, Kootenay, Ktunaxa, and Ksanka, is the native language of the Kutenai people of Montana and Idaho in the United States and British Columbia in Canada. It is typically considered a language isolate, unrelated to the Salishan family of languages spoken by neighboring tribes on the coast and in the interior Plateau. The Kutenai also speak ʔa·qanⱡiⱡⱡitnam, Ktunaxa Sign Language.
 W
WMalecite–Passamaquoddy is an endangered Algonquian language spoken by the Maliseet and Passamaquoddy peoples along both sides of the border between Maine in the United States and New Brunswick, Canada. The language consists of two major dialects: Malecite, which is mainly spoken in the Saint John River Valley in New Brunswick; and Passamaquoddy, spoken mostly in the St. Croix River Valley of eastern Maine. However, the two dialects differ only slightly, mainly in accent. The indigenous people widely spoke Malecite-Passamaquoddy in these areas until around the post-World War II era when changes in the education system and increased marriage outside of the speech community caused a large decrease in the number of children who learned or regularly used the language. As a result, in both Canada and the U.S. today, there are only 600 speakers of both dialects, and most speakers are older adults. Although the majority of younger people cannot speak the language, there is growing interest in teaching the language in community classes and in some schools.
 W
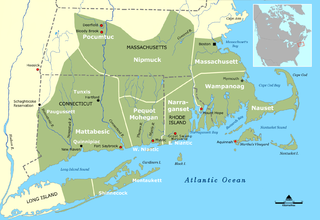
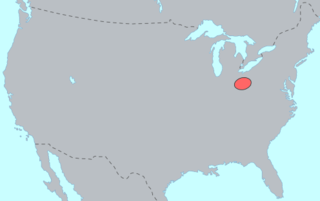
WThe Massachusett language is an Algonquian language of the Algic language family, formerly spoken by several peoples of eastern coastal and southeastern Massachusetts. In its revived form, it is spoken in four communities of Wampanoag people. The language is also known as Natick or Wôpanâak (Wampanoag), and historically as Pokanoket, Indian or Nonantum.
 W
WThe Salish or Séliš language, also known as Kalispel–Pend d'oreille, Kalispel–Spokane–Flathead, or, to distinguish it from the Salish language family to which it gave its name, Montana Salish, is a Salishan language spoken by about 64 elders of the Flathead Nation in north central Montana and of the Kalispel Indian Reservation in northeastern Washington state, and by another 50 elders of the Spokane Indian Reservation of Washington. As of 2012, Salish is "critically endangered" in Montana and Idaho according to UNESCO.
 W
WMura is a language of Amazonas, Brazil. It is most famous for Pirahã, its sole surviving dialect. Linguistically, it is typified by agglutinativity, a very small phoneme inventory, whistled speech, and the use of tone.
 W
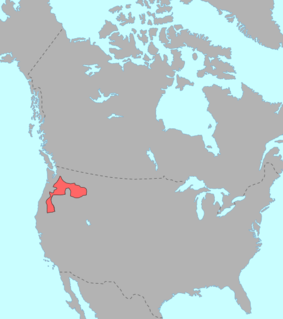
WNez Perce, also spelled Nez Percé or called Nimipuutímt, is a Sahaptian language related to the several dialects of Sahaptin. Nez Perce comes from the French phrase nez percé, "pierced nose"; however, Nez Perce, who call themselves Nimiipuu, meaning "the people", did not pierce their noses. This misnomer may have occurred as a result of confusion on the part of the French, as it was surrounding tribes who did so.
 W
WThe Ofayé or Opaye language, also Ofaié-Xavante, Opaié-Shavante, forms its own branch of the Macro-Jê languages. It is spoken by only a couple of the small Ofayé people, though language revitalization efforts are underway. Grammatical descriptions have been made by the Pankararú linguist Maria das Dores de Oliveira (Pankararu), as well as by Sarah C. Gudschinsky and Jennifer E. da Silva, from the Universidade Federal do Mato Grosso do Sul.
 W
WOsage is a Siouan language that was spoken by the Osage people of Oklahoma.
 W
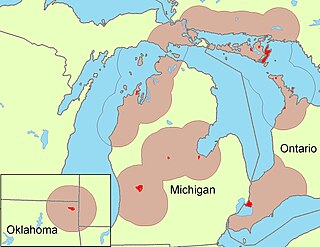
WThe Ottawa, also known as the Odawa dialect of the Ojibwe language is spoken by the Ottawa people in southern Ontario in Canada, and northern Michigan in the United States. Descendants of migrant Ottawa speakers live in Kansas and Oklahoma. The first recorded meeting of Ottawa speakers and Europeans occurred in 1615 when a party of Ottawas encountered explorer Samuel de Champlain on the north shore of Georgian Bay. Ottawa is written in an alphabetic system using Latin letters, and is known to its speakers as Nishnaabemwin "speaking the native language" or Daawaamwin "speaking Ottawa".
 W
WThe Pawnee language is a Caddoan language spoken by some Pawnee Native Americans who now live in north-central Oklahoma. Their traditional historic lands were along the Platte River in what is now Nebraska.
 W
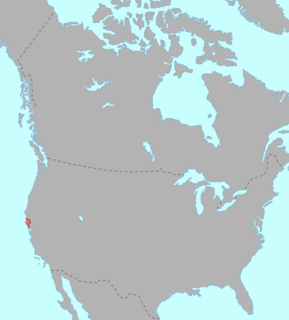
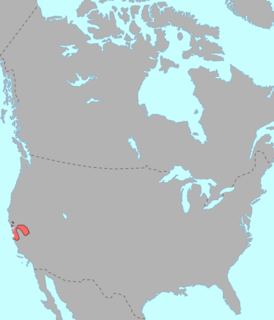
WThe Pomoan, or Pomo, languages are a small family of seven languages indigenous to northern California spoken by the Pomo people, whose ancestors lived in the valley of the Russian River and the Clear Lake basin. Four languages are extinct, and all surviving languages except Kashaya have fewer than ten speakers.
Purépecha, often called Tarascan, is a language isolate or small language family that is spoken by some 140,000 Purépecha in the highlands of Michoacán, Mexico.
 W
WThe Rikbaktsa language, also spelled Aripaktsa, Erikbatsa, Erikpatsa and known ambiguously as Canoeiro, is a language spoken by the Rikbaktsa people of Mato Grosso, Brazil, that forms its own branch of the Macro-Gê languages.
 W
WThe Shawnee language is a Central Algonquian language spoken in parts of central and northeastern Oklahoma by the Shawnee people. It was originally spoken by these people in a broad territory throughout the Eastern United States, mostly north of the Ohio River. They occupied territory in Ohio, West Virginia, Kentucky, and Pennsylvania.
 W
WSouthern Pomo is one of seven mutually unintelligible Pomoan languages which were formerly spoken and is currently spoken by the Pomo people in Northern California along the Russian River and Clear Lake. The Pomo languages have been grouped together with other so-called Hokan languages. Southern Pomo is unique among the Pomo languages in preserving, perhaps, the greatest number of syllables inherited from Proto-Pomo.
 W
WSouthern Sierra Miwok is a Utian language spoken by the Native American people called the Southern Sierra Miwok of Northern California. Southern Sierra Miwok is a member of the Miwok language family along with Lake Miwok, Coast Miwok (extinct), Saclan (extinct), Plains Miwok (extinct), Northern Sierra Miwok and Central Sierra Miwok. The Miwok languages are a part of the larger Penutian language stock. The original territory of the Southern Sierra Miwok people is similar to modern day Mariposa County, California. The Southern Sierra Miwok language is nearly extinct with only a few speakers existing today. However, as of 2012, an active revitalization program is underway.
 W
WTehuelche is one of the Chonan languages of Patagonia. Its speakers were nomadic hunters who occupied territory in present-day Chile, north of Tierra del Fuego and south of the Mapuche people. It is also known as Aonikenk or Aonekko 'a'ien.
 W
WThe Tunica or Luhchi Yoroni language is a language isolate that was spoken in the Central and Lower Mississippi Valley in the United States by Native American Tunica peoples. There are no native speakers of the Tunica language, but as of 2017, there are 32 second language speakers.
 W
WWarao is the native language of the Warao people. A language isolate, it is spoken by about 33,000 people primarily in northern Venezuela, Guyana and Suriname. It is notable for its unusual object–subject–verb word order. The 2015 Venezuelan film Gone with the River was spoken in Warao.
 W
WWasho is an endangered Native American language isolate spoken by the Washo on the California–Nevada border in the drainages of the Truckee and Carson Rivers, especially around Lake Tahoe. While there are only 20 elderly native speakers of Washo, since 1994 there has been a small immersion school that has produced a number of moderately fluent younger speakers. The immersion school has since closed its doors and the language program now operates through the Cultural Resource Department for the Washoe Tribe. The language is still very much endangered; however, there has been a renaissance in the language revitalization movement as many of the students who attended the original immersion school have become teachers.
 W
WWichita is an extinct Caddoan language once spoken in Oklahoma by the Wichita and Affiliated Tribes. The last fluent heritage speaker, Doris Lamar-McLemore, died in 2016, although in 2007 there were three first-language speakers alive. This has rendered Wichita functionally extinct; however, the tribe offers classes to revitalize the language and works in partnership with the Wichita Documentation Project of the University of Colorado, Boulder.
 W
WWintuan is a family of languages spoken in the Sacramento Valley of central Northern California.
 W
WYuchi (Euchee) is the language of the Tsoyaha, also known as Yuchi people, now living in Oklahoma. Historically, they lived in what is now known as the southeastern United States, including eastern Tennessee, western Carolinas, northern Georgia, and Alabama, during the period of early European colonization. Many speakers of the Yuchi language became allied with the Muscogee Creek when they migrated into their territory in Georgia and Alabama. They were forcibly relocated with them to Indian Territory in the early 19th century.