 W
WThe glossopharyngeal nerve, known as the ninth cranial nerve, is a mixed nerve that carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. It exits the brainstem out from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, while the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.
 W
WThe carotid branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve is a small branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve that innervates the carotid sinus and carotid body. It is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve that runs downwards, anterior to the internal carotid artery. It communicates with the vagus nerve and sympathetic trunk and then divides in the angle of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery to innervate the carotid body and carotid sinus. It carries impulses from the baroreceptors in the carotid sinus to the vasomotor center in the brainstem and from chemoreceptors in the carotid body.
 W
WThe inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve is a sensory ganglion. It is larger than and below the superior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve. It is located within the jugular foramen.
 W
WThe salivatory nuclei are the superior salivatory nucleus, and the inferior salivatory nucleus that innervate the salivary glands. They are located in the pontine tegmentum in the brainstem. They both are examples of cranial nerve nuclei.
 W
WJugular foramen syndrome, or Vernet's syndrome, is characterized by paresis of the glossopharyngeal, vagal, and accessory nerves.
 W
WThe lesser petrosal nerve is the general visceral efferent (GVE) component of the glossopharyngeal nerve, carrying parasympathetic preganglionic fibers from the tympanic plexus to the parotid gland. It synapses in the otic ganglion, from where the postganglionic fibers emerge.
 W
WThe otic ganglion is a small parasympathetic ganglion located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve. It is functionally associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve and innervates the parotid gland for salivation.
 W
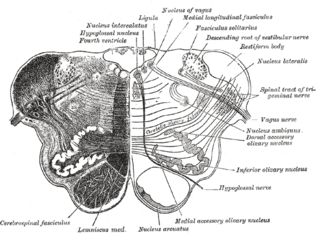
WIn the human brainstem, the solitary nucleus (SN) is a series of purely sensory nuclei forming a vertical column of grey matter embedded in the medulla oblongata. Through the center of the SN runs the solitary tract, a white bundle of nerve fibers, including fibers from the facial, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves, that innervate the SN. The SN projects to, among other regions, the reticular formation, parasympathetic preganglionic neurons, hypothalamus and thalamus, forming circuits that contribute to autonomic regulation. Cells along the length of the SN are arranged roughly in accordance with function; for instance, cells involved in taste are located in the rostral part, while those receiving information from cardio-respiratory and gastrointestinal processes are found in the caudal part.
 W
WThe solitary tract is a compact fiber bundle that extends longitudinally through the posterolateral region of the medulla. The solitary tract is surrounded by the nucleus of the solitary tract, and descends to the upper cervical segments of the spinal cord. It was first named by Theodor Meynert in 1872.
 W
WThe spinal trigeminal nucleus is a nucleus in the medulla that receives information about deep/crude touch, pain, and temperature from the ipsilateral face. In addition to the trigeminal nerve, the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves also convey pain information from their areas to the spinal trigeminal nucleus. Thus the spinal trigeminal nucleus receives input from cranial nerves V, VII, IX, and X.
 W
WThe superior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve is a sensory ganglion of the peripheral nervous system. It is located within the jugular foramen where the glossopharyngeal nerve exits the skull. It is smaller than and above the inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
 W
WThe tympanic nerve is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve found near the ear.
 W
WIn the tympanic cavity, the tympanic nerve divides into branches which, along with sympathetic fibres from the carotid plexus, form the tympanic plexus. This plexus is located on the surface of the promontory.