 W
WAn internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is applied typically to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into useful kinetic energy and is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. This replaced the external combustion engine for applications where weight or size of the engine is important.
 W
WA Bendix drive is a type of engagement mechanism used in starter motors of internal combustion engines. The device allows the pinion gear of the starter motor to engage or disengage the ring gear automatically when the starter is powered or when the engine fires, respectively. It is named after its inventor, Vincent Hugo Bendix.
 W
WA consumption map or efficiency map shows the brake-specific fuel consumption in g per kWh over mean effective pressure per rotational speed of an internal combustion engine.
 W
WA consumption map or efficiency map shows the brake-specific fuel consumption in g per kWh over mean effective pressure per rotational speed of an internal combustion engine.
 W
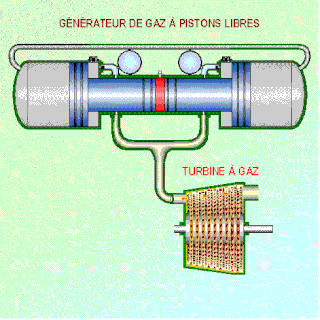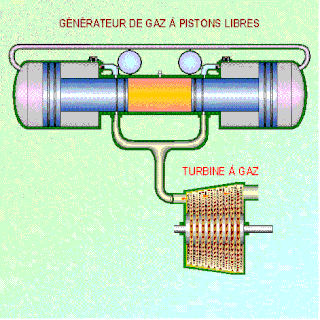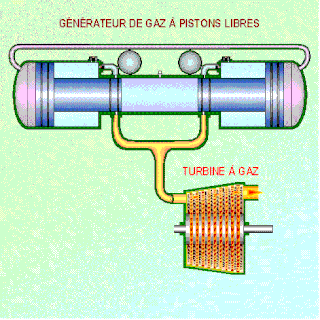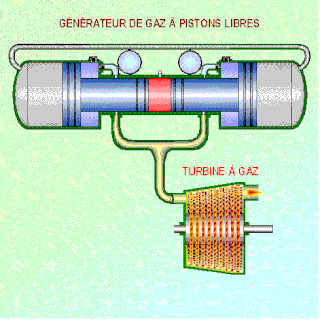
WA free-piston engine is a linear, 'crankless' internal combustion engine, in which the piston motion is not controlled by a crankshaft but determined by the interaction of forces from the combustion chamber gases, a rebound device and a load device.
 W
WVarious scientists and engineers contributed to the development of internal combustion engines. In 1791, the English inventor John Barber patented a gas turbine. In 1794 Thomas Mead patented a gas engine. Also in 1794 Robert Street patented an internal-combustion engine, which was also the first to use the liquid fuel (petroleum) and built an engine around that time. In 1798, John Stevens designed the first American internal combustion engine. In 1807, French engineers Nicéphore and Claude Niépce ran a prototype internal combustion engine, using controlled dust explosions, the Pyréolophore. This engine powered a boat on the Saône river, France. The same year, the Swiss engineer François Isaac de Rivaz built and patented a hydrogen and oxygen powered internal-combustion engine. The fuel was stored in a balloon and the spark was electrically ignited by a hand-operated trigger. Fitted to a crude four-wheeled wagon, François Isaac de Rivaz first drove it 100 meters in 1813, thus making history as the first car-like vehicle known to have been powered by an internal-combustion engine. In 1823, Samuel Brown patented the first internal combustion engine to be applied industrially in the U.S.; one of his engines pumped water on the Croydon Canal from 1830 to 1836. He also demonstrated a boat using his engine on the Thames in 1827, and an engine-driven carriage in 1828. Father Eugenio Barsanti, an Italian engineer, together with Felice Matteucci of Florence invented the first real internal combustion engine in 1853. Their patent request was granted in London on June 12, 1854, and published in London's Morning Journal under the title "Specification of Eugene Barsanti and Felix Matteucci, Obtaining Motive Power by the Explosion of Gasses". In 1860, Belgian Jean Joseph Etienne Lenoir produced a gas-fired internal combustion engine. In 1864, Nicolaus Otto patented the first atmospheric gas engine. In 1872, American George Brayton invented the first commercial liquid-fueled internal combustion engine. In 1876, Nicolaus Otto, working with Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach, patented the compressed charge, four-stroke cycle engine. In 1879, Karl Benz patented a reliable two-stroke gas engine. In 1892, Rudolf Diesel developed the first compressed charge, a compression ignition engine. In 1926, Robert Goddard launched the first liquid-fueled rocket. In 1939, the Heinkel He 178 became the world's first jet aircraft. In 1954 German engineer Felix Wankel patented a "pistonless" engine using an eccentric rotary design.
 W
WThe Internal Fire Museum of Power is a museum of internal combustion engines in West Wales. The museum's collection is mostly of larger stationary diesel engines, as used for generating sets and pumping stations. The museum is located at Tan-y-groes, Ceredigion, near Cardigan.
 W
WA naturally aspirated engine, also known as a normally aspirated engine or NA, is an internal combustion engine in which air intake depends solely on atmospheric pressure and does not have forced induction through a turbocharger or a supercharger. Many sports cars specifically use naturally aspirated engines to avoid turbo lag.
 W
WNon-road engines are engines that are used for other purposes than a motor vehicle that is used on a public roadway. The term is commonly used by regulators to classify the engines in order to control their emissions.
 W
WA small engine is the general term for a wide range of small-displacement, low-powered internal combustion engines used to power lawn mowers, generators, concrete mixers and many other machines that require independent power sources. These engines often have simple designs, for example an air-cooled single-cylinder petrol engine with a pull-cord starter, capacitor discharge ignition and a gravity-fed carburettor.
 W
WSquish is an effect in internal combustion engines which creates sudden turbulence of the air-fuel mixture as the piston approaches top dead centre (TDC).
 W
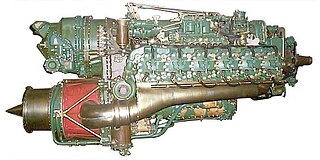
WA turbo-compound engine is a reciprocating engine that employs a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust gases. Instead of using that energy to drive a turbocharger as found in many high-power aircraft engines, the energy is instead sent to the output shaft to increase the total power delivered by the engine. The turbine is usually mechanically connected to the crankshaft, as on the Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, but electric and hydraulic power recovery systems have been investigated as well.
 W
WThe Volkswagen-Audi V8 engine family is a series of mechanically similar, gasoline-powered and diesel-powered, V-8, internal combustion piston engines, developed and produced by the Volkswagen Group, in partnership with Audi, since 1988. They have been used in various Volkswagen Group models, and by numerous Volkswagen-owned companies. The first spark-ignition gasoline V8 engine configuration was used in the 1988 Audi V8 model; and the first compression-ignition diesel V8 engine configuration was used in the 1999 Audi A8 3.3 TDI Quattro. V8 gasoline and diesel engine configurations have and variants been used in most Audi, Volkswagen, Porsche, Bentley, and Lamborghini models ever since. The larger-displacement diesel V8 engine configuration has also been used in various Scania commercial vehicles; such as in trucks, buses, and marine applications.