 W
WBaathism is an Arab nationalist ideology which promotes the creation and development of a unified Arab state through the leadership of a vanguard party over a progressive revolutionary government. The ideology is officially based on the theories of the Syrian intellectuals Michel Aflaq, Zaki al-Arsuzi, and Salah al-Din al-Bitar. Baathist leaders of the modern era include the former leader of Iraq, Saddam Hussein, former President of Syria, Hafez al-Assad and the current President of Syria, Bashar al-Assad.
 W
WBanal nationalism refers to the everyday representations of the nation which build a shared sense of national belonging amongst humans, a sense of tribalism through national identity. The term is derived from English academic, Michael Billig's 1995 book of the same name and is intended to be understood critically. Billig's book has been described as 'the fourth most cited work on nationalism ever published'. Billig devised the concept of 'banal nationalism' to highlight the routine and often unnoticed ways that established nation-states are reproduced from day to day. The concept has been highly influential, particularly within the discipline of political geography, with continued academic interest since the book's publication in the 1995. Today the term is used primarily in academic discussion of identity formation, geopolitics, and the nature of nationalism in contemporary political culture.
 W
WBorder Art is a contemporary art practice rooted in the socio-political experience(s), such as of those on the U.S.-Mexico borderlands, or frontera. Since its conception in the mid-80's, this artistic practice has assisted in the development of questions surrounding homeland, borders, surveillance, identity, race, ethnicity, and national origin(s).
 W
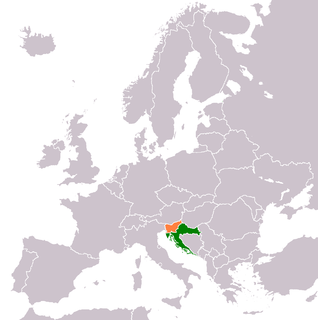
WFollowing the breakup of Yugoslavia in 1991, Slovenia and Croatia became independent countries. As the border between the countries had not been determined in detail prior to independence, several parts of the border were disputed, both on land and at the sea, namely in the Gulf of Piran.
 W
WDacianism is a Romanian term describing the tendency to ascribe, largely relying on questionable data and subjective interpretation, an idealized past to the country as a whole. While particularly prevalent during the regime of Nicolae Ceaușescu, its origin in Romanian scholarship dates back more than a century.
 W
WThe term enemy of the people or enemy of the nation, is a designation for the political or class opponents of the subgroup in power within a larger group. The term implies that by opposing the ruling subgroup, the "enemies" in question are acting against the larger group, for example against society as a whole. It is similar to the notion of "enemy of the state". The term originated in Roman times as Latin: hostis publicus, typically translated into English as the "public enemy". The term in its "enemy of the people" form has been used for centuries in literature.
 W
WThe term enemy of the people or enemy of the nation, is a designation for the political or class opponents of the subgroup in power within a larger group. The term implies that by opposing the ruling subgroup, the "enemies" in question are acting against the larger group, for example against society as a whole. It is similar to the notion of "enemy of the state". The term originated in Roman times as Latin: hostis publicus, typically translated into English as the "public enemy". The term in its "enemy of the people" form has been used for centuries in literature.
 W
WFascism is a form of far-right, authoritarian ultranationalism characterized by dictatorial power, forcible suppression of opposition, and strong regimentation of society and of the economy, which came to prominence in early 20th-century Europe. The first fascist movements emerged in Italy during World War I, before spreading to other European countries. Opposed to anarchism, democracy, liberalism, and Marxism, fascism is placed on the far right-wing within the traditional left–right spectrum.
 W
WA homeland is the concept of the place where a cultural, national, or racial identity had formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethnic nationalist connotations. A homeland may also be referred to as a fatherland, a motherland, or a mother country, depending on the culture and language of the nationality in question.
 W
WA homeland is the concept of the place where a cultural, national, or racial identity had formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethnic nationalist connotations. A homeland may also be referred to as a fatherland, a motherland, or a mother country, depending on the culture and language of the nationality in question.
 W
WIndependence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of a dependent territory.
 W
WInvented traditions are cultural practices that are presented or perceived as traditional, arising from the people starting in the distant past, but which in fact are relatively recent and often even consciously invented by identifiable historical actors. The concept was highlighted in the 1983 book The Invention of Tradition, edited by Eric Hobsbawm and Terence Ranger. Hobsbawm's introduction argues that many "traditions" which "appear or claim to be old are often quite recent in origin and sometimes invented." This "invention" is distinguished from "starting" or "initiating" a tradition which does not then claim to be old. The phenomenon is particularly clear in the modern development of the nation and of nationalism, creating a national identity promoting national unity, and legitimising certain institutions or cultural practices.
 W
WJingoism is nationalism in the form of aggressive and proactive foreign policy, such as a country's advocacy for the use of threats or actual force, as opposed to peaceful relations, in efforts to safeguard what it perceives as its national interests. Colloquially, jingoism is excessive bias in judging one's own country as superior to others – an extreme type of nationalism.
 W
WAtatürk's nationalism is a civic nationalist patriotic ideology that bases the definition of the nation on the values of identity and political unity, regardless of religion, as stated in Article 88 of the Turkish Constitution of 1924 and Atatürk's Principles.
 W
WThe Khmer Rouge is the name that was popularly given to members of the Communist Party of Kampuchea (CPK) and by extension to the regime through which the CPK ruled Cambodia between 1975 and 1979. The name was coined in the 1960s by prime minister Norodom Sihanouk to describe his country's heterogeneous, communist-led dissidents, with whom he allied after his 1970 overthrow.
 W
W"A land without a people for a people without a land" is a widely cited phrase associated with the movement to establish a Jewish homeland in Palestine during the 19th and 20th centuries.
 W
WThe melting pot is a monocultural metaphor for a heterogeneous society becoming more homogeneous, the different elements "melting together" with a common culture; an alternative being a homogeneous society becoming more heterogeneous through the influx of foreign elements with different cultural backgrounds, possessing the potential to create disharmony within the previous culture. Historically, it is often used to describe the cultural integration of immigrants to the United States.
 W
WA national myth is an inspiring narrative or anecdote about a nation's past. Such myths often serve as an important national symbol and affirm a set of national values. A national myth may sometimes take the form of a national epic or be incorporated into a civil religion. A group of related myths about a nation may be referred to as the national mythos, from μῦθος, the original Greek word for "myth".
 W
WNasserism is a Arab nationalist, socialist political ideology based on the thinking of Gamal Abdel Nasser, one of the two principal leaders of the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, and Egypt's second President. Spanning the domestic and international spheres, it combines elements of Arab socialism, republicanism, nationalism, anti-imperialism, developing world solidarity, and international non-alignment.
 W
WNational cinema is a term sometimes used in film theory and film criticism to describe the films associated with a specific nation-state. Although there is little relatively written on theories of national cinema it has an irrefutably important role in globalization. Film provides a unique window to other cultures, particularly where the output of a nation or region is high.
 W
WPancasila is the official, foundational philosophical theory of Indonesia. Pancasila comprises two Old Javanese words originally derived from Sanskrit: "pañca" ("five") and "śīla" ("principles").
 W
WPatriotism or national pride is the feeling of love, devotion, and sense of attachment to a homeland or the country and alliance with other citizens who share the same sentiment to create a feeling of oneness among the people. This attachment can be a combination of many different feelings, language relating to one's own homeland, including ethnic, cultural, political or historical aspects. It encompasses a set of concepts closely related to nationalism and mostly liberal nationalism.
 W
WProto-fascism refers to the direct predecessor ideologies and cultural movements that influenced and formed the basis of fascism. A prominent proto-fascist figure is Gabriele D'Annunzio, the Italian nationalist whose politics influenced Benito Mussolini and Italian Fascism. Proto-fascist political movements include the Italian Nationalist Association, the German National Association of Commercial Employees and the German National People's Party.
 W
WThe right to exist is said to be an attribute of nations. According to an essay by the nineteenth-century French philosopher Ernest Renan, a state has the right to exist when individuals are willing to sacrifice their own interests for the community it represents. Unlike self-determination, the right to exist is an attribute of states rather than of peoples. It is not a right recognized in international law. The phrase has featured prominently in the Arab–Israeli conflict since the 1950s.
 W
WRomantic nationalism is the form of nationalism in which the state derives its political legitimacy as an organic consequence of the unity of those it governs. This includes such factors as language, race, ethnicity, culture, religion, and customs of the nation in its primal sense of those who were born within its culture. It can be applied to ethnic nationalism as well as civic nationalism. Romantic nationalism arose in reaction to dynastic or imperial hegemony, which assessed the legitimacy of the state from the top down, emanating from a monarch or other authority, which justified its existence. Such downward-radiating power might ultimately derive from a god or gods (see the divine right of kings and the Mandate of Heaven).
 W
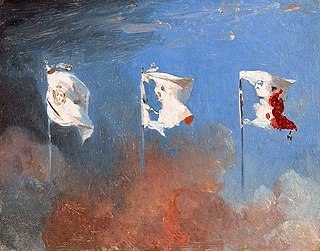
WA tricolour or tricolor is a type of flag or banner design with a triband design which originated in the 16th century as a symbol of republicanism, liberty or indeed revolution. The flags of France, Italy, Romania, Mexico, and Ireland were all first adopted with the formation of an independent republic in the period of the French Revolution to the Revolutions of 1848, with the exception of the Irish tricolour, which dates from 1848 but was not popularised until the Easter Rising in 1916 and adopted in 1919.
 W
W"United we stand, divided we fall" is a phrase used in many different kinds of mottos, most often to inspire unity and collaboration. Its core concept lies in the collectivist notion that if individual members of a certain group with binding ideals – such as a union, coalition, confederation or alliance – work on their own instead of as a team, they are each doomed to fail and will all be defeated. The phrase is also often referred to with only the words "United we stand".
 W
WWelfare chauvinism or welfare state nationalism is the political notion that welfare benefits should be restricted to certain groups, particularly to the natives of a country as opposed to immigrants. It is used as an argumentation strategy by right-wing populist parties, which describes a claimed connection between the problems of the welfare state and, in essence, immigration, but also other social groups such as welfare recipients and the unemployed. The focus is placed on categorizing state residents in two extremes: the "nourishing" and "debilitating" and the contradiction between them in the competition for the society's scarce resources.