 W
WAlgerian Saharan Arabic is a variety of Arabic indigenous to and spoken predominantly in the Algerian Sahara. Its ISO 639-3 language code is "aao," and it belongs to Maghrebi Arabic.
 W
WArabic is a Semitic language that first emerged in the 1st to 4th centuries CE. It is now the lingua franca of the Arab world. It is named after the Arabs, a term initially used to describe peoples living in the Arabian Peninsula bounded by eastern Egypt in the west, Mesopotamia in the east, and the Anti-Lebanon mountains and Northern Syria in the north, as perceived by ancient Greek geographers. The ISO assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form, Modern Standard Arabic, also referred to as Literary Arabic, which is modernized Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as al-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā or simply al-fuṣḥā (اَلْفُصْحَىٰ). Modern Standard Arabic is an official language of 26 states and 1 disputed territory, the third most after English and French.
 W
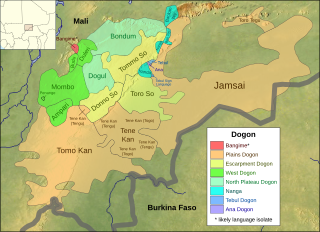
WBangime is a language isolate spoken by 3,500 ethnic Dogon in seven villages in southern Mali, who call themselves the bàŋɡá–ndɛ̀. Bangande is the name of the ethnicity of this community and their population grows at a rate of 2.5% per year. The Bangande consider themselves to be Dogon, but other Dogon people insist they are not. Bangime is an endangered language classified as 6a - Vigorous by Ethnologue. Long known to be highly divergent from the (other) Dogon languages, it was first proposed as a possible isolate by Blench (2005). Research since then has confirmed that it appears to be unrelated to neighbouring languages. Heath and Hantgan have hypothesized that the cliffs surrounding the Bangande valley provided isolation of the language as well as safety for Bangande people. Even though Bangime is not related to Dogon languages, the Bangande still consider their language to be Dogon. Hantgan and List report that Bangime speakers seem unaware that it is not mutually intelligible with any Dogon language.
 W
WThe Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages, are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related languages spoken by the Berbers, who are indigenous to North Africa. The languages were traditionally written with the ancient Libyco-Berber script, which now exists in the form of Tifinagh.
 W
WDyula is a language of the Mande language family spoken in Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast and Mali. It is one of the Manding languages and is most closely related to Bambara, being mutually intelligible with Bambara as well as Malinke. It is a trade language in West Africa and is spoken by millions of people, either as a first or second language. Like the other Mande languages, it uses tones. It may be written in the Latin, Arabic or N'Ko scripts.
 W
WThe Dogon languages are a small closely-related language family that is spoken by the Dogon people of Mali and may belong to the proposed Niger–Congo family. There are about 600,000 speakers of its dozen languages. They are tonal languages, and most, like Dogul, have two tones, but some, like Donno So, have three. Their basic word order is subject–object–verb.
 W
WFrench is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French.
 W
WFula, also known as Fulani or Fulah, is a Senegambian language spoken by more than 65 million people as a set of various dialects in a continuum that stretches across some 20 countries in West and Central Africa. Along with other related languages such as Serer and Wolof, it belongs to the Senegambian branch within the Niger–Congo family, which does not have tones, unlike most other Niger–Congo languages. More broadly, it belongs to the Atlantic geographic grouping within Niger–Congo. It is spoken as a first language by the Fula people from the Senegambia region and Guinea to Cameroon, Nigeria, and Sudan and by related groups such as the Toucouleur people in the Senegal River Valley. It is also spoken as a second language by various peoples in the region, such as the Kirdi of northern Cameroon and northeastern Nigeria.
 W
WPulaar is a Fula language spoken primarily as a first language by the Fula and Toucouleur peoples in the Senegal River valley area traditionally known as Futa Tooro and further south and east. Pulaar speakers, known as Haalpulaar'en live in Senegal, Mauritania, the Gambia, and western Mali. The two main speakers of Pulaar are the Toucouleur people and the Fulɓe. Pulaar is the second most spoken local language in Senegal, being a first language for around 22% of the population. This correlates with 23.7% of the country in which Pulaar is the population’s ethnicity. Pulaar is one of the national languages of Senegal alongside 13 others. It was admitted as an official language of Senegal by Presidential decree in 1971. There are around 28 known dialects of Pulaar, most of which are mutually intelligible with each other. The Pulaar dialects, as well as other West African languages, are usually referenced under the umbrella term ‘Fula’. Pulaar as a language, however, is not usually referenced as ‘Fula’.
 W
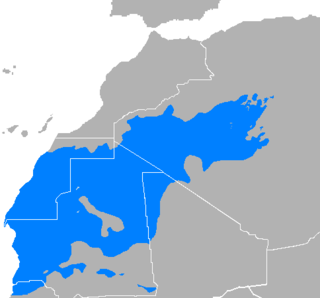
WHassānīya is a variety of Maghrebi Arabic spoken by Mauritanian Arab-Berbers and the Sahrawi. It was spoken by the Beni Ḥassān Bedouin tribes, who extended their authority over most of Mauritania and Morocco's southeastern and Western Sahara between the 15th and 17th centuries. Hassaniya Arabic was the language spoken in the pre-modern region around Chinguetti.
 W
WHumburi Senni, or Central Songhay, is a variety of Southern Songhai spoken in the Hombori region, straddling the Burkina–Mali border.
 W
WKoyra Chiini, or Western Songhay, is a member of the Songhay languages spoken in Mali by about 200,000 people along the Niger River in Timbuktu and upriver from it in the towns of Diré, Tonka, Goundam and Niafunké as well as in the Saharan town of Araouane to its north. In this area, Koyra Chiini is the dominant language and the lingua franca, although minorities speaking Hassaniya Arabic, Tamasheq and Fulfulde are found. Djenné Chiini [dʒɛnːɛ tʃiːni], the dialect spoken in Djenné, is mutually comprehensible, but has noticeable differences, in particular two extra vowels and syntactic differences related to focalisation.
 W
WKoyraboro Senni is a member of the Songhay languages of Mali and is spoken by some 400,000 people along the Niger River from the town of Gourma-Rharous, east of Timbuktu, through Bourem, Gao and Ansongo to the Mali–Niger border.
 W
WMinyanka is a northern Senufo language spoken by about 750,000 people in southeastern Mali. It is closely related to Supyire. Minyanka is one of the national languages of Mali.
 W
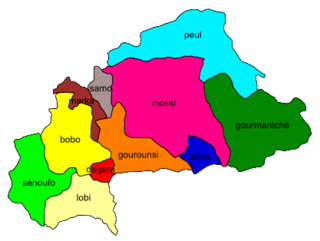
WThe Mossi language is a Gur language of the Oti–Volta branch and one of two official regional languages of Burkina Faso, closely related to the Frafra language spoken just across the border in the northern half of Ghana and less-closely to Dagbani and Mampruli farther south. It is the language of the Mossi people, spoken by approximately 5 million people in Burkina Faso, plus another 60,000+ in Mali and Togo.
 W
WThe Songhay, Songhai or Ayneha languages are a group of closely related languages/dialects centred on the middle stretches of the Niger River in the West African countries of Mali, Niger, Benin, Burkina Faso and Nigeria. In particular, they are spoken in the cities of Timbuktu, Niamey and Gao. They have been widely used as a lingua franca in that region ever since the era of the Songhai Empire. In Mali, the government has officially adopted the dialect of Gao as the dialect to be used as a medium of primary education.
 W
WSupyire, or Suppire, is a Senufo language spoken in the Sikasso Region of southeastern Mali and in adjoining regions of Ivory Coast and Burkina Faso, where it is known as Shempire (Syenpire). In their native language, the noun sùpyìré means both "the people" and "the language spoken by the people".
 W
WTadaksahak is a Songhay language spoken by the pastoralist Idaksahak of the Ménaka Region of Mali. Its phonology, verb morphology and vocabulary has been strongly influenced by the neighbouring Tuareg languages, Tamasheq and Tamajaq.
 W
WTommo So is a language spoken in the eastern part of Mali's Mopti Region. It is placed under the Dogon language family, a subfamily of the Niger-Congo language family.
 W
WTondi Songway Kiini is a variety of Southern Songhai spoken in several villages in the area of Kikara, Mali, about 120 km west of Hombori. Westerners documented the existence of Tondi Songway Kiini in 1998.
 W
WAmerican Sign Language (ASL) developed in the United States and Canada, but has spread around the world. Local varieties have developed in many countries, but there is little research on which should be considered dialects of ASL and which have diverged to the point of being distinct languages.