 W
WAfrican French is the generic name of the varieties of the French language spoken by an estimated 141 million people in Africa in 2018, spread across 34 countries and territories. This includes those who speak French as a first or second language in these 34 African countries and territories, but it does not include French speakers living in other African countries. Africa is thus the continent with the most French speakers in the world. French arrived in Africa as a colonial language; these African French speakers are now a large part of the Francophonie.
 W
WBelize Kriol is an English-based creole language closely related to Miskito Coastal Creole, Jamaican Patois, San Andrés-Providencia Creole, Bocas del Toro Creole, Colón Creole, Rio Abajo Creole, and Limón Coastal Creole.
 W
WFrench Guianese Creole is a French-based creole language spoken in French Guiana, and to a lesser degree, in Suriname and Guyana. It resembles Antillean Creole, but there are some lexical and grammatical differences between them. Antilleans can generally understand French Guianese Creole, though there may be some instances of confusion. The differences consist of more French and Brazilian Portuguese influences. There are also words of Amerindian and African origin. There are French Guianese communities in Suriname and Guyana who continue to speak the language.
 W
WGullah is a creole language spoken by the Gullah people, an African-American population living in coastal regions of South Carolina and Georgia as well as extreme northeastern Florida and the extreme southeast of North Carolina.
 W
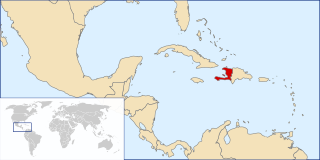
WHaitian Creole, commonly referred to as simply Creole, is a French-based creole language spoken by 10–12 million people worldwide, and is one of the two official languages of Haiti, where it is the native language of a majority of the population.
 W
WIyaric, also called Dread Talk, is a dialect of English consciously created by members of the Rastafari movement. African languages were lost among Africans when they were taken into captivity as part of the slave trade, and adherents of Rastafari teachings believe that English is an imposed colonial language. Their remedy for this situation has been the creation of a modified vocabulary and dialect, reflecting a desire to take language forward and to confront what they see as the confusion of a corrupt and decadent society they call "Babylon". This is accomplished by avoiding sounds and words with negative connotations, such as "back", and changing them to positive ones. Iyaric sometimes also plays a liturgical role among Rastas, in addition to Amharic and Ge'ez.
 W
WJamaican Patois, is an English-based creole language with West African influences, spoken primarily in Jamaica and among the Jamaican diaspora. A majority of non-English loan words in Patois come from the west African Akan language. It is spoken by the majority of Jamaicans as a native language.
 W
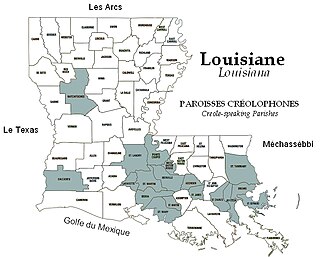
WLouisiana Creole is a French-based creole language spoken by fewer than 10,000 people, mostly in the state of Louisiana. It is spoken today by people who racially identify as white, black, mixed, and Native American, as well as Cajun and Louisiana Creole. It should not be confused with its sister language, Louisiana French, a dialect of the French language.
 W
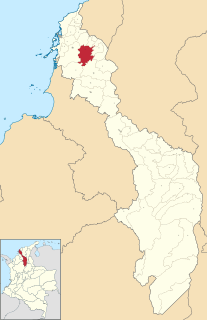
WPalenquero or Palenque is a Spanish-based creole language spoken in Colombia. It is a mixture of Kikongo and Spanish. Palenquero is the only Spanish-based creole in Latin America, if Papiamento is excluded. The ethnic group which speaks this creole consisted of 6,637 people in 2018. It is primarily spoken in the village of San Basilio de Palenque which is southeast of Cartagena, and in some neighbourhoods of Barranquilla.
Papiamento or Papiamentu is a Spanish and Portuguese-based creole language spoken in the Dutch Caribbean. It is the most widely spoken language on the Caribbean ABC islands having official status in Aruba and Curaçao. Papiamento is also a recognized language in the Dutch public bodies of Bonaire, Sint-Eustatius and Saba.
 W
WSwahili, also known by its native name Kiswahili, is a Bantu language and the native language of the Swahili people. It is one of two official languages of the East African Community (EAC) countries, namely Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. It is a lingua franca of other areas in the African Great Lakes region and East and Southern Africa, including some parts of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Malawi, Mozambique, Somalia, and Zambia. Swahili is also one of the working languages of the African Union and of the Southern African Development Community. The exact number of Swahili speakers, be they native or second-language speakers, is estimated to be between 50 million to 150 million.