 W
WThe history of books became an acknowledged academic discipline in the 1980s. Contributors to the discipline include specialists from the fields of textual scholarship, codicology, bibliography, philology, palaeography, art history, social history and cultural history. Its key purpose is to demonstrate that the book as an object, not just the text contained within it, is a conduit of interaction between readers and words.
 W
WAkhlak E Hindi is the first Urdu book printed in printing-press in 1803. The book was written by Mir Bahadur Ali Hussaini and deals with ethics.
 W
WBook burning is the deliberate destruction by fire of books or other written materials, usually carried out in a public context. The burning of books represents an element of censorship and usually proceeds from a cultural, religious, or political opposition to the materials in question.
 W
WBook History is the official publication of the Society for the History of Authorship, Reading and Publishing. It was established in 1998 and is published annually by the Johns Hopkins University Press.
 W
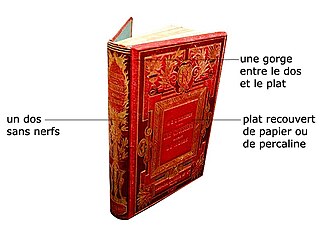
WA Bradel binding is a style of book binding with a hollow back. It most resembles a case binding in that it has a hollow back and visible joint, but unlike a case binding, it is built up on the book. Characteristic of the binding is that the material covering the outside boards is separate from that covering the spine. Many bookbinders consider the Bradel binding to be stronger than the Case binding.
 W
WThe history of the book in Brazil focuses on the development of the access to publishing resources and acquisition of the book in the country, covering a period extending from the beginning of the editorial activity during colonization to today's publishing market, including the history of publishing and bookstores that allowed the modern accessibility to the book.
 W
WA Companion to the History of the Book is a book first published by Wiley-Blackwell in 2007 in the Blackwell Companions series. It was issued in a second edition in two volumes in 2019. The editors are Simon Eliot, professor of the History of the Book at the University of London, and Jonathan Rose.
 W
WLibraries have been deliberately or accidentally destroyed or badly damaged. Sometimes a library is purposely destroyed as a form of cultural cleansing.
 W
WThe Ego and Its Own is a philosophical work by German philosopher Max Stirner (1806-1856), first published in 1844.
 W
WThe German friendship book was an early form of the poetry book and the modern friendship book. It emerged during the reformation period, during which it was popular to collect autographs from noted reformers. In the 1700s, the trend of the friendship book was still mainly limited to the protestant people instead of the Catholics. These books were particularly popular with university students into the early decades of the 19th century. Noteworthy are the pre-printed pages of a friendship book from 1770 onwards, published as a loose-leaf collection by the bookbinder and pressman Johannes Carl Wiederhold (1743-1826) from Göttingen.
 W
WGoogle Books is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical character recognition (OCR), and stored in its digital database. Books are provided either by publishers and authors through the Google Books Partner Program, or by Google's library partners through the Library Project. Additionally, Google has partnered with a number of magazine publishers to digitize their archives.
 W
WThe selling of books dates back to ancient times. The founding of libraries in c.300 BC stimulated the energies of the Athenian booksellers. In Rome, toward the end of the republic, it became the fashion to have a library, and Roman booksellers carried on a flourishing trade.
 W
WAs of 2018, Wolters Kluwer ranks as the Dutch biggest publisher of books in terms of revenue. Other notable Dutch houses include Brill and Elsevier.
 W
WThe history of the Qur'an — that is the timeline and origin of the written compilations or manuscripts of the holy book of Islam, based on historical findings — spans several centuries, and forms a major part of the early history of Islam.
 W
WScriptorium, literally "a place for writing", is commonly used to refer to a room in medieval European monasteries devoted to the writing, copying and illuminating of manuscripts commonly handled by monastic scribes.
 W
WA scroll, is a roll of papyrus, parchment, or paper containing writing. The history of scrolls dates back to ancient Egypt. In most ancient literate cultures scrolls were the earliest format for longer documents written in ink or paint on a flexible background, preceding bound books; rigid media such as clay tablets were also used but had many disadvantages in comparison. For most purposes scrolls have long been superseded by the codex book format, but they are still produced for some ceremonial or religious purposes, notably for the Jewish Torah scroll for use in synagogues.
 W
WSophistication of books is the practice of making a book complete by replacing missing leaves with leaves from another copy. In some cases this is done with the intent to deceive or mislead, modifying and offering books for sale in an attempt to sell them for a higher value. When offered for sale, a book's description should be clear and unambiguous, and indicate exactly and in detail any changes that have been made to the book.
 W
WA Term Catalogue is a serial publication compiled to inform customers—most importantly book traders from other cities—of the book production as available on the book fairs. The first such catalogue was issued by Georg Willer in Augsburg in 1564. Several projects followed the model including the series of English Term Catalogues issued by John Starkey and Robert Clavell under the title Mercurius Librarius, or, a catalogue of books from 1668 to 1711. "Term" referred to the dates of the fairs that would be held as platforms of the trade.
 W
W