 W
WThe native Taíno tribes have played a major role in the history and culture of the island of Puerto Rico. At the head of each tribe was a cacique who, along with the nitaínos, governed each of the yucayeques, or villages of the island.
 W
WFa'amatai is the indigenous political ('chiefly') system of Samoa, central to the organization of Samoan society. It is the traditional indigenous form of governance in both Samoas, comprising American Samoa and the Independent State of Samoa. The term comprises the prefix fa'a and the word matai.
 W
WSachems and sagamores are paramount chiefs among the Algonquians or other Native American tribes of northeastern North America. The two words are anglicizations of cognate terms from different Eastern Algonquian languages. The Sagamore was a lesser chief than the Sachem. Both of these chiefs are elected by their people. Sagamores are chosen by single bands to represent them, and the Sachem is chosen to represent a tribe or group of bands. Neither title is hereditary but each requires selection by the band thus led.
 W
WAbd el-Kader bel Hach Tieb was a Riffian tribal leader, caïd of the Beni Sicar, in northeastern Morocco.
 W
WIn many parts of West Africa, there is an old chieftaincy tradition, and the Akan people have developed their own hierarchy, which exists alongside the democratic structure of the country. The Akan word for the ruler or one of his various courtiers is "Nana". In colonial times, Europeans translated it as "chief", but that is not an exact equivalent. Other sources speak of "kings", which is also not entirely correct, especially in the case of the said courtiers. The term "chief" has become common even among modern Ghanaians, though it would be more correct to use the expression "Nana" without translation wherever possible.
 W
WAsser Rig – a.k.a. Asser Rig Skjalmsen Hvide – was a jarl and chieftain from Zealand, Denmark, a son of Skjalm Hvide and Signe Asbjørnsdatter.
 W
WChief White Eagle was a Native American politician and American civil rights leader who served as the hereditary chief of the Ponca from 1870 until 1904. His 34-year tenure as the Ponca head of state spanned the most consequential period of cultural and political change in their history, beginning with the unlawful Ponca Trail of Tears in 1877 and continuing through his successful effort to obtain justice for his people by utilizing the American media to wage a public relations campaign against the United States and President Rutherford B. Hayes. His advocacy against America's Indian removal policy following the Ponca Trail of Tears marked a shift in public opinion against the federal government's Indian policy that ended the policy of removal, placing him at the forefront of the nascent Native American civil rights movement in the second half of the 19th century.
 W
WCockacoeske was a 17th-century leader of the Pamunkey tribe in what is now the U.S. state of Virginia. During her thirty-year reign, she worked within the English colonial system in Virginia, trying to recapture the former power of past paramount chiefs and maintain peaceful unity among the several tribes under her leadership. She was the first of the tribal leaders to sign the Virginia-Indian Treaty of Middle Plantation.
 W
WLoir Botor Dingit was a rattan farmer and Paramount Chief from Indonesia. He was awarded the Goldman Environmental Prize in 1997 for his efforts on forest protection.
 W
WEsbern Snare, also known as Esbern the Resolute, (1127–1204) was a høvding, or chieftain, royal chancellor and crusader. His family were members of the powerful Hvide clan. In 1192, during the Crusades and after the fall of Jerusalem, he led a small group of Danish soldiers to the Holy Land. Upon his return, he had the Church of Our Lady, Kalundborg built.
 W
WFendi Abbas Salameh Al Fayez was an Arab leader from the Al-Fayez family who was the chief Sheikh of the Bani Sakher Clan from the 1820s up until his death. He is widely regarded as the most influential figure in the Bani Sakher and one of the most powerful tribal figures in Arabia in the 19th century. Fendi's first documented tribal battle was as early as 1820 when he was just twenty years old.
 W
WGundonaa Hajia Samata Abudu is the Paramount woman Chief of the Dagbon traditional area in the Northern Region of Ghana. All women Chiefs in that area are subordinate to her. She heads the Gundogu skin, the female equivalent of the Yendi skin, which is headed by the Yaa-Naa. The Gundonaa is the only Chief, be it male or female, who is able to veto the Yaa-Naa’s word. She is assisted in her duties by the Kpatunaa, a female Chief of the Kpatuya clan.
 W
WYa-ha Hadjo was a member of the Creek Nation who avoided forced relocation to Indian Territory with his band by moving south to the Florida Territory where he joined with the Seminole and retained his position as chief. In 1826 while still in Georgia, Mad Wolf visited Washington, D.C. as part of a Creek delegation.
 W
WVictor Koumorico was a Congolese politician who served as President of the Senate of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from July 1961 until November 1962.
 W
WMassasoit Sachem or Ousamequin was the sachem or leader of the Wampanoag confederacy. Massasoit means Great Sachem.
 W
WGazon Matodya was gaanman of the Okanisi or Ndyuka people of Suriname, South America, one of six Maroon peoples in the area. He lived in Diitabiki (Drietabbetje), a village located on the Tapanahony River. Gaanman Gazon belonged to the Otoo Lo clan, from which most of the Aukan chiefs have come. He was one of the longest-living chiefs to date.
 W
WMithqal Sattam Fendi Al Fayez (Arabic: مثقال الفايز, was a historical Jordanian political and tribal figure whose work helped the establishment of The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. Mithqal was one of the two leading sheikhs of Bani Sakhr; he took power in the early twentieth century, and headed the Al-Twaga half of the Bani Sakhr tribe, which consisted of the Al-Ghbein, Al-Amir, Al-Ka'abna, Al-Hgeish, Al-Saleet, and Al-Taybeen clans. He also headed his own clan, Al-Fayez.
Birsa Munda pronunciation (help·info) was an Indian tribal freedom fighter, religious leader, and folk hero who belonged to the Munda tribe. He spearheaded a tribal religious millenarian movement that arose in the Bengal Presidency in the late 19th century, during the British Raj, thereby making him an important figure in the history of the Indian independence movement. The revolt mainly concentrated in the Munda belt of Khunti, Tamar, Sarwada and Bandgaon.
 W
WNana Kofi Abuna V is the Paramount chief of Essipun in the Western Region of Ghana.
 W
WThe Nigerian Chieftaincy is the chieftaincy system that is native to Nigeria. Consisting of everything from the country's monarchs to its titled family elders, the chieftaincy as a whole is one of the oldest continuously existing institutions in Nigeria and is legally recognized by its government.
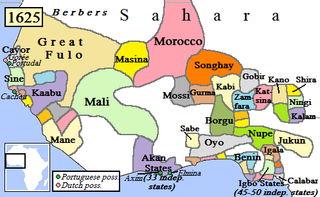 W
WNigerian traditional rulers often derive their titles from the rulers of independent states or communities that existed before the formation of modern Nigeria. Although they do not have formal political power, in many cases they continue to command respect from their people and have considerable influence.
 W
WOpechancanough was paramount chief of the Powhatan Confederacy in present-day Virginia from 1618 until his death. He had been a leader in the confederacy formed by his older brother Powhatan, from whom he inherited the paramountcy.
 W
WPowhatan, whose proper name was Wahunsenacawh, was the leader of the Powhatan, an alliance of Algonquian-speaking American Indians living in Tsenacommacah, in the Tidewater region of Virginia at the time when English settlers landed at Jamestown in 1607.
 W
WRobin Cassacinamon (c.1620s-1692) was a Pequot Indian governor appointed by the United Colonies to govern Pequots in southeastern Connecticut.
 W
WRichard G. Sneed is the 28th Principal Chief of the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians. Sneed succeeded former Principal Chief Patrick Lambert following Lambert's impeachment, only the second such impeachment since the 19th century.
 W
WTraditional leadership of Namibia is a governing structure in Namibia based on the ethnicity of the indigenous people of the territory. Acceptance of a traditional authority is vested in the Government of Namibia. There are 51 recognised traditional authorities and a further 40 pending applications.
 W
WUncas was a sachem of the Mohegans who made the Mohegans the leading regional Indian tribe in lower Connecticut, through his alliance with the New England colonists against other Indian tribes.