 W
WBalangao or Balangaw is an Austronesian language spoken in northern Luzon, Philippines. It is spoken in the central area of Mountain Province, and into Tanudan municipality of Kalinga Province.
 W
WBantoanon or Asi is a regional Bisayan language spoken, along with Romblomanon and Onhan, in the province of Romblon, Philippines. Asi originated in the island of Banton, Romblon and spread to the neighboring islands of Sibale, Simara, and the towns of Odiongan and Calatrava on Tablas Island. The Asi spoken in Odiongan is called Odionganon, Calatravanhon in Calatrava, Sibalenhon in Concepcion, Simaranhon in Corcuera, and Bantoanon in Banton.
 W
WBintauna is a Philippine language spoken in North Sulawesi (Celebes), Indonesia.
 W
WThe Central Luzon languages are a group of languages belonging to the Philippine languages. These are predominantly spoken in the western portions of Central Luzon in the Philippines. One of them, Kapampangan, is the major language of the Pampanga-Mount Pinatubo area. However, despite having three to four million speakers, it is threatened by the diaspora of its speakers after the June 1991 eruption of that volcano. Globalization also threatened the language, with the younger generation more on using and speaking Tagalog and English, but promotion and everyday usage boosted the vitality of Kapampangan.
 W
WCoastal Bikol is one of the three groups or family languages of Bikol languages. It includes the extinct languages of Mt. Isarog Agta and Mt. Iraya Agta, and Central Bikol that includes Viracnon dialect.
 W
WGa'dang is an Austronesian language spoken in northern Luzon, Philippines. Ga'dang spoken in Paracelis, Mountain Province, Luzon; Potia, Ifugao Province; and Tabuk, Kalinga Province.
 W
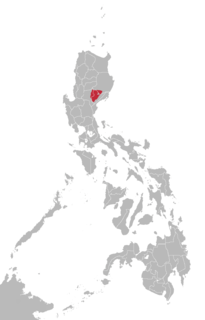
WThe Ibaloi language belongs to the Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian languages family. It is closely related to the Pangasinan language, which is spoken primarily in central and southern Benguet, and western Nueva Vizcaya. Its dialects include Daklan, Kabayan, and Bokod.
 W
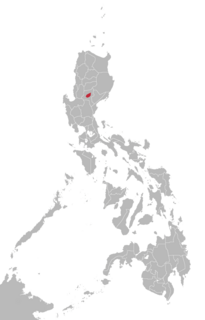
WBugkalot is a language of the indigenous Bugkalot people of northern Luzon, Philippines.
 W
WThe Iranun language also Iranon, Illanun is an Austronesian language belonging to the Danao languages spoken in the provinces of Maguindanao and other part of Lanao del Sur and Lanao del Norte, coastal municipalities of Zamboanga del Sur from Tukuran to Dumalinao and Cotabato in southern Philippines and the Malaysian state of Sabah. It is the second most spoken language in Maguindanao after the Maguindanao language.
 W
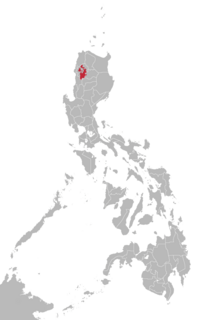
WIsinai is a Northern Luzon language primarily spoken in Nueva Vizcaya province in the northern Philippines. By linguistic classification, it is more divergent from other Central Cordilleran languages, such as Kalinga, Itneg or Ifugao and Kankanaey.
 W
WThe Itbayat language, Itbayaten, also known generically as Ibatan, is an Austronesian language, in the Batanic group, spoken in the Batanes Islands.
 W
WItneg is a South-Central Cordilleran dialect continuum found in the island of Luzon, Philippines. This language and Ilocano are spoken by the Itneg people in Abra.
 W
WIwaak is a South-Central Cordilleran language spoken by almost 3,300 people around the Cordillera Central mountain range of Luzon, Philippines. It is a Pangasinic language which makes it closely related to Pangasinan, one of the regional languages in the country, with around 1.2 million speakers.
 W
WKalanguya, also called Kallahan, is a dialect cluster spoken by the Kalanguya people of northern Luzon, Philippines.
 W
WKalinga is a dialect continuum of Kalinga Province in the Philippines, spoken by the Kalinga people, alongside Ilocano. The Banao Itneg variety is not one of the neighboring Itneg languages.
 W
WKarao is a language of northern Luzon, Philippines. It is spoken in the Karao, Ekip, and Bokod areas of western Benguet Province, and in the southwestern corner of Ifugao Province. The language is named after the barangay of Karaw in Bokod municipality, Benguet.
 W
WMaguindanao or Maguindanaon is an Austronesian language spoken by a majority of the population of Maguindanao province in the Philippines. It is also spoken by sizable minorities in different parts of Mindanao such as the cities of Zamboanga, Davao, and General Santos, and the provinces of North Cotabato, Sultan Kudarat, South Cotabato, Sarangani, Zamboanga del Sur, Zamboanga Sibugay, as well as Metro Manila. This was the language of the historic Sultanate of Maguindanao, which existed before and during the Spanish colonial period from 1500 to 1888.
 W
WMaranao is an Austronesian language spoken by the Maranao people in the provinces of Lanao del Norte and Lanao del Sur in the Philippines, and in Sabah, Malaysia.
 W
WNorthern Alta is a distinctive Aeta language of the mountains of northern Philippines. It is not close to Southern Alta or to other languages of Luzon.
 W
WThe Northern Luzon languages are one of the few established large groups within Philippine languages. These are mostly located in and around the Cordillera Central of northern Luzon in the Philippines. Among its major languages are Ilokano, Pangasinan and Ibanag.
 W
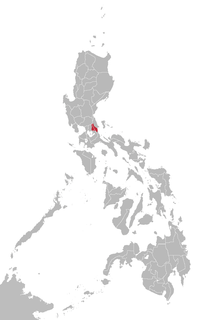
WParanan Agta is an Aeta language of Palanan, Isabela northern Philippines. Lexically it is extremely close to Paranan. However, this is due to convergence of that languages; the sources of the two languages are different, and this is reflected in their grammar.
 W
WRemontado, also known as Sinauna, Kabalat, Remontado Dumagat, and Hatang-Kayi, is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in Tanay, Rizal, General Nakar, Quezon, Rodriguez, Rizal and Antipolo, in the Philippines. It is one of the Philippine Negrito languages.
 W
WThe South Mindanao or Bilic languages are a group of related languages spoken by the Bagobo, B'laan, T'boli, and Tiruray peoples of the southern coast of Mindanao Island in the Philippines. They are not part of the Mindanao language family that covers much of the island. The languages are:Blaan Tboli Tiruray
 W
WTagabawa is a Manobo language of Davao City and Mount Apo in Mindanao, the Philippines. Tagabawa is spoken in Cotabato and Davao del Sur provinces, and on the slopes of Mount Apo west of Davao City (Ethnologue). The language is notably spoken by the Bagobo Tagabawa people who have a culture of high respect towards Philippine eagles, known in their language as banog.
 W
WTalaud is an Austronesian language spoken on the Talaud Islands north of Sulawesi, Indonesia.
 W
WTuwali language is a native language indigenous to Ifugao. It is mainly spoken in the whole province. Its different varieties distinguish the municipality.
 W
WYogad is an Austronesian language spoken primarily in Echague, Isabela and other nearby towns in the province in northern Philippines. The 1990 census claimed there were around 16,000 speakers.