 W
WSerbia has only one nationwide official language, which is Serbian. Other languages spoken in Serbia include Hungarian, Romanian, Slovak, Rusyn, Croatian, Bosnian, Romani, Albanian, Vlach, Bulgarian, Macedonian, Montenegrin, Bunjevac, etc.
 W
WAlbanian is an Indo-European language spoken by the Albanians in the Balkans and the Albanian diaspora in the Americas, Europe and Oceania. With about 7.5 million speakers, it comprises an independent branch within the Indo-European languages and is not closely related to any other Indo-European language.
 W
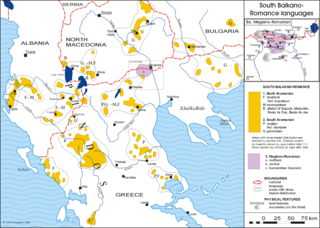
WThe Aromanian language, also known as Macedo-Romanian or Vlach, is an Eastern Romance language, similar to Megleno-Romanian, Istro-Romanian and Romanian, spoken in Southeastern Europe. Its speakers are called Aromanians or Vlachs. Some scholars, mostly Romanian ones, consider Aromanian a dialect of Romanian.
 W
WThe Bosnian language is the standardized variety of Serbo-Croatian mainly used by ethnic Bosniaks. Bosnian is one of three such varieties considered official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina, along with Croatian and Serbian. It is also an officially recognized minority language in Croatia, Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia and Kosovo.
 W
WBulgarian is a South Slavic language spoken in Southeastern Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of Bulgarians.
 W
WCroatian is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian language used by Croats, principally in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Serbian province of Vojvodina, and other neighboring countries. It is the official and literary standard of Croatia and one of the official languages of the European Union. Croatian is also one of the official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and a recognized minority language in Serbia and neighboring countries.
 W
WThe Declaration on the Common Language was issued in 2017 by a group of intellectuals and NGOs from Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and Serbia who were working under the banner of a project called "Language and Nationalism". The Declaration states that Croats, Bosniaks, Serbs and Montenegrins have a common standard language of the polycentric type.
 W
WHungarian is a Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by communities of Hungarians in present-day Slovakia, western Ukraine (Subcarpathia), central and western Romania (Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia and eastern Austria.
 W
WLanguages spoken in the Serbian province of Vojvodina include South Slavic languages, West Slavic languages, East Slavic languages, Hungarian, Romanian, German, Romani, Albanian, and others.
Macedonian is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken as a first language by around two million people, it serves as the official language of North Macedonia. Most speakers can be found in the country and its diaspora, with a smaller number of speakers throughout the transnational region of Macedonia. Macedonian is also a recognized minority language in parts of Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Romania, and Serbia and it is spoken by emigrant communities predominantly in Australia, Canada and the United States.
 W
WMegleno-Romanian is a Balkan Romance language, similar to Aromanian or a dialect of the Romanian language. It is spoken by the Megleno-Romanians in a few villages in the Moglena region that spans the border between the Greek region of Macedonia and North Macedonia. It is also spoken by emigrants from these villages and their descendants in Romania and by a small Muslim group in Turkey. It is considered an endangered language.
 W
WSerbia has only one nationwide official language, which is Serbian. Other languages spoken in Serbia include Hungarian, Romanian, Slovak, Rusyn, Croatian, Bosnian, Romani, Albanian, Vlach, Bulgarian, Macedonian, Montenegrin, Bunjevac, etc.
 W
WPannonian Rusyn, formerly also known as Yugoslav Rusyn, is a variety of the Rusyn language, spoken by the Pannonian Rusyns, primarily in the regions of Vojvodina and Slavonia, and also in Pannonian Rusyn diaspora in the USA and Canada. Since Rusyns are officially recognized as a national minority both in Serbia and Croatia, their language is also recognized as a minority language, and in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina (Serbia) it is employed as one of six official provincial languages.
 W
WRomani is an Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani communities. According to Ethnologue, seven varieties of Romani are divergent enough to be considered languages of their own. The largest of these are Vlax Romani, Balkan Romani (600,000), and Sinte Romani (300,000). Some Romani communities speak mixed languages based on the surrounding language with retained Romani-derived vocabulary – these are known by linguists as Para-Romani varieties, rather than dialects of the Romani language itself.
 W
WRomanian is a Balkan Romance language spoken by approximately 22–26 million people as a native language, primarily in Romania and Moldova, and by another 4 million people as a second language. According to another estimate, there are about 34 million people worldwide who can speak Romanian, of whom 30 million speak it as a native language. It is an official and national language of both Romania and Moldova and is one of the official languages of the European Union.
 W
WSerbian is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Serbs. It is the official and national language of Serbia, one of the three official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and co-official in Montenegro and Kosovo. It is a recognized minority language in Croatia, North Macedonia, Romania, Hungary, Slovakia, and the Czech Republic.
 W
WSerbo-Croatian – also called Serbo-Croat, Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin.
 W
WSlovak is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union.
 W
WSlovene, or alternatively Slovenian, is a South Slavic language spoken by the Slovenes. It is spoken by about 2.5 million speakers worldwide, the majority of whom live in Slovenia, where it is one of the three official languages. As Slovenia is part of the European Union, Slovene is also one of its 24 official and working languages.