 W
WThe Ahrensburg culture or Ahrensburgian was a late Upper Paleolithic nomadic hunter culture in north-central Europe during the Younger Dryas, the last spell of cold at the end of the Weichsel glaciation resulting in deforestation and the formation of a tundra with bushy arctic white birch and rowan. The most important prey was the wild reindeer. The earliest definite finds of arrow and bow date to this culture, though these weapons might have been invented earlier. The Ahrensburgian was preceded by the Hamburg and Federmesser cultures and superseded by the Maglemosian and Swiderian cultures. Ahrensburgian finds were made in southern and western Scandinavia, the North German plain and western Poland. The Ahrensburgian area also included vast stretches of land now at the bottom of the North and Baltic Sea, since during the Younger Dryas the coastline took a much more northern course than today.
 W
WThe Baalberge Group was a late neolithic "culture" in Central Germany and Bohemia between 4000 and 3150 BC. Because of issues with the archaeological use of the term culture it is now often referred to as the Baalberge Ceramic style. It is named after its first findspot: on the Schneiderberg at Baalberge, Salzlandkreis, Saxony-Anhalt. The Baalberge group is generally seen as part of the Funnelbeaker culture. In the Middle Elbe/Saale region it is part of Funnelbeaker phase TRB-MES II and III.
 W
WThe Bromme culture is a late Upper Paleolithic culture dated to c. 11,600 to 9,800 cal BC, which corresponds to the second half of the Allerød Oscillation.
 W
WThe Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 2900 BCE – 2350 BCE, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a vast area, from the contact zone between the Yamnaya culture and the Corded ware culture in south Central Europe, to the Rhine on the west and the Volga in the east, occupying parts of Northern Europe, Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The Corded Ware culture is thought to have originated from the westward migration of Yamnaya-related people from the steppe-forest zone into the territory of late Neolithic European cultures such as the Globular Amphora and Funnelbeaker cultures, and is considered to be a likely vector for the spread of some or all of the core Indo-European languages, excluding the Anatolian languages and Tocharian.
 W
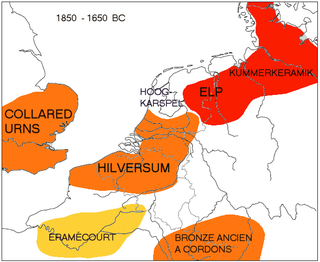
WThe Elp culture is a Bronze Age archaeological culture of the Netherlands having earthenware pottery of low quality known as "Kümmerkeramik" as a marker. The initial phase is characterized by tumuli, strongly tied to contemporary tumuli in Northern Germany and Scandinavia, and apparently related to the Tumulus culture in Central Europe. This phase was followed by a subsequent change featuring Urnfield (cremation) burial customs.
 W
WThe Ertebølle culture is the name of a hunter-gatherer and fisher, pottery-making culture dating to the end of the Mesolithic period. The culture was concentrated in Southern Scandinavia. It is named after the type site, a location in the small village of Ertebølle on Limfjorden in Danish Jutland. In the 1890s, the National Museum of Denmark excavated heaps of oyster shells there, mixed with mussels, snails, bones and bone, antler and flint artifacts, which were evaluated as kitchen middens, or refuse dumps. Accordingly, the culture is less commonly named the Kitchen Midden. As it is approximately identical to the Ellerbek culture of Schleswig-Holstein, the combined name, Ertebølle-Ellerbek is often used. The Ellerbek culture is named after a type site in Ellerbek, a community on the edge of Kiel, Germany.
 W
WThe Funnel(-neck-)beaker culture, in short TRB or TBK was an archaeological culture in north-central Europe. It developed as a technological merger of local neolithic and mesolithic techno-complexes between the lower Elbe and middle Vistula rivers. These predecessors were the Lengyel-influenced Stroke-ornamented ware culture (STK) groups/Late Lengyel and Baden-Boleráz in the southeast, Rössen groups in the southwest and the Ertebølle-Ellerbek groups in the north. The TrB introduced farming and husbandry as a major source of food to the pottery-using hunter-gatherers north of this line.
 W
WThe Globular Amphora culture, c. 3400–2800 BC, is an archaeological culture in Central Europe. Marija Gimbutas assumed an Indo-European origin, though this is contradicted by newer genetic studies that show a connection to the earlier wave of Neolithic farmers rather than to invaders from the Ukrainian and western-southern Russian steppes.
 W
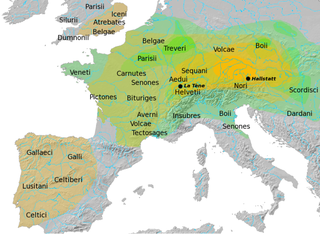
WThe Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western and Central European culture of Late Bronze Age from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC and followed in much of its area by the La Tène culture. It is commonly associated with Proto-Celtic populations. Older assumptions of the early 20th century of Illyrians having been the bearers of especially the Eastern Hallstatt culture are indefensible and archeologically unsubstantiated.
 W
WThe Hamburg culture or Hamburgian was a Late Upper Paleolithic culture of reindeer hunters in northwestern Europe during the last part of the Weichsel Glaciation beginning during the Bölling interstadial. Sites are found close to the ice caps of the time. They extend as far north as the Pomeranian ice margin.
 W
WThe Hinkelstein culture is a Neolithic archaeological culture situated in Rhine-Main and Rhenish Hesse, Germany. It is a Megalithic culture, part of the wider Linear Pottery horizon, dating to approximately the 50th to 49th century BC.
 W
WThe House Urns culture was an early Iron Age culture of the 7th century BC in central Germany, in the Region between Harz Mountains and the junction of river Saale to river Elbe. It was the western periphery of the bronze and Iron Age Lusatian culture.
 W
WThe Jastorf culture was an Iron Age material culture in what are now north Germany and Denmark, spanning the 6th to 1st centuries BC, forming the southern part of the Pre-Roman Iron Age. The culture evolved out of the Nordic Bronze Age, through influence from the Hallstatt culture farther south.
 W
WThe La Tène culture was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age, succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscans, and Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences.
 W
WThe Lengyel culture is an archaeological culture of the European Neolithic, centered on the Middle Danube in Central Europe. It flourished from 5000 to 4000 BC, ending with phase IV, e.g., in Bohemia represented by the 'Jordanow/Jordansmühler culture'. It is followed by the Funnel Neck Beaker/TrB culture. The eponymous type site is at Lengyel in Tolna county, Hungary.
 W
WLincombian-Ranisian-Jerzmanowician (LRJ) was a culture or technocomplex (industry) dating to the beginning Upper Paleolithic, about 43,000 years ago. It is characterised by leaf points made on long blades, which are thought to have been made by the last Neanderthals, although some researchers have suggested that it could be a culture of the first anatomically modern humans in Europe. It is rarely found, but extends across northwest Europe from Wales to Poland.
 W
WThe Linear Pottery culture is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic, flourishing c. 5500–4500 BC. It is abbreviated as LBK, and is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Incised Ware culture, and falls within the Danubian I culture of V. Gordon Childe.
 W
WThe Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age in most of what is now Poland and parts of the Czechia, Slovakia, eastern Germany and western Ukraine. It covers the Periods Montelius III to V of the Northern European chronological scheme.
 W
WThe Magdalenian cultures are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years ago. It is named after the type site of La Madeleine, a rock shelter located in the Vézère valley, commune of Tursac, in France's Dordogne department.
 W
WMaglemosian is the name given to a culture of the early Mesolithic period in Northern Europe. In Scandinavia, the culture was succeeded by the Kongemose culture.
 W
WThe Michelsberg culture is an important Neolithic culture in Central Europe. Its dates are c. 4400–3500 BC. Its conventional name is derived from that of an important excavated site on Michelsberg hill near Untergrombach, between Karlsruhe and Heidelberg (Baden-Württemberg).
 W
WThe Nordic Bronze Age is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from c. 1700–500 BC.
 W
WThe Prague-Korchak culture was an archaeological culture attributed to the Early Slavs. The other contemporary main Early Slavic culture was the Prague-Penkovka culture situated further south, with which it makes up the "Prague-type pottery" group. The largest part of sites dates to the late 5th and early 6th century AD according to Late Roman iron fibulae. Settlements were as a rule placed at rivers, near water sources, and were typically unfortified, with 8–20 households with courtyards. Burial sites were both flat graves and barrows (kurgans), and cremation was dominant.
 W
WThe Przeworsk culture was an Iron Age material culture in the region of what is now Poland, that dates from the 3rd century BC to the 5th century AD. It takes its name from the town Przeworsk, near the village where the first artifacts were identified.
 W
WThe Rössen culture or Roessen culture is a Central European culture of the middle Neolithic.
 W
WThe Single Grave culture was a Chalcolithic culture which flourished on the western North European Plain from ca. 2,800 BC to 2,200 BC. It is characterized by the practice of single burial, the deceased usually being accompanied by a battle-axe, amber beads, and pottery vessels. The Single Grave culture was a local variant of the Corded Ware culture, and appears to have emerged as a result of a migration of peoples from the Pontic–Caspian steppe. It was succeeded by the Bell Beaker culture, which according to the "Dutch model" appears to have been ultimately derived from the Single Grave culture. More recently, the accuracy of this model has been questioned.
 W
WThe Stroke-ornamented ware (culture) or (German) Stichbandkeramik, Stroked Pottery culture, Danubian Ib culture of V. Gordon Childe, or Middle Danubian culture is the successor of the Linear Pottery culture, a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic in Central Europe. The STK flourishes during approximately 4600-4400 BC. Centered on Silesia in Poland, eastern Germany and the northern Czech Republic, it overlaps with the Lengyel horizon to the south, and the Rössen culture to the west.
 W
WThe Tumulus culture dominated Central Europe during the Middle Bronze Age.
 W
WThe Únětice culture or Aunjetitz culture is an archaeological culture at the start of the Central European Bronze Age, dated roughly to about 2300–1800 BC. The eponymous site for this culture, the village of Únětice, is located in the central Czech Republic, northwest of Prague. There are about 1,400 documented Únětice culture sites in the Czech Republic and Slovakia, 550 sites in Poland, and, in Germany, about 500 sites and loose finds locations. The Únětice culture is also known from north-eastern Austria, and from western Ukraine.
 W
WThe Urnfield culture was a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe, often divided into several local cultures within a broader Urnfield tradition. The name comes from the custom of cremating the dead and placing their ashes in urns which were then buried in fields. Over much of Europe, the Urnfield culture followed the Tumulus culture and was succeeded by the Hallstatt culture. Some linguists and archaeologists have associated this culture with the Proto-Celtic language, or a pre-Celtic language family.