 W
WCultural geography is a subfield within human geography. Though the first traces of the study of different nations and cultures on Earth can be dated back to ancient geographers such as Ptolemy or Strabo, cultural geography as academic study firstly emerged as an alternative to the environmental determinist theories of the early 20th century, which had believed that people and societies are controlled by the environment in which they develop. Rather than studying pre-determined regions based upon environmental classifications, cultural geography became interested in cultural landscapes. This was led by the "father of cultural geography" Carl O. Sauer of the University of California, Berkeley. As a result, cultural geography was long dominated by American writers.
 W
WAuto-segregation or self-segregation is the separation of a religious or ethnic group from the rest of society in a state by the group itself. This could also mean inability for a normal social interaction and a form of social exclusion.
 W
WCartopology is an academic and artistic discipline that aims to combine anthropological methods with cartographic ways to translate experiences and insights of architectural spaces into maps. The knowledge that these maps create is mainly used by policy makers in the field of regional development, city planning or cross-border cooperation. Occasionally, cartopological maps are displayed in art exhibitions about design or spatial planning.
 W
WChildren's street culture refers to the cumulative culture created by young children. Collectively, this body of knowledge is passed down from one generation of urban children to the next, and can also be passed between different groups of children. It is most common in children between the ages of seven and twelve. It is strongest in urban working-class industrial districts where children are traditionally free to "play out" in the streets for long periods without supervision.
 W
WA civilization is a complex society that is characterized by urban development, social stratification, a form of government, and symbolic systems of communication.
 W
WThe Clash of Civilizations is a thesis that people's cultural and religious identities will be the primary source of conflict in the post–Cold War world. The American political scientist Samuel P. Huntington argued that future wars would be fought not between countries, but between cultures. It was proposed in a 1992 lecture at the American Enterprise Institute, which was then developed in a 1993 Foreign Affairs article titled "The Clash of Civilizations?", in response to his former student Francis Fukuyama's 1992 book, The End of History and the Last Man. Huntington later expanded his thesis in a 1996 book The Clash of Civilizations and the Remaking of World Order.
 W
WColonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their religion, language, economics, and other cultural practices. The foreign administrators rule the territory in pursuit of their interests, seeking to benefit from the colonised region's people and resources. It is associated with but distinct from imperialism.
 W
WCultural landscape is a term used in the fields of geography, ecology, and heritage studies, to describe a symbiosis of human activity and environment. As defined by the World Heritage Committee, it is the "cultural properties [that] represent the combined works of nature and of man" and falls into three main categories:"a landscape designed and created intentionally by man" an "organically evolved landscape" which may be a "relict landscape" or a "continuing landscape" an "associative cultural landscape" which may be valued because of the "religious, artistic or cultural associations of the natural element."
 W
WCultural mapping, also known as cultural resource mapping or cultural landscape mapping, refers to a wide range of research techniques and tools used to "map" distinct peoples' tangible and intangible cultural assets within local landscapes around the world. Institutions concerned about safeguarding cultural diversity use the term. In its Universal Declaration on Cultural Diversity, UNESCO notes the importance of States adopting inclusive ways of encouraging cultural diversity...
 W
WDeglobalization or deglobalisation is the process of diminishing interdependence and integration between certain units around the world, typically nation-states. It is widely used to describe the periods of history when economic trade and investment between countries decline. It stands in contrast to globalization, in which units become increasingly integrated over time, and generally spans the time between periods of globalization. While globalization and deglobalisation are antitheses, they are no mirror images.
 W
WCultural diversity is the quality of diverse or different cultures, as opposed to monoculture, the global monoculture, or a homogenization of cultures, akin to cultural evolution. The term cultural diversity can also refer to having different cultures respect each other's differences. Moreover, it is often used to mention the variety of human societies or cultures in a specific region, or in the world as a whole. It refers to the inclusion of different cultural perspectives in an organization or society.
 W
WThe cultural perspective on Earth, or the world, varies by society and time period. Religious beliefs often include a creation belief as well as personification in the form of a deity. The exploration of the world has modified many of the perceptions of the planet, resulting in a viewpoint of a globally integrated ecosystem. Unlike the remainder of the planets in the Solar System, mankind didn't perceive the Earth as a planet until the sixteenth century.
 W
WKorean ethnic nationalism, or racial nationalism, is a political ideology and a form of ethnic identity that is widely prevalent in modern North and South Korea. It is based on the belief that Koreans form a nation, a race, and an ethnic group that shares a unified bloodline and a distinct culture. It is centered on the notion of the minjok, a term that had been coined in Imperial Japan ("minzoku") in the early Meiji period. Minjok has been translated as "nation", "people", "ethnic group", "race", and "race-nation".
 W
WA homeland is the concept of the place where a cultural, national, or racial identity had formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethnic nationalist connotations. A homeland may also be referred to as a fatherland, a motherland, or a mother country, depending on the culture and language of the nationality in question.
 W
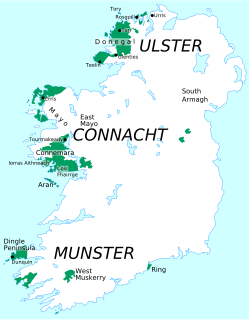
WGaeltacht is an Irish term referring individually to any, or collectively to all, of the districts where the government recognises that the Irish language is the predominant vernacular, or language of the home.
 W
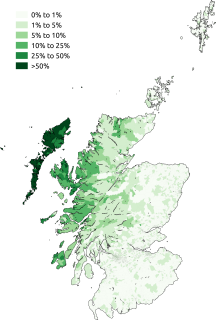
WThe Gàidhealtachd usually refers to the Highlands and Islands of Scotland and especially the Scottish Gaelic-speaking culture of the area. The corresponding Irish word Gaeltacht refers strictly to Irish-speaking areas.
 W
WA global city, also called a power city, world city, alpha city or world center, is a city which is a primary node in the global economic network. The concept comes from geography and urban studies, and the idea that globalization is created and furthered in strategic geographic locales according to a hierarchy of importance to the operation of the global system of finance and trade.
 W
WCultural globalization refers to the transmission of ideas, meanings and values around the world in such a way as to extend and intensify social relations. This process is marked by the common consumption of cultures that have been diffused by the Internet, popular culture media, and international travel. This has added to processes of commodity exchange and colonization which have a longer history of carrying cultural meaning around the globe. The circulation of cultures enables individuals to partake in extended social relations that cross national and regional borders The creation and expansion of such social relations is not merely observed on a material level. Cultural globalization involves the formation of shared norms and knowledge with which people associate their individual and collective cultural identities. It brings increasing interconnectedness among different populations and cultures.
 W
WGreek East and Latin West are terms used to distinguish between the two parts of the Greco-Roman world, specifically the eastern regions where Greek was the lingua franca and the western parts where Latin filled this role. During the Roman Empire a divide had persisted between Latin- and Greek-speaking areas; this divide was encouraged by administrative changes in the empire's structure between the 3rd and 5th centuries, which led ultimately to the establishment of separate administrations for the Eastern and Western halves of the Empire.
 W
WA homeland is the concept of the place where a cultural, national, or racial identity had formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethnic nationalist connotations. A homeland may also be referred to as a fatherland, a motherland, or a mother country, depending on the culture and language of the nationality in question.
 W
WCultural identity is a part of a person's identity, or their self-conception and self-perception, and is related to nationality, ethnicity, religion, social class, generation, locality or any kind of social group that has its own distinct culture. In this way, cultural identity is both characteristic of the individual but also of the culturally identical group of members sharing the same cultural identity or upbringing.
 W
WCultural imperialism, also called cultural colonialism, comprises the cultural aspects of imperialism. "Imperialism" here refers to the creation and maintenance of unequal relationships between civilisations, favouring a more powerful civilisation. Thus cultural imperialism is the practice of promoting and imposing a culture over a less powerful society. This may take the form of cultural hegemony of industrialised or politically and economically influential countries influencing general cultural values and standardising (globalising) civilisations elsewhere.
 W
WThis article contains lists of countries ranked by ethnic and cultural diversity level.
 W
WA Persianate society is a society that is based on or strongly influenced by the Persian language, culture, literature, art and/or identity.
 W
WThe right to homeland is according to some legal scholars a universal human right, which is derived from the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, including its Article 9. The concept evolved in German jurisprudence and is recognized in German constitutional law to a certain degree. Notable proponents of the concept include legal scholars Kurl Rabl, Rudolf Laun, Otto Kimminich, Dieter Blumenwitz, Felix Ermacora and Alfred-Maurice de Zayas. The concept is relevant to debates concerning ethnic cleansing in Europe after World War II, ethnic cleansing in Palestine, Cyprus and other areas.
 W
WTriadization is a proposed alternative to the theory of globalization. It states that political, economic and socio-cultural integration have been limited to three regions of the world: Japan and the newly industrialized countries of Southeast Asia, Western Europe and North America.
 W
WA truce term is a word or short phrase accepted within a community of children as an effective way of calling for a temporary respite or truce during a game or activity, such as tag or its variants. Common examples in English speaking cultures are barley, fainites, crosses, kings and exe(s)in the United Kingdom, pegs and nibs in New Zealand and variants of barley in Australia. In the United States, terms based on time-out have, from the 1950s onwards, largely supplanted earlier common terms based on kings and exe(s). Since the late 1980s time-out has been recorded in other English speaking cultures besides the US. Examples of use of truce terms are if a child has a stitch or wants to raise a point on the rules of the game.