 W
Walluc.ee (pronounced: "all-you-see") was a user-generated online video directory for TV shows, movies, music videos, sport, pornography, anime and cartoons, and later a search engine. Alluc did not host any content itself nor contain any download links; all links were to streaming video sharing websites. Users provided the links in the right category and published links to the site after being reviewed by the administrators. Video hosting sites that were linked to on Alluc included YouTube, Dailymotion, and Veoh, amongst others.
 W
WAnsarada is an Australian private company that develops AI-powered virtual data rooms and Material Information Platforms. It is created for business transactions and material events such as mergers and acquisitions, fundraising, tenders and IPOs.
 W
WaXXo is the Internet alias of an individual who released and standardized commercial film DVDs as free downloads on the Internet between 2005 and 2009. The files, which were usually new films, were popular among the file sharing community using peer-to-peer file sharing protocols such as BitTorrent. A download-tracking firm BigChampagne found — in a sampling period in late 2008 — that almost 33.5% of all movie downloads were aXXo torrents. aXXo encoded files to approximately 700 MB – the same size for a compact disc. Due to the re-encoded quality of an aXXo file, the suffix "aXXo" was often used by imitators.
 W
WBox, Inc. is a public company based in Redwood City, California. It develops and markets cloud-based content management, collaboration, and file sharing tools for businesses. Box was founded in 2005 by Aaron Levie and Dylan Smith. Initially, it focused on consumers, but around 2009 and 2010 Box pivoted to focus on business users. The company raised about $500 million over numerous funding rounds, before going public in 2015. Its software allows users to store and manage files in an online folder system accessible from any device. Users can then comment on the files, share them, apply workflows, and implement security and governance policies.
 W
WWayne Chang is an American entrepreneur, angel investor, film producer, and philanthropist. He is best known for founding Crashlytics, a startup acquired by Twitter in 2013; creating a filesharing network called i2hub; making seed investments in companies including JetSmarter, Draftkings, and Gusto; and his lawsuit against the Winklevoss brothers.
 W
WClipix is a privately funded company offering an online bookmarking, file sharing, and organizational tool. The utility is available in 13 languages, and as of 2014 had users in 154 countries. Clipix allows users to save online content and other documents to private or public "clipboards." By dragging a “clip” button onto the browser bar, users click and clip online items for later reference. Clipix users can also add digital files they want to access, including Excel spreadsheets, Microsoft Word documents, PDF files, and email messages. To organize content further, Clipix also offers multiboards, which are created by dragging several clipboards into one "Main Category" clipboard. Syncboards are synchronized clipboards that multiple users can access and add to, in order to work collaboratively. The company’s "Price Drop Alert" allows users to name the price they’d like to pay for any item that is sold online. Once a "Price Drop Alert" is set, Clipix notifies the user when an item has been discounted to his or her preferred price. The Clipix app for iPad, iPhone, and Android synchronizes with the Clipix web interface.
 W
WA content delivery network, or content distribution network (CDN), is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers. The goal is to provide high availability and performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end users. CDNs came into existence in the late 1990s as a means for alleviating the performance bottlenecks of the Internet as the Internet was starting to become a mission-critical medium for people and enterprises. Since then, CDNs have grown to serve a large portion of the Internet content today, including web objects, downloadable objects, applications, live streaming media, on-demand streaming media, and social media sites.
 W
WCopyright infringement is the use of works protected by copyright law without permission for a usage where such permission is required, thereby infringing certain exclusive rights granted to the copyright holder, such as the right to reproduce, distribute, display or perform the protected work, or to make derivative works. The copyright holder is typically the work's creator, or a publisher or other business to whom copyright has been assigned. Copyright holders routinely invoke legal and technological measures to prevent and penalize copyright infringement.
 W
WA distributed hash table (DHT) is a distributed system that provides a lookup service similar to a hash table: key-value pairs are stored in a DHT, and any participating node can efficiently retrieve the value associated with a given key. The main advantage of a DHT is that nodes can be added or removed with minimum work around re-distributing keys. Keys are unique identifiers which map to particular values, which in turn can be anything from addresses, to documents, to arbitrary data. Responsibility for maintaining the mapping from keys to values is distributed among the nodes, in such a way that a change in the set of participants causes a minimal amount of disruption. This allows a DHT to scale to extremely large numbers of nodes and to handle continual node arrivals, departures, and failures.
 W
WShawn Fanning is an American computer programmer, entrepreneur, and angel investor. He developed Napster, one of the first popular peer-to-peer ("P2P") file sharing platforms, in 1999. The popularity of Napster was widespread and Fanning was featured on the cover of Time magazine.
 W
WFilesTube was a metasearch engine established in 2007, which specialized in searching files in various file sharing and uploading services, such as Mega. It also included sections for videos, games, lyrics and software.
 W
WFreenet is a peer-to-peer platform for censorship-resistant, anonymous communication. It uses a decentralized distributed data store to keep and deliver information, and has a suite of free software for publishing and communicating on the Web without fear of censorship. Both Freenet and some of its associated tools were originally designed by Ian Clarke, who defined Freenet's goal as providing freedom of speech on the Internet with strong anonymity protection.
 W
WGroupLogic, Inc., founded in 1988 and headquartered in Arlington, Virginia, USA, is an enterprise software company that develops, sells and supports software for moving and storing data including activEcho, mobilEcho, ArchiveConnect, MassTransit and ExtremeZ-IP. GroupLogic’s products are used by information technology organizations to allow employees to access and manage corporate files regardless of the type of computing platform the employee is using to access the network.
 W
WHotfile was a one-click file hosting website founded by Hotfile Corp in 2006 in Panama City, Panama. On December 4, 2013, Hotfile ceased all operations, the same day as signing a $4 million settlement with the Motion Picture Association of America (MPAA); the settlement had previously been misreported as $80 million.
 W
WAn illegal number is a number that represents information which is illegal to possess, utter, propagate, or otherwise transmit in some legal jurisdiction. Any piece of digital information is representable as a number; consequently, if communicating a specific set of information is illegal in some way, then the number may be illegal as well.
 W
WMagnet is a URI scheme that defines the format of magnet links, a de facto standard for identifying files (URN) by their content, via cryptographic hash value rather than by their location.
 W
WMediaFire is a file hosting, file synchronization, and cloud storage service based in Shenandoah, Texas, United States. Founded in June 2006 by Derek Labian and Tom Langridge, the company provides client software for Microsoft Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS, BlackBerry 10, and web browsers. MediaFire has 43 million registered users and attracted 1.3 billion unique visitors to its domains in 2012.
 W
WThe Missionary Church of Kopimism, is a congregation of file sharers who believe that copying information is a sacred virtue and was founded by Isak Gerson, a 19-year-old philosophy student, and Gustav Nipe in Uppsala, Sweden in the autumn of 2010. The Church, based in Sweden, has been officially recognized by the Legal, Financial and Administrative Services Agency as a religious community in January 2012, after three application attempts.
 W
WmobilEcho, created by GroupLogic, Inc. is a mobile file management system for iPhone and iPad. It was first introduced on May 23, 2011 at TechCrunch Disrupt in New York City. mobilEcho (mE) is information technology (IT) software for securely integrating iPhones, iPads and Android phones and tablets with corporate file servers and networks. mobilEcho is installed on corporate file servers by IT departments and installed on iPhones, iPads and Android phones and tablet computers by users; it allows for storage and secure transfer of files back and forth directly between servers and iPhones, iPads and Android phones and tablets.
 W
WThe Multi Protocol File System (MPFS) is a multi-path network filesystem technology developed and sold by EMC Corporation. MPFS is intended to allow hundreds to thousands of client computer nodes to access shared computer data with higher performance than conventional NAS file sharing protocols such as NFS.
 W
WA music download is the digital transfer of music via the Internet into a device capable of decoding and playing it, such as a personal computer, portable media player, MP3 player or smartphone. This term encompasses both legal downloads and downloads of copyrighted material without permission or legal payment. According to a Nielsen report, downloadable music accounted for 55.9 percent of all music sales in the US in 2012. By the beginning of 2011, Apple's iTunes Store alone made US$1.1 billion of revenue in the first quarter of its fiscal year. Music downloads are typically encoded with modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) audio data compression, particularly the Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) format used by iTunes as well as the MP3 audio coding format.
 W
WOdex's actions against file sharing were Japan copyright owners' pre-action discovery to Singapore Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to request for subscribers details in Singapore who were traced to illegal download activities of their licensed anime series. Odex is a Singapore-based company that licenses and releases anime for local and regional Southeast Asian consumption. As Japanese copyright owners are located in Japan, Odex, being holder of the Japanese anime license in Singapore, were appointed to submit legal documents and court proceedings on their behalf in Singapore.
 W
WOnline piracy is the practice of downloading and distributing copyrighted content digitally without permission, such as music or software. The principle behind piracy has predated the creation of the Internet, but its online popularity arose alongside the internet. Despite its explicit illegality in many developed countries, online piracy is still widely practiced, due to both the ease with which it can be done and the often defensible ethics behind it.
 W
WPeer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application. They are said to form a peer-to-peer network of nodes.
 W
WThe Pirate Party is a political party in Sweden founded in 2006. Its sudden popularity has given rise to parties with the same name and similar goals in Europe and worldwide, forming the International Pirate Party movement.
 W
WA PirateBox is a portable electronic device, often consisting of a Wi-Fi router and a device for storing information, creating a wireless network that allows users who are connected to share files anonymously and locally. By design, this device is disconnected from the Internet.
 W
WThe seizure of Megaupload, a popular filesharing website with 150 million registered users, occurred on January 19, 2012, following a US indictment accusing Megaupload of harbouring millions of copyrighted files. According to the indictment, Megaupload was costing copyright holders over $500 million in lost revenues.
 W
WStage6 was a video sharing website owned and operated by DivX, Inc., where users could upload, share, and view video clips. Stage6 was different from other video services in that it streamed high quality video clips that were user-encoded with DivX and Xvid video codecs.
 W
WSteal This Film is a film series documenting the movement against intellectual property directed by Jamie King, produced by The League of Noble Peers and released via the BitTorrent peer-to-peer protocol.
 W
WTor, short for The Onion Router, is free and open-source software for enabling anonymous communication. It directs Internet traffic through a free, worldwide, volunteer overlay network, consisting of more than six thousand relays, for concealing a user's location and usage from anyone conducting network surveillance or traffic analysis. Using Tor makes it more difficult to trace the Internet activity to the user. Tor's intended use is to protect the personal privacy of its users, as well as their freedom and ability to conduct confidential communication by keeping their Internet activities unmonitored.
 W
WTPB AFK: The Pirate Bay Away From Keyboard is a 2013 Swedish documentary film directed and produced by Simon Klose. It focuses on the lives of the three founders of The Pirate Bay – Peter Sunde, Fredrik Neij, and Gottfrid Svartholm – and the Pirate Bay trial. Filming began sometime in 2008, and concluded on 28 February 2012.
 W
WA USB dead drop is a USB mass storage device installed in a public space. For example, a USB flash drive might be mounted in an outdoor brick wall and fixed in place with fast concrete. Members of the public are implicitly invited to find files, or leave files, on a dead drop by directly plugging their laptop into the wall-mounted USB stick in order to transfer data. The dead drops can therefore be regarded as an anonymous, offline, peer-to-peer file sharing network. However, in practice USB dead drops are often used for social or artistic reasons, rather than for practical ones.
 W
WWarez is a common computing and broader cultural term referring to pirated software that is distributed via the Internet. Warez is used most commonly as a noun, a plural form of ware, and is intended to be pronounced like the word wares. The circumvention of copy protection (cracking) is an essential step in generating warez, and based on this common mechanism, the software-focused definition has been extended to include other copyright-protected materials, including movies and games. The global array of warez groups has been referred to as "The Scene", deriving from its earlier description as "the warez scene". Distribution and trade of copyrighted works without payment of fees or royalties generally violates national and international copyright laws and agreements. The term warez covers supported as well as unsupported (abandonware) items, and legal prohibitions governing creation and distribution of warez cover both profit-driven and "enthusiast" generators and distributors of such items.
 W
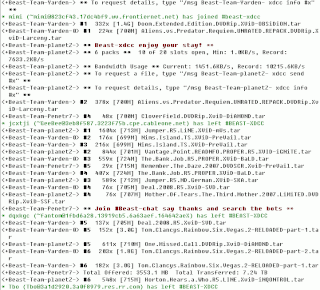
WXDCC is a computer file sharing method which uses the Internet Relay Chat (IRC) network as a host service.