 W
WArtenacian culture, named after the archaeological site of Artenac in Charente, appeared in the Late Chalcolithic, c. 2400 BC, apparently as reaction to migrations of Danubian peoples into Western France.
 W
WThe Arzachena culture was a pre-Nuragic culture of the Late Neolithic Age occupying Gallura and part of southern Corsica from approximately the 4th to the 3rd millennium BC. It takes its name from the Sardinian town of Arzachena.
 W
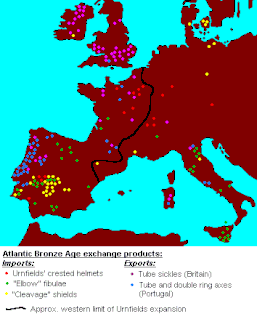
WThe Atlantic Bronze Age is a cultural complex of the Bronze Age period in Prehistoric Europe of approximately 1300–700 BC that includes different cultures in Britain, France, Ireland, Portugal, and Spain.
 W
WThe Azilian is a name given by archaeologists to an industry in the Franco-Cantabrian region of northern Spain and southern France. It dates approximately 10,000–12,500 years ago. Diagnostic artifacts from the culture include Azilian points, crude flat bone harpoons and pebbles with abstract decoration. The latter were first found in the River Arize at the type-site for the culture, the Grotte du Mas d'Azil at Le Mas-d'Azil in the French Pyrenees. These are the main type of Azilian art, showing a great reduction in scale and complexity from the Magdalenian Art of the Upper Palaeolithic.
 W
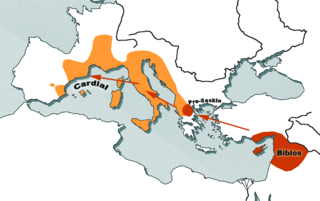
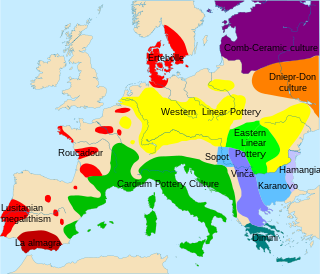
WCardium pottery or Cardial ware is a Neolithic decorative style that gets its name from the imprinting of the clay with the heart-shaped shell of the Corculum cardissa , a member of the cockle family Cardiidae. These forms of pottery are in turn used to define the Neolithic culture which produced and spread them, commonly called the "Cardial culture".
 W
WThe Châtelperronian is a proposed industry of the Upper Palaeolithic, the existence of which is debated. It represents both the only Upper Palaeolithic industry made by Neanderthals and the earliest Upper Palaeolithic industry in Central and Southwestern France, as well as in Northern Spain. It derives its name from Châtelperron, Allier, France.
 W
WThe Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 2900 BCE – 2350 BCE, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a vast area, from the contact zone between the Yamnaya culture and the Corded ware culture in south Central Europe, to the Rhine on the west and the Volga in the east, occupying parts of Northern Europe, Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The Corded Ware culture is thought to have originated from the westward migration of Yamnaya-related people from the steppe-forest zone into the territory of late Neolithic European cultures such as the Globular Amphora and Funnelbeaker cultures, and is considered to be a likely vector for the spread of some or all of the core Indo-European languages, excluding the Anatolian languages and Tocharian.
 W
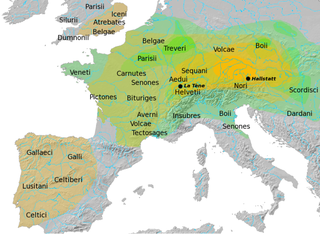
WThe Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western and Central European culture of Late Bronze Age from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC and followed in much of its area by the La Tène culture. It is commonly associated with Proto-Celtic populations. Older assumptions of the early 20th century of Illyrians having been the bearers of especially the Eastern Hallstatt culture are indefensible and archeologically unsubstantiated.
 W
WThe Hamburg culture or Hamburgian was a Late Upper Paleolithic culture of reindeer hunters in northwestern Europe during the last part of the Weichsel Glaciation beginning during the Bölling interstadial. Sites are found close to the ice caps of the time. They extend as far north as the Pomeranian ice margin.
 W
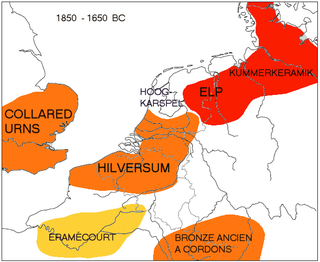
WThe Hilversum culture is a prehistoric material culture found in middle Bronze Age in the region of the southern Netherlands and northern Belgium. It has been associated with the Wessex culture from the same period in southern England, and is one of the material cultures of this part of northwestern continental Europe which has been proposed to have had a "Nordwestblock" language which was Indo-European, but neither Germanic nor Celtic.
 W
WThe La Tène culture was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age, succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscans, and Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences.
 W
WThe Linear Pottery culture is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic, flourishing c. 5500–4500 BC. It is abbreviated as LBK, and is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Incised Ware culture, and falls within the Danubian I culture of V. Gordon Childe.
 W
WThe Magdalenian cultures are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years ago. It is named after the type site of La Madeleine, a rock shelter located in the Vézère valley, commune of Tursac, in France's Dordogne department.
 W
WMaglemosian is the name given to a culture of the early Mesolithic period in Northern Europe. In Scandinavia, the culture was succeeded by the Kongemose culture.
 W
WThe Michelsberg culture is an important Neolithic culture in Central Europe. Its dates are c. 4400–3500 BC. Its conventional name is derived from that of an important excavated site on Michelsberg hill near Untergrombach, between Karlsruhe and Heidelberg (Baden-Württemberg).
 W
WThe Ozieri culture was a prehistoric pre-Nuragic culture that occupied Sardinia from c. 3200 to 2800 BC. The Ozieri was the culmination of the island's Neolithic culture and takes its name from the locality where early findings connected with it have been found, the cave of San Michele near Ozieri, in northern Sardinia. The Ozieri existed contemporaneously with the Arzachena culture, sharing some similarities, and its influence also extended to nearby Corsica.
 W
WThe Rössen culture or Roessen culture is a Central European culture of the middle Neolithic.
 W
WThe Seine–Oise–Marne or SOM culture is the name given by archaeologists to the final culture of the Neolithic and first culture of the Chalcolithic in northern France and southern Belgium.
 W
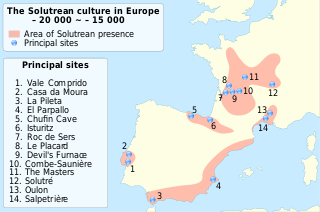
WThe Solutrean industry is a relatively advanced flint tool-making style of the Upper Paleolithic of the Final Gravettian, from around 22,000 to 17,000 BP. Solutrean sites have been found in modern-day France, Spain and Portugal.
 W
WThe Tumulus culture dominated Central Europe during the Middle Bronze Age.
 W
WThe Urnfield culture was a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe, often divided into several local cultures within a broader Urnfield tradition. The name comes from the custom of cremating the dead and placing their ashes in urns which were then buried in fields. Over much of Europe, the Urnfield culture followed the Tumulus culture and was succeeded by the Hallstatt culture. Some linguists and archaeologists have associated this culture with the Proto-Celtic language, or a pre-Celtic language family.