 W
WAlgherese or Alguerese is the variant of Catalan spoken in the city of Alghero, in the northwest of Sardinia, Italy.
 W
WCanadian Gaelic or Cape Breton Gaelic, known in Canadian English as often simply Gaelic, is a collective term for the dialects of Scottish Gaelic spoken in Atlantic Canada.
 W
WChipilo Venetian, or Chipileño, is a diaspora language currently spoken by the descendants of some five hundred 19th century immigrants to Mexico from the Veneto region of Northeastern Italy. The immigrants settled in the State of Puebla, founding the city of Chipilo. The language is also spoken in Mexico in communities in Veracruz and Querétaro, places where the chipileños settled as well.
 W
WGriko, sometimes spelled Grico, is the dialect of Italiot Greek spoken by Griko people in Salento and in Calabria. Some Greek linguists consider it to be a Modern Greek dialect and often call it Katoitaliótika or Grekanika (Γραικάνικα), whereas its own speakers call it Greko or Griko. Griko is spoken in Salento while Greko is spoken in Calabria. Griko and Standard Modern Greek are partially mutually intelligible.
 W
WGullah is a creole language spoken by the Gullah people, an African-American population living in coastal regions of South Carolina and Georgia as well as extreme northeastern Florida and the extreme southeast of North Carolina.
 W
WItaliot Greek, also known as Salentino-Calabrian Greek, Italic-Greek or Apulia-Calabrian Greek refers to two dialects of Modern Greek, spoken in Italy by the Griko people.
 W
WJudaeo-Spanish or Judeo-Spanish, also known as Ladino, is a Romance language derived from Old Spanish. Originally spoken in Spain, and then after the Edict of Expulsion spreading through the then-Ottoman Empire as well as France, Italy, the Netherlands, Morocco and England, it is today spoken mainly by Sephardic minorities in more than 30 countries, with most of the surviving speakers residing in Israel. Although it has no official status in any country, it has been acknowledged as a minority language in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Israel, France, and Turkey. In 2017, it was formally recognised by the Royal Spanish Academy.
 W
WThe London Welsh Centre is a community and arts centre on Gray's Inn Road, in the London Borough of Camden. The centre is owned and run by the London Welsh Trust.
 W
WLouisiana French is an umbrella term for the dialects and varieties of the French language spoken traditionally in colonial Lower Louisiana. As of today Louisiana French is primarily used in the U.S. state of Louisiana, specifically in the southern parishes.
 W
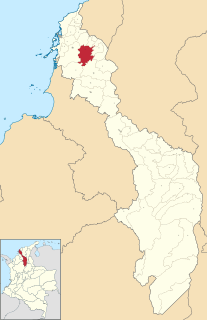
WPalenquero or Palenque is a Spanish-based creole language spoken in Colombia. It is a mixture of Kikongo and Spanish. Palenquero is the only Spanish-based creole in Latin America, if Papiamento is excluded. The ethnic group which speaks this creole consisted of 6,637 people in 2018. It is primarily spoken in the village of San Basilio de Palenque which is southeast of Cartagena, and in some neighbourhoods of Barranquilla.
 W
WPannonian Rusyn, formerly also known as Yugoslav Rusyn, is a variety of the Rusyn language, spoken by the Pannonian Rusyns, primarily in the regions of Vojvodina and Slavonia, and also in Pannonian Rusyn diaspora in the USA and Canada. Since Rusyns are officially recognized as a national minority both in Serbia and Croatia, their language is also recognized as a minority language, and in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina (Serbia) it is employed as one of six official provincial languages.
 W
WPatagonian Welsh is a variety of the Welsh language spoken in Y Wladfa, the Welsh settlement in Patagonia, Chubut Province, Argentina. The decimal numeral system used in Modern Welsh originated in Patagonia in the 1870s, and was subsequently adopted in Wales in the 1940s as a simpler counterpart to the traditional vigesimal system, which still survives in Wales.
 W
WPennsylvania Dutch, referred to as Pennsylvania German in scholarly literature, is a variety of West Central German spoken by the Old Order Amish, Old Order Mennonites and other descendants of German immigrants in the United States and Canada, closely related to the Palatine dialects. There are possibly more than 300,000 native speakers in the United States and Canada. In Pennsylvania, 29.9% of the population currently claim German ancestry.
 W
WSaterland Frisian, also known as Sater Frisian, Saterfrisian or Saterlandic (Seeltersk), is the last living dialect of the East Frisian language. It is closely related to the other Frisian languages: North Frisian, spoken in Germany as well, and West Frisian, spoken in the Dutch province of Friesland.
 W
WWestern Armenian is one of the two standardized forms of Modern Armenian, the other being Eastern Armenian. It is based mainly on the Istanbul Armenian dialect contrary to Eastern Armenian which is mainly based on the Yerevan Armenian dialect.
 W
WYiddish is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a High German-based vernacular fused with many elements taken from Hebrew and to some extent Aramaic; most varieties also have substantial influence from Slavic languages, and the vocabulary contains traces of influence from Romance languages. Yiddish writing uses the Hebrew alphabet. In the 1990s, there were around 1.5–2 million speakers of Yiddish, mostly Hasidic and Haredi Jews. In 2012, the Center for Applied Linguistics estimated the number of speakers to have had a worldwide peak at 11 million, with the number of speakers in the United States and Canada then totaling 150,000. An estimate from Rutgers University gives 250,000 American speakers, 250,000 Israeli speakers, and 100,000 in the rest of the world.