 W
WA braid is a complex structure or pattern formed by interlacing two or more strands of flexible material such as textile yarns, wire, or hair. Braids have been made for thousands of years, in many different cultures around the world, for a variety of uses.
 W
WBraids are a complex hairstyle formed by interlacing three or more strands of hair. Braiding has been used to style and ornament human and animal hair for thousands of years in various cultures around the world.
 W
WAn aiguillette, also spelled aguillette, aiglet or aglet, is a cord with metal tips or lace tags, or the decorative tip itself.
 W
WBox braids are a type of hair-braiding style that is predominantly popular amongst African people and the African diaspora. This type of hairstyle is a "protective style" and is "boxy", consisting of square-shaped hair divisions. Box braids are generally installed by using synthetic hair which helps to add thickness as well as helping the natural hair that is in the braid. Because they are not attached to the scalp like other similar styles such as cornrows, box braids can be styled in a number of different ways. The installation process of box braids can be lengthy, but once installed they can last for six to eight weeks. They are known for being easy to maintain.
 W
WIn mathematics, the braid group on n strands, also known as the Artin braid group, is the group whose elements are equivalence classes of n-braids, and whose group operation is composition of braids. Example applications of braid groups include knot theory, where any knot may be represented as the closure of certain braids ; in mathematical physics where Artin's canonical presentation of the braid group corresponds to the Yang–Baxter equation ; and in monodromy invariants of algebraic geometry.
 W
WA braiding machine is a device that interlaces three or more strands of yarn or wire to create a variety of materials, including rope, reinforced hose, covered power cords, and some types of lace. Braiding materials include natural and synthetic yarns, metal wires, leather tapes, and others.
 W
WCornrows or canerows are a traditional style of braids in which the hair is braided very close to the scalp, using an underhand, upward motion to make a continuous, raised row. Cornrows are often done in simple, straight lines, as the term implies, but they can also be styled in elaborate geometric or curvilinear designs.
 W
WCrochet braids, also known as latch hook braids, are techniques for braiding hair that involve crocheting synthetic hair extensions to a person's natural hair with a latch hook or crochet hook. While crochet braids are a hybrid of traditional braids, they're considered to be more similar to weaves. This method is associated with African hair styles. Known as a protective style, the technique can assist with hair growth if cared for properly. Crochet braids can be worn straight, curly, twisted, or braided.
 W
WFingerloop braiding is a technique of making sturdy and decorative cords from threads. It is a type of braiding known as loop manipulation. The braid is made from loops of thread, attached at a central point, and the loops placed over the fingers and interlaced in different ways.
 W
WThe fourragère is a military award, distinguishing military units as a whole, in the form of a braided cord. The award was first adopted by France, followed by other nations such as the Netherlands, Belgium, Portugal, and Luxembourg. Fourragères have been awarded to units of both national and foreign militaries, except for that of Luxembourg, which has not been awarded to any foreign units.
 W
WA French braid, also called French plait is a type of braided hairstyle. The three-strand gathered plait includes three sections of hair that are braided together from the crown of the head to the nape of the neck.
 W
WGalloon is a decorative woven trim sometimes in the form of a braid and commonly made of metallic gold or silver thread, lace, or embroidery. Galloon is used in the trim of military and police uniforms, ecclesiastical dress, and as trim on textiles, drapery, and upholstery.
 W
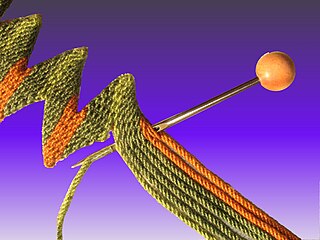
WThe German Armed Forces Badge for Weapons Proficiency is a decoration of the Bundeswehr, the armed forces of the Federal Republic of Germany.
 W
WThe gripfid is an invention of knotting expert Stuart Grainger. It is a small knotter's fid with an added "grip", a hollow shaft that ends near the point with a vee that acts as a jamming cleat.
 W
WThe infantry blue cord is a United States military decoration worn over the right shoulder of all infantry-qualified U.S. Army soldiers. It is a fourragere in light blue, specifically PMS 5415, worn under the right shoulder and under the right epaulette of a U.S. Army infantry soldier's Class A dress blue uniform jacket or Class B shirt. The cord is composed of a series of alternating left and right half knots that are tied around a leader cord to form a "Solomon bar".
 W
WKumihimo is a traditional Japanese artform of making braids and cords. Literally meaning "gathered threads", kumihimo are made by interlacing reels of yarn, commonly silk, with the use of traditional, specialised looms - either a marudai (丸台) or a takadai (高台).
 W
WA lucet is a tool used in cordmaking or braiding which is believed to date back to the Viking and Medieval periods, when it was used to create cords that were used on clothing, or to hang items from the belt. Lucet cord is square, strong, and slightly springy. It closely resembles knitted I-cord or the cord produced on a knitting spool. Lucet cord is formed by a series of loop like knots, and therefore will not unravel if cut. Unlike other braiding techniques such as kumihimo, finger-loop braiding or plaiting, where the threads are of a finite length, lucetted braids can be created without pre-measuring threads and so it is a technique suited for very long cords.
 W
WA marudai meaning "round stand" is the most common of the traditional frames used for making kumihimo, a type of Japanese braid.
 W
WIn Ancient Egyptian society, hair was an embodiment of identity. It could carry religious and erotic significance and portray information about gender, age, and social status. During the New Kingdom, more elaborate hairstyles for men and women, incorporating curls and plaits, began to be favored over the traditional, simple hairstyles of the Old and Middle Kingdoms.
 W
WIn particle physics, a plekton is a theoretical kind of particle that obeys a different style of statistics with respect to the interchange of identical particles. That is, it would be neither a boson nor a fermion, but subject to a braid statistics. Such particles have been discussed as a generalization of the braid characteristics of the anyon to dimension > 2.
 W
WPly-split braiding is a technique where one twisted cord ("splitter") passes through another twisted cord or cords splitting the plies of the latter cords. This is unlike weaving or many forms of braiding where cloth is formed by threads interlacing in an over-under sequence. Pattern is formed by cord color, and splitting order.
 W
WSprang is an ancient method of constructing fabric that has a natural elasticity. Its appearance is similar to netting, but unlike netting sprang is constructed entirely from warp threads. Archaeological evidence indicates that sprang predates knitting; the two needlework forms bear a visible resemblance and serve similar functions but require different production techniques.
 W
WA takadai (高台), also called kōdai, is a frame used for making kumihimo, a type of Japanese braid. The braids created on the takadai are flat as opposed to the braids created on the marudai which have a round or polygonal section. The threads are attached to weighted bobbins called tamas and lay on wood pieces with pegs that are called koma. A wooden sword is used to lightly beat the braid once the braiding has been done. The braiding progresses on a 'V' front, as opposed to weaving on a regular loom that progresses on a straight front.
 W
WThe traditional wedding cord, also known as the wedding lasso, is a piece of wedding paraphernalia used in some Christian Catholic wedding ceremonies. This is actually a representation of a loop of rosary beads made out of white satin or silk. During the wedding proper, this is traditionally formed into a figure-of-eight shape, and then placed around the neck areas of the bride and the groom after they have made their wedding vows, and are already kneeling on pillows for the pronouncement of a wedding prayer. This cord symbolizes lifetime unity or the everlasting union of the bride and groom when they officially become husband and wife, as well as a symbol of marital protection; while the loops formed signifies their love for one another. After the wedding, this marital twine is typically kept by the bride as a wedding souvenir. Use of the traditional wedding cord for weddings is common in Hispanic countries such as Mexico, the Philippines, and Spain.
 W
W