 W
WPrecious metals are rare, naturally occurring metallic chemical elements of high economic value. Chemically, the precious metals tend to be less reactive than most elements. They are usually ductile and have a high lustre. Historically, precious metals were important as currency but are now regarded mainly as investment and industrial commodities. Gold, silver, platinum, and palladium each have an ISO 4217 currency code.
 W
WBullion is non-ferrous metal that has been refined to a high standard of elemental purity. The term is ordinarily applied to bulk metal used in the production of coins and especially to precious metals such as gold and silver. It comes from the Anglo-Norman term for a melting-house where metal was refined, and earlier from French bouillon, "boiling". Although precious metal bullion is no longer used to make coins for general circulation, it continues to be held as an investment with a reputation for stability in periods of economic uncertainty. To assess the purity of gold bullion, the centuries-old technique of fire assay is still employed, together with modern spectroscopic instrumentation, to accurately determine its quality.
 W
WThe Edinburgh Assay Office is the last remaining Assay Office in Scotland and one of four which remain in the United Kingdom.
 W
WGold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and atomic number 79, making it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. In a pure form, it is a bright, slightly reddish yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native) form, as nuggets or grains, in rocks, in veins, and in alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver, naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium and also as mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium.
 W
WOf all the precious metals, gold is the most popular as an investment. Investors generally buy gold as a way of diversifying risk, especially through the use of futures contracts and derivatives. The gold market is subject to speculation and volatility as are other markets. Compared to other precious metals used for investment, gold has been the most effective safe haven across a number of countries.
 W
WGold parting is the separating of gold from silver. Gold and silver are often extracted from the same ores and are chemically similar and therefore hard to separate. Over the centuries special means of separation have been invented.
 W
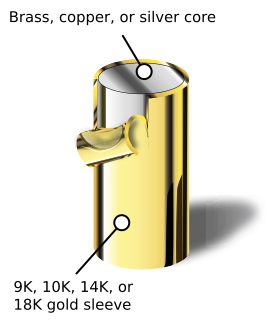
WGold-filled jewelry is jewelry composed of a solid layer of gold mechanically bonded to a base of either sterling silver or some base metal. The related terms "rolled gold plate" and "gold overlay" may legally be used in some contexts if the layer of gold constitutes less than 5% of the item's weight.
 W
WIridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, iridium is considered to be the second-densest naturally occurring metal with a density of 22.56 g/cm3 as defined by experimental X-ray crystallography. However, at room temperature and standard atmospheric pressure, iridium has been calculated to have a density of 22.65 g/cm3, 0.04 g/cm3 higher than osmium measured the same way. Still, the experimental X-ray crystallography value is considered to be the most accurate, and as such iridium is considered to be the second densest element. It is the most corrosion-resistant metal, even at temperatures as high as 2000 °C. Although only certain molten salts and halogens are corrosive to solid iridium, finely divided iridium dust is much more reactive and can be flammable.
 W
WIronstone’s Crown Jewel is the world’s largest piece of crystalline gold. At 44 lbs troy (16.4 kg), it is substantially larger than the Fricot "Nugget" and the Whopper, the next two largest specimens.
 W
WNines are an informal, logarithmic notation for proportions very near to one, or equivalently percentages very near 100%. Their common uses include grading the purity of materials.
 W
WOsmium is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white transition metal in the platinum group that is found as a trace element in alloys, mostly in platinum ores. Osmium is the densest naturally occurring element. When experimentally measured using x-ray crystallography, it has a density of 22.59 g/cm3. Manufacturers use its alloys with platinum, iridium, and other platinum-group metals to make fountain pen nib tipping, electrical contacts, and in other applications that require extreme durability and hardness.
 W
WPalladium is a chemical element with the symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired by her when she slew Pallas. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs). They have similar chemical properties, but palladium has the lowest melting point and is the least dense of them.
 W
WPallion designs, manufactures, and distributes precious metal products and related services. It is the largest precious metal services group in Australasia. Pallion is the result of the merger of the ABC Bullion and Palloys Group of companies founded in 1972 and 1951 respectively. The group maintains its headquarters in Sydney NSW Australia and is a wholly privately owned group of companies with manufacturing facilities and offices in Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane and Perth in Australia, Hong Kong (SAR) and mainland China.
 W
WPlatinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platino, meaning "little silver".
 W
WPlatinum as an investment has a much shorter history in the financial sector than gold or silver, which were known to ancient civilizations. Experts posit that platinum is about 15–20 times scarcer than gold, on the basis of annual mine production. Since 2014, platinum rates have fallen significantly lower than gold rates. More than 75% of global platinum is mined in South Africa.
 W
WRuthenium is a chemical element with the symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most other chemicals. Russian-born scientist of Baltic-German ancestry Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element in 1844 at Kazan State University and named ruthenium in honor of Russia. Ruthenium is usually found as a minor component of platinum ores; the annual production has risen from about 19 tonnes in 2009 to some 35.5 tonnes in 2017. Most ruthenium produced is used in wear-resistant electrical contacts and thick-film resistors. A minor application for ruthenium is in platinum alloys and as a chemistry catalyst. A new application of ruthenium is as the capping layer for extreme ultraviolet photomasks. Ruthenium is generally found in ores with the other platinum group metals in the Ural Mountains and in North and South America. Small but commercially important quantities are also found in pentlandite extracted from Sudbury, Ontario and in pyroxenite deposits in South Africa.
 W
WSchatzkammer, a German word which means "treasury" or "treasure chamber", is a term sometimes used in English for the collection of treasures, especially objets d’art in precious metals and jewels, of a ruler or other collector which are kept in a secure room and often found in the basement of a palace or castle. It also often included the wider types of object typical of the Renaissance cabinet of curiosities. A very small but evocative Renaissance room in a tower at Lacock Abbey was designed for keeping and viewing the treasures of the newly rich owner.
 W
WSilver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form, as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc refining.
 W
WSilver may be used as an investment like other precious metals. It has been regarded as a form of money and store of value for more than 4,000 years, although it lost its role as legal tender in developed countries when the use of the silver standard came to a final end in 1935. Some countries mint bullion and collector coins, however, such as the American Silver Eagle with nominal face values. In 2009, the main demand for silver was for industrial applications (40%), jewellery, bullion coins, and exchange-traded products. In 2011, the global silver reserves amounted to 530,000 tonnes.
 W
WThe Texas Bullion Depository is a bullion depository based in Texas in the United States. It was the first state-administered depository to be established in the United States; previous depositories were either at federal level or private companies. Texas Comptroller Glenn Hegar announced it was open for business on June 6, 2018.
 W
WTroy weight is a system of units of mass that originated in 15th-century England, and is primarily used in the precious metals industry. The Troy weights are the grain, the pennyweight, the troy ounce, and the troy pound. The troy grain is equal to the grain-unit of the avoirdupois system, yet the troy ounce is heavier than the avoirdupois ounce, and the troy pound is lighter than the avoirdupois pound.
 W
WValcambi is a precious metals refining company located in Balerna, Switzerland, and a company of Rajesh Exports Limited. Valcambi is owned by European Gold Refineries, which is owned by Global Gold Refineries AG, which in turn is 95% owned by REL Singapore PTE Ltd. and 5% by Rajesh Exports Limited India. Valcambi is thus 100% controlled by Rajesh Exports, the parent company of REL Singapore.