 W
WThe Cambridge Grammar of the English Language (CGEL) is a descriptive grammar of the English language. Its primary authors are Rodney Huddleston and Geoffrey K. Pullum. Huddleston was the only author to work on every chapter. It was published by Cambridge University Press in 2002 and has been cited more than 7,000 times.
 W
WIn corpus linguistics, a collocation is a series of words or terms that co-occur more often than would be expected by chance. In phraseology, a collocation is a type of compositional phraseme, meaning that it can be understood from the words that make it up. This contrasts with an idiom, where the meaning of the whole cannot be inferred from its parts, and may be completely unrelated.
 W
WA Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language is a descriptive grammar of English written by Randolph Quirk, Sidney Greenbaum, Geoffrey Leech, and Jan Svartvik. It was first published by Longman in 1985.
 W
WCorpus of Written Tatar is an electronic corpus of the Tatar language, which has been made available online. This collection of Tatar texts in electronic form is intended for the use of those interested in the structure, present condition and prospects of the Tatar language. The Corpus of Written Tatar language is indispensable for everyone who wants to study Tatar by the methods of corpus linguistics. Site opened March 15, 2012. Current address http://corpus.tatar. Available in the Tatar, Russian and English languages.
 W
WThe Global Language Monitor (GLM) is a company based in Austin, Texas that collectively documents, analyzes, and tracks trends in language usage worldwide, with a particular emphasis upon the English language. It is particularly known for its Word of the Year, political analysis, college and university rankings, High Tech buzzwords, and media analytics.
 W
WIn corpus linguistics, a hapax legomenon is a word or an expression that occurs only once within a context: either in the written record of an entire language, in the works of an author, or in a single text. The term is sometimes incorrectly used to describe a word that occurs in just one of an author's works but more than once in that particular work. Hapax legomenon is a transliteration of Greek ἅπαξ λεγόμενον, meaning "being said once".
 W
WLingua Libre is an online collaborative project and tool by the Wikimedia France association, which aims to build a collaborative, multilingual, audiovisual corpus under free license.
 W
WLIVAC is an uncommon language corpus dynamically maintained since 1995. Different from other existing corpora, LIVAC has adopted a rigorous and regular as well as "Windows" approach in processing and filtering massive media texts from representative Chinese speech communities such as Hong Kong, Macau, Taipei, Singapore, Shanghai, Beijing, as well as Guangzhou, and Shenzhen. The contents are thus deliberately repetitive in most cases, represented by textual samples drawn from editorials, local and international news, cross-Formosan Straits news, as well as news on finance, sports and entertainment. By 2020, 2.7 billion characters of news media texts have been filtered so far, of which 680 million characters have been processed and analyzed and have yielded an expanding Pan-Chinese dictionary of 2.3 million words from the Pan-Chinese printed media. Through rigorous analysis based on computational linguistic methodology, LIVAC has at the same time accumulated a large amount of accurate and meaningful statistical data on the Chinese language and their speech communities in the Pan-Chinese region, and the results show considerable and important variations.
 W
WLongman Grammar of Spoken and Written English (LGSWE) is a descriptive grammar of English written by Douglas Biber, Stig Johansson, Geoffrey Leech, Susan Conrad, and Edward Finegan, first published by Longman in 1999. It is an authoritative description of modern English, a successor to A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language (ComGEL) published in 1985 and a predecessor of the Cambridge Grammar of the English Language (CamGEL) published in 2002. The authors and some reviewers consider it a complement rather than a replacement of the former since it follows – with few exceptions – the grammatical framework and concepts from ComGEL, which is also corroborated by the fact that one of LGSWE's authors, Geoffrey Leech, is also a co-author of ComGEL.
 W
WIn the fields of computational linguistics and probability, an n-gram is a contiguous sequence of n items from a given sample of text or speech. The items can be phonemes, syllables, letters, words or base pairs according to the application. The n-grams typically are collected from a text or speech corpus. When the items are words, n-grams may also be called shingles.
 W
WŌno's lexical law, or simply Ōno's law, is a statistical law for the varying rate that four word classes appear in the lexicon of classical Japanese literary works. The law was discovered by Japanese linguist Susumu Ōno and published in 1956.
 W
WA parallel text is a text placed alongside its translation or translations. Parallel text alignment is the identification of the corresponding sentences in both halves of the parallel text. The Loeb Classical Library and the Clay Sanskrit Library are two examples of dual-language series of texts. Reference Bibles may contain the original languages and a translation, or several translations by themselves, for ease of comparison and study; Origen's Hexapla placed six versions of the Old Testament side by side. A famous example is the Rosetta Stone, whose discovery allowed the Ancient Egyptian language to begin being deciphered.
 W
WSketch Engine is a corpus manager and text analysis software developed by Lexical Computing Limited since 2003. Its purpose is to enable people studying language behaviour to search large text collections according to complex and linguistically motivated queries. Sketch Engine gained its name after one of the key features, word sketches: one-page, automatic, corpus-derived summaries of a word's grammatical and collocational behaviour. Currently, it supports and provides corpora in 90+ languages.
 W
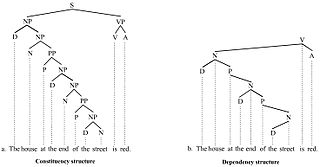
WIn linguistics, a treebank is a parsed text corpus that annotates syntactic or semantic sentence structure. The construction of parsed corpora in the early 1990s revolutionized computational linguistics, which benefitted from large-scale empirical data.
 W
WA word sketch is a one-page, automatic, corpus-derived summary of a word’s grammatical and collocational behaviour. Word sketches were first introduced by the British corpus linguist Adam Kilgarriff and exploited within the Sketch Engine corpus management system. They are an extension of the general collocation concept used in corpus linguistics in that they group collocations according to particular grammatical relations. The collocation candidates in a word sketch are sorted either by their frequency or using a lexicographic association score like Dice, T-score or MI-score.
 W
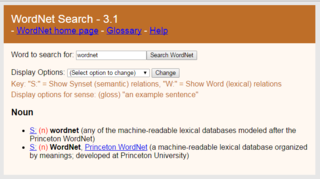
WWordNet is a lexical database of semantic relations between words in more than 200 languages. WordNet links words into semantic relations including synonyms, hyponyms, and meronyms. The synonyms are grouped into synsets with short definitions and usage examples. WordNet can thus be seen as a combination and extension of a dictionary and thesaurus. While it is accessible to human users via a web browser, its primary use is in automatic text analysis and artificial intelligence applications. WordNet was first created in the English language and the English WordNet database and software tools have been released under a BSD style license and are freely available for download from that WordNet website.
 W
WZipf's law is an empirical law formulated using mathematical statistics that refers to the fact that for many types of data studied in the physical and social sciences, the rank-frequency distribution is an inverse relation. The Zipfian distribution is one of a family of related discrete power law probability distributions. It is related to the zeta distribution, but is not identical.