 W
WAmerican Memorial Park on the island of Saipan, Northern Mariana Islands, was created as a living memorial honoring the sacrifices made during the Marianas Campaign of World War II. Recreational facilities, a World War II museum, and flag monument keep alive the memory of over 4,000 United States military personnel and local islanders who died in June 1944.
 W
WThe Atauloma Girls School is a historic parochial school building in Afao village on the island of Tutuila in American Samoa. The London Missionary Society opened it in 1900 as the second secondary school on Tutuila, and the first to admit girls. For most of its history it prepared girls primarily to be pastors' wives, and after 1913 provided graduates to the nursing school at the naval station at Pago Pago. Its establishment saved Tutuila girls the necessity of travel to Upolu for secondary school, which separated them from their families and exposed them to the dangers of the international port at Apia. Atauloma was abandoned by 1970.
 W
WBanzai Cliff is a historic site at the northern tip of Saipan island in the Northern Mariana Islands, overlooking the Pacific Ocean. Towards the end of the Battle of Saipan in 1944, hundreds of Japanese civilians and soldiers jumped off the cliff to their deaths in the ocean and rocks below, to avoid being captured by the Americans. Not far away, a high cliff named Suicide Cliff overlooks the coastal plain, and was another site of numerous suicides. At Banzai Cliff, some who jumped did not die and were captured by American ships.
 W
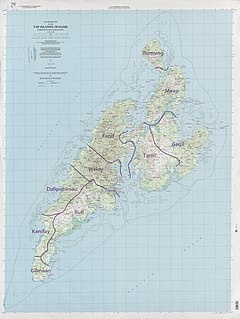
WBechiyal, also variously Bechiel or Bechyal, is a village in the municipality of Maap in the state of Yap, Federated States of Micronesia. When visited in the 1984 it had a population of about ten. The village was once larger, with a documented population of about 200 in the early 20th century. There are a significant number of stone platforms, sites where houses would have stood, and the village site is considered archaeologically sensitive. It was listed on the United States National Register of Historic Places in 1983.
 W
WThe Breakers Point Naval Guns are a historic World War II-era defensive fortification on the island of Tutuila in American Samoa. It consists of two six-inch Mark 8 Model 2 naval guns, mounted on circular concrete platforms about 200 feet above sea level at the end of Papatele Ridge, which flanks the east side of Pago Pago Harbor. The guns, manufactured in 1907, were emplaced in 1941 amid fears of a Japanese invasion of the island, and were left in situ after invasion fears subsided. They were brought to the site by an innovative railway system that used locally crafted rails fashioned out of ifil wood when steel rails were not available. The guns are located on private family-owned land, but may be hiked to with permission.
 W
WThe Campaneyan Kriso Rai, also known as the Catholic Belltower, is a historic church tower in Garapan, the largest village on Saipan island in the Northern Mariana Islands. Built in 1932, it is the only element of the island's most prominent Roman Catholic church to survive bombardment in World War II. The tower, a concrete structure 3 metres (9.8 ft) square and 10 metres (33 ft) tall, was built by Spanish Jesuits brought in by the Japanese South Pacific Mandate administration, and stood next to an 1860 wood-frame church.
 W
WThe Catholic Belltower is a historic tower at the Catholic Mission in Kolonia, on the island of Pohnpei in the Federated States of Micronesia. The belltower and adjoining masonry apse are all that remain of a church built in 1909 by German Capuchin missionaries, when Ponape and the other Caroline Islands were administered as part of German New Guinea. The rest of the church was destroyed during the fighting of World War II. The tower is 4.8 metres (16 ft) square, rising to a height of 20.7 metres (68 ft), and the shell of the apse is about 10 metres (33 ft) in height. The tower has a foundation of basalt rock and lime mortar, and is constructed out of concrete bricks.
 W
WThe Chief Agriculturist House is a historic house in Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State in the Federated States of Micronesia. It is a steel and concrete structure, built in the mid-1920s when Pohnpei and the other Caroline Islands were part of the Japanese South Seas Mandate. It was one of the highest-quality buildings constructed on Pohnpei during the Japanese administration, and was the home of the Japanese weatherman and agricultural overseer, said to be the second most powerful figure in Japanese Micronesia.
 W
WThe Chugai' Pictograph Site is a prehistoric rock art site on the island of Rota in the Northern Mariana Islands. The rock art is located in a limestone cave on the southeastern side of the island, in the I'Chenchon Bird Sanctuary. It consists of a large panel, 185 feet (56 m) in length, of about 90 painted drawings, believed to be of late pre-contact origin. The site is accessed via a trail cut by the Japanese during the South Seas Mandate period.
 W
WThe Commissioner's Office is a rare surviving example of transitional Spanish-Japanese architecture on the island of Rota in the Northern Mariana Islands, an insular area of the United States in the western Pacific Ocean. It is a single-story structure with walls of manposteria, a construction method adopted during the Spanish period. The window trim consists of ifil lintels, and the building's cornice is Japanese in style. At the time of the building's listing on the National Register of Historic Places in 1981, it was in deteriorated condition, lacking a roof and with one collapsed wall. The structure was built in the 1930s by the local Chamorro people, who had been displaced to that part of the island by Japanese settlement undertaken as part of the South Seas Mandate. The building housed the offices of a local commissioner, or village head responsible to the Japanese authorities. Many buildings built by the Japanese during the mandate period were destroyed in World War II.
 W
WThe Courthouse of American Samoa, formerly Administration Building, Navy No. 21, is a historic building near Pago Pago Harbor in Fagatogo, American Samoa. It is a two-story wood-frame building mounted on concrete piers, with a two-story veranda on three sides. A concrete vault is located at the back of the building. The court house was reported by the local commander to have been completed about 1904. It housed the offices and other facilities from which the United States Navy administered the island from its construction until 1952, and was where advisory councils of the island's indigenous leaders were held. The building is one of the oldest standing in American Samoa, having survived typhoons and other perils.
 W
WThe deBrum House, located on Likiep Island, of Likiep Atoll, in the Marshall Islands, is a plantation house that was built by 1888 by Joachim deBrum. Also known as Debrum House, it was listed on the United States National Register of Historic Places in 1976.
 W
WThe German Cemetery is a historic cemetery in Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State in the Federated States of Micronesia. Pohnpei and the other Caroline Islands had become a German protectorate in 1899, after the Spanish–American War, and were administered as part of German New Guinea. This cemetery is a historical reminder of the period of German administration, although it was in deteriorated condition in 1976, accessible only by hiking through a mangrove swamp, with its wrought iron fence and gate in disrepair. Two German governors were buried here.
 W
WThe Governor H. Rex Lee Auditorium, also called Fale Laumei in Samoan, is the largest indoor meeting space in the United States territory of American Samoa. It is located in the village of Utulei, surrounded by other government buildings. The main body of the building is a roughly ovoid structure, with a curved roof that is reminiscent of the thatch roofs of traditional Samoan structures. The auditorium was built in 1962 under orders from Governor Hyrum Rex Lee as part of a major initiative to modernize the territory's infrastructure and facilities. It was built by a construction squadron of the United States Navy, and was completed in time for the 1962 South Pacific Conference. It was later named in honor of Lee, who was the territory's longest-serving governor, and oversaw much of its modernization.
 W
WThe Hachiman Jinja is a derelict Shinto shrine off Kagman Road on the island Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands, and one of the few on those islands to survive relatively intact. The shrine, dedicated to the kami Hachiman, was probably built in the 1930s by the Japanese administration of the South Seas Mandate as part of a program to Japanize the large number of Ryukyuan and Korean workers on the island. The shrine survived the World War II Battle of Saipan in remarkably good condition, although its main torii fell, and two komainu were lost. The main honden received some maintenance in the 1970s, and the property has received some maintenance from a local landholder. As of 2019, it is in total disrepair.
 W
WThe Japanese 20mm Cannon Blockhouse is one of many relics of World War II on the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. It is a concrete blockhouse, semi-circular in shape with a diameter of about 6 metres (20 ft). Its walls are 1.22 metres (4.0 ft) thick with four firing ports large enough to accommodate 20mm cannons, originally equipped with steel sliding shutters. A steel door 25 millimetres (0.98 in) thick provides access to the structure at the rear, sheltered by a concrete wall and covered defensively by a machine gun port. The blockhouse is located near the center of what is locally called Big Agingan Beach, on the south coast of the island, about 20 metres (66 ft) from the shore. It was built in some haste by the Japanese forces defending Saipan in 1944, and was captured by Allied forces early in the Battle of Saipan.
 W
WThe World War II Japanese Army Headquarters for the defense of Tonowas, an island in what is now Chuuk State in the Federated States of Micronesia, was located in an underground bunker in the village of Roro. The underground facilities, including an office, communications center, print shop, supply room, and health clinic, were built in response to American air raids against the facilities, which were associated with the major naval facility of the Imperial Japanese Navy in Chuuk Lagoon.
 W
WThe Japanese Artillery Road and Pohndolap Area are a historic area on Sokehs Island in the Federated States of Micronesia. Sokehs has a prominent north-south ridge (known locally as "Pohndolap", overlooking the state capital Kolonia, and was fortified by the Japanese during World War II. They built a road to the summit area and emplaced anti-aircraft guns on the ridge. The ridge was also a key site in the 1910 Sokehs Rebellion against Japanese rule, and the remnants of a Pohnpeian fort are also in the area. The surviving elements of these fortifications were listed on the United States National Register of Historic Places in 1976. The old road is now part of a hiking trail, leading up to the fortifications.
 W
WThe Japanese Coastal Defense Gun near Songsong on Rota in the Northern Marianas Islands, is a historic site that is listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. The gun emplacement was built by the Japanese military in 1941. It was listed on the National Register in 1984.
 W
WThe Japanese Elementary School for Ponapean Children is a historic school building in Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State in the Federated States of Micronesia. The surviving building is one of two reinforced concrete buildings, constructed c. 1920-21 by the Japanese authorities of the South Seas Mandate, which included the island of Pohnpei, then known as "Ponape". These buildings were the sole educational facility on the island for native children, those of Japanese dependents attending a separate, segregated facility. They were heavily damaged by bombing during World War II, with one of them being demolished and the other restored for use as part of the island's hospital.
 W
WThe former Japanese Hospital building on the island of Rota in the Northern Mariana Islands is one of the few remaining Japanese-era buildings on the island. It is a single-story L-shaped concrete structure. When listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1981, it was described as being in derelict condition, being little more than the concrete structure, lacking a roof, windows, and most of its woodwork. The window openings are sheltered by typical Japanese concrete canopies. The building was built by the Japanese about 1930, during the South Seas Mandate period; most Japanese-built structures on Rota were destroyed during World War II.
 W
WThe Japanese Hospital or Saipan Byoin is a historic World War II-era hospital complex on Route 3 in Garapan, a village on the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. The three concrete buildings are the largest Japanese-built structures to survive the war. The main hospital building is an L-shaped structure with a domed entrance at the crook of the L. A second, smaller building housed the pharmacy, while the third is an underground circular chamber of unknown purpose. All were in deteriorating condition when surveyed in the early 1970s. The complex has since undergone restoration, and the main hospital building now houses the Northern Mariana Islands Museum.
 W
WThe Japanese Hydro-electric Power Plant is a former hydroelectric power generation plant and historic site in Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State in the Federated States of Micronesia. The site is historically and culturally important as a representative of three different eras in the island's history. The site is important in the culture of Pohnpei as a location of high-quality stones gathered for use in ritual ceremonies involving the pounding of kava and drinking preparations from the plant. In the early 1900s, when Pohnpei was administered as part of German New Guinea, the German administration established an experimental forest, planting a diversity of trees from around the world, some of which continue to thrive in the area. Finally, in the 1920s, during the Japanese South Pacific Mandate, a hydroelectrict facility was built here. When the property was listed on the United States National Register of Historic Places in 1976 the concrete power plant building and water catchment basin survived.
 W
WThe Japanese Jail Historic and Archeological District in Garapan (Saipan), MP, is a historic district that was listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places in 2011. The listing included two contributing structures and 15 contributing sites. It includes ruins of a jail that was built in 1930 and was used until 1944.
 W
WThe Japanese Shrine is a Shinto shrine in Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State in the Federated States of Micronesia. The official name at that time was "Nan'yō Government Ponape National School Ho an den" .
 W
WThe Jean P. Haydon Museum is a museum in Pago Pago dedicated to the culture and history of the United States territory of American Samoa. It contains a collection of canoes, coconut-shell combs, pigs’ tusk armlets and native pharmacopoeia. It also houses exhibits on natural history, tapa making, traditional tattooing, as well as a collection of war clubs, kava bowls, and historic photographs. Constructed in 1913 as U.S. Naval Station Tutuila Commissary, the building was home to Tutuila Island's Post Office from 1950–1971. The museum has displays of various aspects of the Samoan Islands’ culture and history. It is the official repository for collections of artifacts for American Samoa. Funded by the American Samoa Council on Arts, Culture and the Humanities, it is the venue used for numerous of the cultural resource activities in American Samoa.
 W
WKed Ra Ngchemiangel, also known as the Kamyangel Terraces, are a series of sculpted landforms in Aimeliik, a state on the island of Babeldaob, the largest in the island nation of Palau. Located near the Kamyangel River near its entry into Ngchemiangel Bay, the terraced hills are clearly manmade forms created in unknown antiquity, and are arrayed in a curve overlooking the bay. When viewed from head-on, many of these terraces have a stepped "crown and brim" appearance similar to that of a brimmed hat. One of the hills is terraced to a height of 190 feet (58 m).
 W
WThe Laulau Kattan Latte Site is a prehistoric archaeological site on the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. Located near the shore of Laulau Bay, it is a small village site containing the remains of four latte stone house foundations, and an extensive scattering of pottery artifacts. When first reported by the pioneering archaeologist Alexander Spoehr in the 1940s, the latte stones were described as mostly fallen over and extremely weathered.
 W
WLikinlulem is a major archaeological site on the island of Kosrae in the Federated States of Micronesia. The site encompasses more than 7 acres (2.8 ha) on either side of Likinlulem Stream on the island's southwestern coast, in an area that is now overgrown mangrove swamp. It includes at least nine large enclosures with extensive internal features, a channelized stream, canoe landing, and a large open platform that is subject to inundation at high tide. Occupancy of the site has been dated to 1200-1800 CE, with one area possibly dating as far back as 1000 CE. The site is an important element of the island's oral history as it was here that its paramount chiefs are said to have held court prior to the ascendancy of Leluh c. 1400. When the site was listed on the United States National Register of Historic Places in 2004, it had been surveyed but not extensively excavated.
 W
WThe Marshall Islands War Memorial Park is a beachfront park located in Delap on Majuro Atoll, Marshall Islands. The park was part of the U.S. Headquarters Command Center for the Marshall Islands, which was responsible for administering the Marshall Islands following World War II. It was located next to the main U.S. airfield on the atoll until 1971, when a new airfield opened; it then became a collection point for World War II artifacts. The park includes weaponry and vehicles, such as Zeros and large ammunition pieces, from throughout the islands.
 W
WThe Masefau Defensive Fortifications consist of a pair of concrete pillboxes on the shores of Masefau Bay on the island of Tutuila in the United States territory of American Samoa. These octagonal structures differ from others found in western Tutuila in that they have no separate interior space for the storage of ammunition. The structures were exposed by a typhoon in 2009.
 W
WMeteu 'L Klechem is a historic stone monolith in Melekeok, a community on the island of Babeldaob, the largest island in the nation of Palau. It is a roughly octagonal stone, 7 feet (2.1 m) long and 2 feet (0.61 m) thick, and weighing about 3,000 pounds (1,400 kg). When recorded in 1976, it was used as a bridge across a local stream. The monolith is historically significant for its association with Metau, a warrior of the late 18th century. In 1785 Metau was ambushed and killed on Koror Island in revenge for attacks he had made on Yapese boats headed there. His body was held as a ransom, and was laid on this stone. Metau's brother Reklai paid the ransom, and in 1795 the stone and body were transported to Melekeok for burial. The stone sat at the main pier at Beriber until 1948, when it was moved to its present location.
 W
WThe Michael J. Kirwan Educational Television Center, also known as KVZK-TV or KVZK Building, is a historic and current television center in Utulei, American Samoa. It is named for U.S. congressman Michael J. Kirwan, from Ohio, who took an interest in the development of American Samoa, and was instrumental in securing funding for a wide variety of improvements in the territory's infrastructure. It is a utilitarian concrete structure, roughly cruciform in shape, with a corrugated metal gable roof, located behind the Department of Education building on Route 1 in Utulei. It was built in 1964 as part of an innovative initiative to reform American Samoa's then-primitive educational facilities by broadcasting lessons from a central facility to the territory's remote schools. This initiative resulted in the widespread electrification of the territory's islands, and the construction of roads and new schools, and was widely regarded as a model for improving education in underdeveloped parts of the world. By the 1970s use of the broadcast facilities for education declined.
 W
WMochong or Mochon is a major prehistoric archaeological site on the island of Rota in the Northern Mariana Islands. It is an extensive village site on the northern side of the island with 47 latte stone house sites, including an extremely rare structure with 14 columns. It also has a latte stone wall, consisting of six columns and five slabs, that is more than 50 feet (15 m) long. The site has been radiocarbon dated to c. 1000 BCE. The site was first sketched in the early 19th century by the French explorer Louis de Freycinet, and was in remarkably intact condition in the 1980s.
 W
WThe Nan'yō Kōhatsu Kabushiki Kaisha Sugar Mill is a former industrial facility in the village of Songsong on the island of Rota in the Northern Mariana Islands. Its ruins are a significant reminder of the South Seas Mandate period, when Imperial Japan engaged in large-scale sugar cane farming in the Northern Marianas, and are the only brick structure in the Northern Marianas. The sugar mill on Rota was one of the major installations of the Nan'yō Kōhatsu Kabushiki Kaisha, the Japanese company responsible for economic development of the mandate area. The remnants of this sugar mill, all that survived the Allied capture of Rota during World War II, are located on the north side of the peninsula that projects southwest from Songsong, and consist of fragments of brick and concrete structures. The most impressive single element is a brick and concrete tunnel 42.5 metres (139 ft) long, from which openings lead to the locations of other parts of the once-extensive complex.
 W
WNavy Building 38 is a historic building on Route 1 in Fagatogo, American Samoa. Located on the north side of the road, it is a roughly square single-story building with a shallow-sloping pyramidal roof, that extends beyond the concrete block walls to create a lanai supported by fluted cast metal columns. The concrete blocks used in its construction were locally manufactured. The building was constructed about 1917 by the United States Navy as part of Naval Station Tutuila, to provide a home for high-powered radio transmission equipment capable of communicating directly with naval facilities in Hawaii during the First World War. It is one of three buildings known to have been built at the time with this combination of materials.
 W
WOld Vatia is a prehistoric village site on the north side of Tutuila, the largest island of American Samoa. The site is located on the Faiga ridge, above the modern village of Vatia in the National Park of American Samoa. It is stretched linearly along the ridge, with terraced areas that have features such as stone house foundations and pavement. The site, believed to have been occupied c. 1300–1750, is one of the island's few upland village sites. It was first identified in the 1960s and recorded in detail in 1989.
 W
WOngeluluul is a historic stone platform in Melekeok, a community on Babeldaob, the largest island of the island nation of Palau. It is located in Old Melekok Village, about 100 yards (91 m) from the boathouse at the shore. It is separated from the main road by a small creek. The platform measures about 20 by 20 feet, and was originally fashioned out of finely paved stones, although it was in deteriorated condition when surveyed in 1976. The site is of local historical significance as a place where important secret meetings of local leaders took place, and is a type of site other major Palauan communities have. This platform was erected in 1750, and was the site of two significant peace treaties in Palauan history: one in 1793 and the other in 1870. The latter peace treaty marked the end of organized warfare between the clans of Palau.
 W
WThe Poloa Defensive Fortifications are a set of historic military structures on the island of Tutuila in American Samoa. Consisting of three concrete pillboxes along the beach, these fortifications were built by American Marines as part of a system of defenses against a feared Japanese amphibious invasion of Samoa during the early part of World War II. The Poloa pillboxes stand out from other emplacements on Tutuila for their relatively less robust construction, possibly reflecting American tactical planning for greater defense in depth at this location. The threat of invasion eased by late 1942, and the fortifications never saw combat.
 W
WThe Rectory on the island of Rota in the Northern Mariana Islands is a rare example of transitional Spanish-Japanese architecture in the archipelago, now a United States commonwealth. It was built about 1930, during the South Seas Mandate period of Japanese administration, when the native Chamorro people were displaced to this area by workers imported by the Japanese to work in the sugar fields. The rectory is an L-shaped concrete structure measuring 13.7 by 19.8 metres, and originally had a wood-framed second floor and roof. Although only the concrete frame remains, elements such as its massive steps and window placement are typical of the earlier Spanish period, while decorative elements such as its porch columns and window opening details are distinctly Japanese.
 W
WThe Rose Island Concrete Monument is a historic commemorative marker on Rose Island, part of Rose Atoll, a remote island located in the far eastern reaches of the territorial waters of American Samoa. The marker is a concrete structure in the shape of a truncated pyramid with a rectangular cross-section. It is 1.53 metres (5.0 ft) wide, 1.59 metres (5.2 ft) high, and 0.74 metres (2.4 ft) deep. On the west side of the marker is raised lettering stating "ROSE ISLAND / AMERICAN SAMOA / TRESPASSING PROHIBITED / WARREN J. TERHUNE / JAN 10 1920 GOVERNOR". A brass plaque on the opposite side of the monument conveys a similar message. The monument was placed in 1920 by the order of Naval Governor Warren J. Terhune during a tour he made of all of the islands of the territory of American Samoa, and serves as a continuing reminder of the American claim to the atoll.
 W
WThe Sadie Thompson Inn is a historic building in Malaloa, one of the constituent villages of Pago Pago in American Samoa. The building is noted as the guest house where from mid-December 1916 author W. Somerset Maugham resided for six weeks during an extended trip through the South Sea Islands. He described it as a "dilapidated lodging house with a corrugated tin roof" and complained that he contracted "a stubborn rash, no doubt fungus" while at the hotel, and of the weeks it took to cure it.
 W
WThe Satala Cemetery is located on the north side of Pago Pago Harbor on the island of Tutuila, the largest in American Samoa. The cemetery was established, apparently late in the 19th century, by the United States Navy, as an interment site for foreigners on the island. Traditional Samoan burial practice is to bury family members on their property, a method not available to outsiders. One section of the cemetery is dedicated to graves of Korean fishermen.
 W
WThe Sokehs Mass Grave Site is the location where fifteen participants of the 1910/1911 Sokehs Rebellion on the island of Pohnpei were buried by German colonial authorities. The rebellion broke out in October 1910 on Sokehs Island and was suppressed by German naval forces by early 1911. At a summary trial of 36 Sokehs rebels, 17 were convicted of murder and insurrection, and 15 subsequently executed by firing squad and buried in this mass grave. All members of the Sokehs tribe were then exiled to Babelthuap. The mass grave site is a roughly square area 16 feet (4.9 m) on each side, surrounded by a low stone wall. The site is now identified by a memorial marker.
 W
WThe Spanish Fort in Colonia, the capital of Yap State in the Federated States of Micronesia, is a historic seat of power on the island of Yap. Only foundational remnants of the 19th-century Spanish fortification survive, on a property now occupied by the local government. The site was also where German and Japanese administrators had their headquarters during their respective periods of administration in the decades of the 20th century before World War II. The foundation was built of stone and cement, and is still accessible via its original steps.
 W
WThe Spanish Wall is the deteriorating remnant of Spanish Fort Alphonso XIII in Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State in the Federated States of Micronesia. When built, the wall was about 0.5 miles (0.80 km) in length and 8 feet (2.4 m) in height with a parapet that ranged in height from 2–3 feet (0.61–0.91 m). The wall was built by Spanish administrators of Pohnpei in 1887 after a local uprising drove the local Spanish authorities onto a ship in the harbor. Most of the wall was taken down by the German administration that took over in the early 20th century, after the Spanish–American War. The remains of the wall, about 700 feet (210 m) and two arches, are now part of a local park.
 W
WSuicide Cliff is a cliff above Marpi Point Field near the northern tip of Saipan, Northern Mariana Islands, which achieved historic significance late in World War II.
 W
WTonnachau Mountain, is a mountain on Moen Island in Chuuk State of the Federated States of Micronesia. Rising to a height of 1,100 feet (340 m), it is not the highest peak of Moen, which is Mount Teroken to the south. Tonnachau is, however, a prominent landmark rising above Chuuk International Airport. The mountain also has an important place in Chuukese culture and prehistory, with archaeologically significant prehistoric middens and fortifications on its summit ridge which date back as far as 4,000 BCE. Chuukese tradition states that its hero Soukachou built a fort on Tonachau when he arrived from Kosrae and established rule over the lagoon. The mountain also has extensive remains of mainly Japanese fortifications erected during World War II.
 W
WThe Tonotan Guns and Caves are a series of World War II-era military fortification on the island of Weno, the main island of Chuuk State in the Federated States of Micronesia. They consist of an excavation housing an English naval gun, and a series of caves used for housing and operations that provided shelter from aerial bombardment. The installations are located on the lower north flank of Mount Teroken, the island's highest peak.
 W
WThe Tui Manu'a Graves Monument is a funerary marker and grave site on the island Ta'u, the largest island of the Manu'a group in American Samoa. It is located northwest of the junction of Ta'u Village and Ta'u Island Roads on the west side of the island. It consists of a stone platform, about 3 feet (0.91 m) in height, that is roughly rectangular in shape with a projection at one end. Three graves are marked by square sections of smoothed stones, while a fourth is marked by a marble column. A possible fifth grave, unmarked, is in the projection. It is the burial site of several tu'i, or kings, of Manu'a, including Tui Manu'a Matelita and Tui Manu'a Elisala, the Samoan leader whose signature granted the United States hegemony over the islands.
 W
WTurtle and Shark is a place with association to an important legend in the culture of Samoa. It is located on the southern shore of Tutuila, the largest island of American Samoa, a short way south of the village of Vaitogi. The feature known as Turtle and Shark is a U-shaped cove, set between Vaitogi Beach to the north and a basalt cliff to the south. The cove is about 72 metres (236 ft) measured from east to west and 78.5 metres (258 ft) measured from north to south. The topography of the cove is such that it is frequently subjected to high-energy wave action, with spray thrown high into the air. The cove is believed by the Samoan populace to be the location of the climactic scene of the Turtle and Shark legend, one of the island's best-known and popular tales.
 W
WThe Unai Lagua Japanese Defense Pillbox is one of the more unusual surviving World War II-era Japanese fortifications on the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. It is located at the southern end of Unai Lagua, which stretches along the northern shore of the island. The pillbox is fashioned out of poured concrete and coral boulders, and uses natural rock formations as part of its walls. This construction was necessitated by a severe shortage of building materials on the island as the Japanese prepared the island's defenses against the advancing Allied forces in 1943–44. The use of natural materials and terrain had the added benefit of rendering the position nearly invisible to aerial or offshore observation.
 W
WThe Waherak Maihar is a historic outrigger canoe on the island of Saipan in the Northern Mariana Islands. Built in 1958, it is a well-preserved example of a traditional Caroline Islands ocean-going canoe. It is 26 feet (7.9 m) long with a beam of 3 feet (0.91 m). It was constructed by the islanders of Poluwat from native materials, including coconut, pandanus, and breadfruit.