 W
WIn mathematical logic, the arithmetical hierarchy, arithmetic hierarchy or Kleene–Mostowski hierarchy classifies certain sets based on the complexity of formulas that define them. Any set that receives a classification is called arithmetical.
 W
WBiological organisation is the hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems that define life using a reductionistic approach. The traditional hierarchy, as detailed below, extends from atoms to biospheres. The higher levels of this scheme are often referred to as an ecological organisation concept, or as the field, hierarchical ecology.
 W
WA dominance hierarchy, formerly and colloquially called a pecking order, is a type of social hierarchy that arises when members of animal social groups interact, creating a ranking system. In social living groups, members are likely to compete for access to limited resources and mating opportunities. Rather than fighting each time they meet, relative rank is established between members of the same sex. Based on repetitive interactions, a social order is created that is subject to change each time a dominant animal is challenged by a subordinate one. In mammals, a dominant individual is sometimes called an alpha, and the lower rank is sometimes termed a beta.
 W
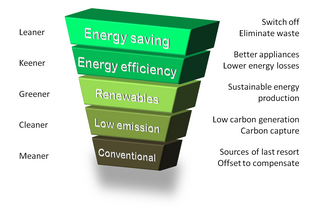
WThe Energy Hierarchy is a classification of energy options, prioritised to assist progress towards a more sustainable energy system. It is a similar approach to the waste hierarchy for minimising resource depletion, and adopts a parallel sequence.
 W
WThe great chain of being is a hierarchical structure of all matter and life, thought by medieval Christianity to have been decreed by God. The chain begins with God and descends through angels, humans, animals, and plants, to minerals.
 W
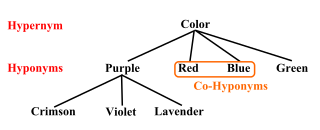
WIn linguistics, hyponymy is a semantic relation between a hyponym denoting a subtype and a hypernym or hyperonym denoting a supertype. In other words, the semantic field of the hyponym is included within that of the hypernym. In simpler terms, a hyponym is in a type-of relationship with its hypernym. For example: pigeon, crow, eagle, and seagull are all hyponyms of bird, their hypernym; which itself is a hyponym of animal, its hypernym.
 W
WJob title inflation is the increasing number and size of grandiose job titles in corporations and organisations, without a corresponding increase in pay. The phenomenon may be caused by employers who want to flatter their workers in a way that doesn't involve paying them more.
 W
WIn computer architecture, the memory hierarchy separates computer storage into a hierarchy based on response time. Since response time, complexity, and capacity are related, the levels may also be distinguished by their performance and controlling technologies. Memory hierarchy affects performance in computer architectural design, algorithm predictions, and lower level programming constructs involving locality of reference.
 W
WA settlement hierarchy is a way of arranging settlements into a hierarchy based upon their population or some other criteria. The term is used by landscape historians and in the National Curriculum for England. The term is also used in the planning system for the UK and for some other countries such as Ireland, India and Switzerland. The term was used without comment by the geographer Brian Roberts in 1972.
 W
WJob title inflation is the increasing number and size of grandiose job titles in corporations and organisations, without a corresponding increase in pay. The phenomenon may be caused by employers who want to flatter their workers in a way that doesn't involve paying them more.
 W
WWaste hierarchy is a tool used in the evaluation of processes that protect the environment alongside resource and energy consumption from most favourable to least favourable actions. The hierarchy establishes preferred program priorities based on sustainability. To be sustainable, waste management cannot be solved only with technical end-of-pipe solutions and an integrated approach is necessary.