 W
WThe Alice is a very small "sugarcube" mobile robot (2x2x2cm) developed at the Autonomous Systems Lab (ASL) at the EPFL in Lausanne, Switzerland between 1998 and 2004. It has been part of the Institute of Robotics and Intelligent Systems (IRIS) at ETH Zurich since 2006.
 W
WDextre, also known as the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator (SPDM), is a two armed robot, or telemanipulator, which is part of the Mobile Servicing System on the International Space Station (ISS), and does repairs otherwise requiring spacewalks. It was launched March 11, 2008 on mission STS-123.
 W
WIceMole is an autonomous ice research probe, incorporating a new type of ice-melting tip for the exploration of polar regions, glaciers, ice sheets, and extraterrestrial regions, developed by a team from the FH Aachen, a Fachhochschule in Aachen, Germany. The advantage over previous probes is that the IceMole can change its direction and can be recovered after being used. A driving ice screw allows the probe to drill through soil layers and other contaminations in the ice.
 W
WIvanAnywhere is a simple, remote-controlled telepresence robot created by Sybase iAnywhere programmers to enable their co-worker, Ivan Bowman, to telecommute to work more efficiently. The robot enables Bowman to be virtually present at conferences and presentations, and to discuss product development with other developers face-to-face. IvanAnywhere is powered by SAP's mobile database product, SQL Anywhere.
 W
WKeepon is a small yellow robot designed to study social development by interacting with children. Keepon was developed by Hideki Kozima while at the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) in Kyoto, Japan. Keepon has four motors, a rubber skin, two cameras in its eyes, and a microphone in its nose.
 W
WThe Khepera is a small (5.5 cm) differential wheeled mobile robot that was developed at the LAMI laboratory of Professor Jean-Daniel Nicoud at EPFL in the mid 1990s. It was developed by Edo. Franzi, Francesco Mondada, André Guignard and others.
 W
WKismet is a robot head made in the 1990s at Massachusetts Institute of Technology by Dr. Cynthia Breazeal as an experiment in affective computing; a machine that can recognize and simulate emotions. The name Kismet comes from a Turkish word meaning "fate" or sometimes "luck".
 W
WThe Legged Squad Support System (LS3) was a DARPA project for a legged robot which could function autonomously as a packhorse for a squad of soldiers or marines. Like BigDog, its quadruped predecessor, the LS3 was ruggedized for military use, with the ability to operate in hot, cold, wet, and dirty environments. The LS3 was put into storage in late 2015.
 W
WLeonardo is a 2.5 foot social robot, the first created by the Personal Robots Group of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Its development is credited to Cynthia Breazeal. The body is by Stan Winston Studios, leaders in animatronics. Its body was completed in 2002. It was the most complex robot the studio had ever attempted as of 2001. Other contributors to the project include NevenVision, Inc., Toyota, NASA's Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center, and the Navy Research Lab. It was created to facilitate the study of human–robot interaction and collaboration. A DARPA Mobile Autonomous Robot Software (MARS) grant, Office of Naval Research Young Investigators Program grant, Digital Life, and Things that Think consortia have partially funded the project. The MIT Media Lab Robotic Life Group, who also studied Robonaut 1, set out to create a more sophisticated social-robot in Leonardo. They gave Leonardo a different visual tracking system and programs based on infant psychology that they hope will make for better human-robot collaboration. One of the goals of the project was to make it possible for untrained humans to interact with and teach the robot much more quickly with fewer repetitions. Leonardo was awarded a spot in Wired Magazine’s 50 Best Robots Ever list in 2006.
 W
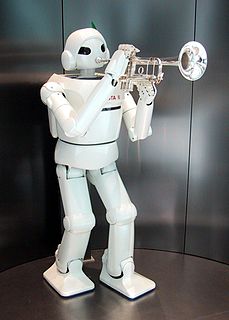
WThe Toyota Partner Robots are a series of humanoid robots developed by Toyota. They debuted playing music on drums and trumpets at the 2005 World EXPO in Aichi, Japan. There are 5 robots in all, most of which have different movement systems. The 5 robots are: Version 1, Version 2, Version 3, Version 4 and the i-Foot . In July 2009, Toyota released a video of the running and standing skills of their partner robot. The robot reaches 7 km/hour, however walking and running can only be achieved on flat surfaces. In 2017, Toyota released its third-generation of humanoid robots, T-HR3, which will be used in space travel.