 W
WAadloun, Adloun or Adlun is a coastal town in South Lebanon, 17 kilometres (11 mi) south of Sidon famous for its cultivation of watermelons. It is also the site of a Phoenician necropolis and prehistoric caves where four archaeological sites have been discovered and dated to the Stone Age. The evidence of human occupation of Abri Zumoffen has been dated as far back as 71,000 BCE with occupation of Bezez Cave dating back even further into the earlier Middle Paleolithic.
 W
WThe Alice and Gwendoline Cave is a limestone cave in County Clare, Ireland. It is known as the site of brown bear bones bearing the mark of butchery, which have pushed back the first known human habitation of Ireland by over two thousand years.
 W
WCafer Hoyuk or Cafer Höyük is an archaeological site located around 40 kilometres (25 mi) northeast of Malatya, Turkey in the Euphrates valley. It was inhabited over ten thousand years ago during the Neolithic revolution.
 W
WCow Cave is a limestone cave system which is situated on the south side of the Chudleigh Rocks, close to the town of Chudleigh, Devon, England. It is listed as a Scheduled Monument by Historic England and was first listed in 1992.
 W
WDederiyeh Cave is a cave in Syria in which systematic excavations have take place since 1987. The cave is located 60 kilometers northwest of Aleppo in the Afrin District, on the left bank of a wadi, at an altitude of 450 meter. Two Neanderthal children were found in the cave, in 1993 and 1997-1998, both of which showed evidence that they were buried.
 W
WEl Kowm or Al Kawm is a circular, 20 km (12 mi) gap in the Syrian mountains that houses a series of archaeological sites. The El Kowm oasis is located northeast of Palmyra in Syria, near Al-Sukhnah. It shows some of the longest and most important cultural sequences in the Middle East, with periods of occupation by humans for over 1 million years.
 W
WHazar Merd is a group of Paleolithic cave sites excavated by Dorothy Garrod in 1928. The caves are located south-southwest of Sulaymaniyah in Sulaymaniyah Governorate in Iraq. Garrod's soundings in two caves in the Hazar Merd group provided evidence of Middle and Epi-Paleolithic occupation.The Dark cave or Ashkawty Tarik in Kurdish has a commanding view of the local valley and is close to a small spring and a village with the same name.
 W
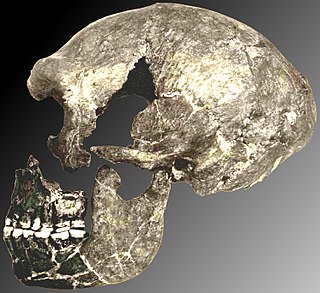
WMasol is a paleontological and prehistoric site in the Himalayan foothills of northwestern India, in the state of Punjab, a few kilometers north of Chandigarh. It dates from the end of the Pliocene. It represents the oldest paleontological record of Homo located outside of Africa.
 W
WLa Quina is a Middle and Early Upper Palaeolithic site in Gardes-le-Pontaroux, Charente, France. Two Neanderthal skulls were found there, La Quina 5 and La Quina 18. It is the type site of the Quina Mousterian.
 W
WRiwat is a Paleolithic site in Punjab, northern Pakistan. Another site, called Riwat Site 55, shows a later occupation dated to around 45,000 years ago.
 W
WRiwat Site 55 is an Upper Palaeolithic archaeological site in the Soan Valley, near the village of Rawat in Punjab, Pakistan. It is approximately 45,000 years old.
 W
W'Ubeidiya, some 3 km south of the Sea of Galilee, in the Jordan Rift Valley, Israel, is an archaeological site of the early Pleistocene, c. 1.5 million years ago, preserving traces of one of the earliest migration of Homo erectus out of Africa, with only the site of Dmanisi in Georgia being older. The site yielded hand axes of the Acheulean type, but very few human remains. The animal remains include a hippopotamus' femur bone, and an immensely large pair of horns belonging to a species of extinct bovid.
 W
WWadi Jilat is a seasonal stream (wadi) in the Badia of eastern Jordan. Part of its course runs through a steeply-incised ravine that retains water for much of the year, an unusual feature in the desert region.