 W
WUkrainian, historically also Ruthenian, is an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family, and is one of Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. It is the native language of Ukrainians and the official state language of Ukraine. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic script.
 W
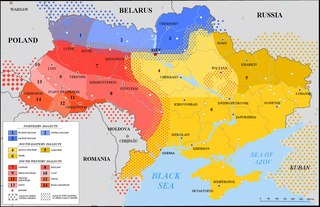
WIn the Ukrainian language there are 3 major dialectal groups according to territory: the southwestern group, the southeastern group and the northern group of dialects.
 W
WThe Ems Ukaz or Ems Ukase, was a secret decree (ukaz) of Tsar Alexander II of Russia issued in 1876, banning the use of the Ukrainian language in print except for reprinting old documents. The ukaz also forbade the import of Ukrainian publications and the staging of plays or lectures in Ukrainian. It was named after the city of Bad Ems, Germany, where it was promulgated.
 W
WA Ukrainophone is a person who speaks the Ukrainian language either natively or by preference. At the same time the term is used in a more specialized meaning to describe the category of people whose cultural background is associated with the Ukrainian language regardless of territorial distinctions.
 W
WOld East Slavic was a language used during the 10th–15th centuries by East Slavs in Kievan Rus' and its successor states, from which the Belarusian, Russian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian languages later evolved.
 W
WOrthography of Smal-Stotskyi and Gartner, also Orthography of Smal-Stotskyi and Scientific Orthography is a Ukrainian orthography created on the basis of Zhelekhivka by Professor Stepan Smal-Stotskyi in collaboration with Theodor Gartner. One of the main innovations of spelling was that the authors also adapted Zhelekhivka for foreign words. In 1891, under the pseudonym Stepan Nahnybida, Smal-Stotskyi published a description of his spelling principles in a 16-page pamphlet On Ruthenian Orthography. In 1893, Smal-Stotskyi and Gartner published the Ruthenian Grammar, which listed all the phonetic rules of this spelling in practice.
 W
WThe following is a list of place names in Canada whose name origin is in the Ukrainian language. Some places – especially in Saskatchewan – were named by ethnic Germans from Ukraine.
 W
WThe Ukrainian Free University is a private graduate university located in Munich, Germany.
 W
WUkrainian Ye is a character of the Cyrillic script. It is a separate letter in the Ukrainian alphabet, the Pannonian Rusyn alphabet, and both the Carpathian Rusyn alphabets; in all of these, it comes directly after Е. In modern Church Slavonic, it is considered a variant form of Ye (Е е). Until the mid-19th century, Є/є was also used in Romanian and Serbian. Other modern Slavonic languages may use Є/є shapes instead of Е/е for decorative purposes. Then, the letter is usually referred to by the older name Yest and the descriptive name Long E.
 W
WUkrainization is a policy or practice of increasing the usage and facilitating the development of the Ukrainian language and promoting other elements of Ukrainian culture, in various spheres of public life such as education, publishing, government and religion. The term is also used to describe a process by which non-Ukrainians or Russified Ukrainians come to accept Ukrainian culture and language as their own.
 W
WThe Valuev Circular of 18 July 1863 was a secret decree (ukaz) of the Minister of Internal Affairs, of the Russian Empire Pyotr Valuev (Valuyev), by which many publications in the Ukrainian language were forbidden, along with belles lettres works.
 W
WYi is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Yi is derived from the Greek letter iota with diaeresis.