 W
WA legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial branches of parliamentary government in the separation of powers model.
 W
WIn Westminster parliamentary systems, a backbencher is a member of parliament (MP) or a legislator who occupies no governmental office and is not a frontbench spokesperson in the Opposition, being instead simply a member of the "rank and file".
 W
WA bill is proposed legislation under consideration by a legislature. A bill does not become law until it is passed by the legislature and, in most cases, approved by the executive. Once a bill has been enacted into law, it is called an act of the legislature, or a statute. Bills are introduced in the legislature and are discussed, debated and voted upon.
 W
WA legislative chamber or house is a deliberative assembly within a legislature which generally meets and votes separately from the legislature's other chambers. Legislatures are usually unicameral, consisting of only one chamber, or bicameral, consisting of two, but there are rare examples of tricameral and tetracameral legislatures. The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia is the only country documented as having a pentacameral legislature.
 W
WA committee or commission is a body of one or more persons subordinate to an assembly. A committee is not itself considered to be a form of assembly. Usually, the assembly sends matters into a committee as a way to explore them more fully than would be possible if the assembly itself were considering them. Committees may have different functions and their types of work differ depending on the type of the organization and its needs.
 W
WCongresses are formal meetings of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter during battle, from the Latin congressus.
 W
WA council is a group of people who come together to consult, deliberate, or make decisions. A council may function as a legislature, especially at a town, city or county/shire level, but most legislative bodies at the state/provincial or national level are not considered councils. At such levels, there may be no separate executive branch, and the council may effectively represent the entire government. A board of directors might also be denoted as a council. A committee might also be denoted as a council, though a committee is generally a subordinate body composed of members of a larger body, while a council may not be. Because many schools have a student council, the council is the form of governance with which many people are likely to have their first experience as electors or participants.
 W
WIn legislatures, a hemicycle is a semicircular, or horseshoe-shaped, debating chamber, where deputies (members) sit to discuss and pass legislation. Although originally of Ancient Greek roots, the term and modern design derive from French politics and practice.
 W
WThe House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In the UK and Canada, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. The leader of the majority party in the House of Commons by convention becomes the prime minister. Other parliaments have also had a lower house called a "House of Commons".
 W
WLegislation is the process or product of enrolling, enacting, or promulgating law by a legislature, parliament, or analogous governing body. Before an item of legislation becomes law it may be known as a bill, and may be broadly referred to as "legislation" while it remains under consideration to distinguish it from other business. Legislation can have many purposes: to regulate, to authorize, to outlaw, to provide (funds), to sanction, to grant, to declare, or to restrict. It may be contrasted with a non-legislative act by an executive or administrative body under the authority of a legislative act.
 W
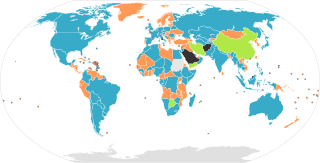
WIn contrast to unicameralism, and bicameralism, multicameralism is the condition in which a legislature is divided into more than two deliberative assemblies, which are commonly called "chambers" or "houses". This usually includes tricameralism with three chambers, but can also describe a system with any amount more. The word "multicameral" can also relate in other ways to its literal meaning of "many chambered" with use in science or biology.
 W
WIn modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. The term is similar to the idea of a senate, synod or congress and is commonly used in countries that are current or former monarchies. Some contexts restrict the use of the word parliament to parliamentary systems, although it is also used to describe the legislature in some presidential systems, even where it is not in the official name.
 W
WRed boxes, or sometimes ministerial boxes, are a type of despatch box produced by Barrow Hepburn & Gale and are used by ministers in the British government and the British monarch to carry government documents. Similar in appearance to a briefcase, they are primarily used to hold and transport official ministerial papers. Red boxes are one modern form of despatch boxes, which have been in government use for centuries. Despatch boxes with a very different design remain in use in the chamber of the lower house of the British and Australian parliaments. Those boxes hold religious books for swearing-in new members of the chamber, but are also used as lecterns by front bench members.
 W
WA senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate, so-called as an assembly of the senior and therefore considered wiser and more experienced members of the society or ruling class.
 W
WThe speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
 W
WLegislative violence broadly refers to any violent clashes between members of a legislature, often physically, inside the legislature and triggered by divisive issues and tight votes. Such clashes have occurred in many countries across time, and notable incidents still regularly occur.