 W
WCarpathian Romani, also known as Central Romani or Romungro Romani, is a group of dialects of the Romani language spoken from southern Poland to Hungary, and from eastern Austria to Ukraine.
 W
WThe Cieszyn Silesian dialect or Teschen Silesian dialect is one of the Silesian dialects. It has its roots mainly in Old Polish and also has strong influences from Czech and German and, to a lesser extent, from Vlach and Slovak. It is spoken in Cieszyn Silesia, a region on both sides of the Polish-Czech border. It remains mostly a spoken language. The dialect is better preserved today than traditional dialects of many other West Slavic regions.
 W
WThe Czechoslovak language was a political sociolinguistic concept used in Czechoslovakia in 1920–1938 for the definition of the state language of the country which proclaimed its independence as the republic of two nations, i.e. ethnic groups, Czechs and Slovaks.
 W
WGothic is an extinct East Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the Codex Argenteus, a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizeable text corpus. All others, including Burgundian and Vandalic, are known, if at all, only from proper names that survived in historical accounts, and from loanwords in other languages such as Portuguese, Spanish, and French.
 W
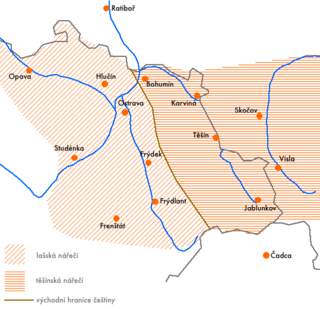
WThe Lachian dialects are a group of West Slavic dialects that form a transition between the Polish and Czech language. They are spoken in parts of Czech Silesia, the Hlučín Region, and northeastern Moravia, as well as in some adjacent villages in Poland. Most Czech researchers consider Lach a dialect of Czech, whereas Polish dialectologists tend to ascribe Polish origins to Lach.
 W
WThe official language of the Czech Republic is Czech. German, Polish, Hungarian, and Ukrainian are recognized as official minority languages. Vietnamese and Belarusian became officially recognised as minority languages in the Czech Republic in 2013, which included the right to use those languages in courts and public places as well as in broadcast radio and television. The Czech Republic signed the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages in 2000. Romany, Slovak and Croatian are also spoken in the country.
 W
WMoravian dialects are the varieties of Czech spoken in Moravia, a historical region in the southeast of the Czech Republic. There are more forms of the Czech language used in Moravia than in the rest of the Czech Republic. The main four groups of dialects are the Bohemian-Moravian group, the Central Moravian group, the Eastern Moravian group and the Lach (Silesian) group. While the forms are generally viewed as regional variants of Czech, some Moravians claim them to be one separate Moravian language.
 W
WSilesian or Upper Silesian is a West Slavic lect of the Lechitic group, spoken in Silesia. Its vocabulary was significantly influenced by Central German due to the existence of numerous Silesian German speakers in the area prior to World War II and after. Some regard it as one of the four major dialects of Polish, while others classify it as a separate language, distinct from Polish.
 W
WSlovak is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union.
 W
WVietnamese is an Austroasiatic language that originated in Vietnam, where it is the national and official language. It is by far the most spoken Austroasiatic language with over 90 million native speakers, at least seven times more than Khmer, the next most spoken Austroasiatic language. Its vocabulary has had significant influence from Chinese and French. It is the native language of the Vietnamese (Kinh) people, as well as a second language or first language for other ethnic groups in Vietnam. As a result of emigration, Vietnamese speakers are also found in other parts of Southeast Asia, East Asia, North America, Europe, and Australia. Vietnamese has also been officially recognized as a minority language in the Czech Republic.