 W
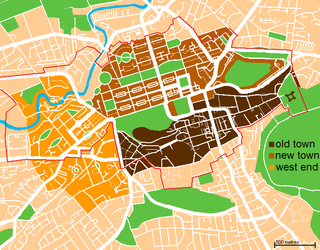
WThe Old Town is the name popularly given to the oldest part of Scotland's capital city of Edinburgh. The area has preserved much of its medieval street plan and many Reformation-era buildings. Together with the 18th/19th-century New Town, it forms part of a protected UNESCO World Heritage Site.
 W
WAugustine United Church is a United Reformed Church in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is in a local ecumenical partnership with St Columba's-by-the-Castle and Greyfriars Tolbooth and Highland Kirk.
 W
WThe Burke and Hare murders were a series of 16 killings committed over a period of about ten months in 1828 in Edinburgh, Scotland. They were undertaken by William Burke and William Hare, who sold the corpses to Robert Knox for dissection at his anatomy lectures.
 W
WChambers Street is a street in Edinburgh, Scotland, in the southern extremity of the Old Town. The street is named after William Chambers of Glenormiston, the Lord Provost of Edinburgh who was the main proponent of the Edinburgh Improvement Act (1867) which led to its creation in 1870. A narrow lane named North College Street and three residential squares built in the 18th century—Adam Square, Argyle Square and Brown Square—disappeared in the process. The street is dominated by University and museum buildings. It also hosts a variety of restaurants and venues.
 W
WCockburn Street is a picturesque street in Edinburgh's Old Town, created as a serpentine link from the High Street to Waverley Station in 1856. It is named after the then recently-deceased Scottish lawyer, judge and literary figure Henry, Lord Cockburn who was influential in urging his fellow citizens to remain vigilant in ensuring that early-Victorian expansion, e.g. improvements such as Cockburn Street, did not irrevocably damage or obliterate the built heritage and environment.
 W
WThe Cowgate is a street in Edinburgh, Scotland, located about 550 yards (500 m) southeast of Edinburgh Castle, within the city's World Heritage Site. The street is part of the lower level of Edinburgh's Old Town, which lies below the elevated streets of South Bridge and George IV Bridge. Consequently, the Cowgate can be quite gloomy and dark in sections. It meets the Grassmarket at its west end and Holyrood Road to the east.
 W
WThe Crown Office and Procurator Fiscal Service is the independent public prosecution service for Scotland, and is a Ministerial Department of the Scottish Government. The department is headed by Her Majesty's Lord Advocate, who under the Scottish legal system is responsible for prosecution, along with the area procurators fiscal. In Scotland, virtually all prosecution of criminal offences is undertaken by the Crown. Private prosecutions are extremely rare.
 W
WThe Dome is a building on George Street in the New Town of Edinburgh, Scotland, United Kingdom. It currently functions as a bar, restaurant and nightclub, although it was first built as the headquarters of the Commercial Bank of Scotland in 1847. The building was designed by David Rhind in a Graeco-Roman style. It stands on the site of the Physicians' Hall, the offices of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh, which was constructed in the 18th century to designs by James Craig, the planner of the New Town. The Dome is a category A listed building.. The current operating business is Caledonian Heritable, a hotel, bars and restaurant group founded by Portobello born entrepreneur Kevin Doyle
 W
WThere have been several town walls around Edinburgh, Scotland, since the 12th century. Some form of wall probably existed from the foundation of the royal burgh in around 1125, though the first building is recorded in the mid-15th century, when the King's Wall was constructed. In the 16th century the more extensive Flodden Wall was erected, following the Scots' defeat at the Battle of Flodden in 1513. This was extended by the Telfer Wall in the early 17th century. The walls had a number of gates, known as ports, the most important being the Netherbow Port, which stood halfway down the Royal Mile. This gave access from the Canongate which was, at that time, a separate burgh.
 W
WThe Edinburgh Vaults or South Bridge Vaults are a series of chambers formed in the nineteen arches of the South Bridge in Edinburgh, Scotland, which was completed in 1788. For around 30 years, the vaults were used to house taverns, workshops for cobblers and other tradesmen, as well as storage space for said merchants. In later years, the vaults were a hotspot for the homeless and for criminal activity such as illegal gambling taverns, illegal whisky distillery and, according to rumour, bodysnatchers stored corpses there overnight. There is however no proof that the serial killers Burke and Hare ever used the vaults.
 W
WIn May 1590, Anne of Denmark was crowned queen consort of Scotland. There was also a ceremony of joyous entry into Edinburgh, an opportunity for spectacle and theatre and allegorical tableaux promoting civic and national identities, similar in many respects to those performed in many other European towns. Celebrations for the arrival of Anne of Denmark in Scotland had been planned and prepared for September 1589, when it was expected she would sail from Denmark with the admirals Peder Munk and Henrik Gyldenstierne. She was delayed by accidents and poor weather and James VI of Scotland joined her in Norway in November. They returned to Scotland in May 1590.
 W
WThe Entry of James VI into Edinburgh was a ceremony marking the coming of age of James VI of Scotland as an adult ruler on Friday 19 October 1579. James VI had spent his childhood at Stirling Castle. Now he came to Edinburgh to begin his adult rule.
 W
WGeorge Heriot's School is a Scottish independent primary and secondary school on Lauriston Place in the Old Town of Edinburgh, Scotland. In the early 21st century, it has more than 1600 pupils, 155 teaching staff, and 80 non-teaching staff. It was established in 1628 as George Heriot's Hospital, by bequest of the royal goldsmith George Heriot, and opened in 1659. It is governed by George Heriot's Trust, a Scottish charity.
 W
WThe Reverend John Glasse (1848–1918) was a Church of Scotland Minister at Greyfriars Kirk, Edinburgh, Scotland, 1877-1909. He was a leading advocate of Christian Socialism, and was described by Sidney Webb as one of the "two most influential Scottish socialists".
 W
WRobert Gourlay or Robin Gourlaw was a wealthy Edinburgh merchant and Customar of Edinburgh who built a house in Edinburgh.
 W
WThe Grassmarket is a historic market place and an event space in the Old Town of Edinburgh, Scotland. In relation to the rest of the city it lies in a hollow, well below surrounding ground levels.
 W
WGreyfriars Bobby was a Skye Terrier who became known in 19th-century Edinburgh for spending 14 years guarding the grave of his owner until he died himself on 14 January 1872. The story continues to be well known in Scotland, through several books and films. A prominent commemorative statue and nearby graves are a tourist attraction.
 W
WGreyfriars Kirk is a parish church of the Church of Scotland, located in the Old Town of Edinburgh, Scotland.
 W
WGreyfriars Kirkyard is the graveyard surrounding Greyfriars Kirk in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located at the southern edge of the Old Town, adjacent to George Heriot's School. Burials have been taking place since the late 16th century, and a number of notable Edinburgh residents are interred at Greyfriars. The Kirkyard is operated by City of Edinburgh Council in liaison with a charitable trust, which is linked to but separate from the church. The Kirkyard and its monuments are protected as a category A listed building.
 W
WThis is a list of Category A listed buildings in the Old Town of Edinburgh, Scotland.
 W
WBaillie John MacMorran, merchant and Baillie of Edinburgh, killed during a riot at Edinburgh High School. His house at Riddle's Court is a valued monument on Edinburgh's Lawnmarket.
 W
WMoubray House, 51 and 53 High Street, is one of the oldest buildings on the Royal Mile, and one of the oldest occupied residential buildings in Edinburgh, Scotland. The façade dates from the early 17th century, built on foundations laid c.1477.
 W
WThe National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland, was formed in 2006 with the merger of the new Museum of Scotland, with collections relating to Scottish antiquities, culture and history, and the adjacent Royal Scottish Museum, with collections covering science and technology, natural history, and world cultures. The two connected buildings stand beside each other on Chambers Street, by the intersection with the George IV Bridge, in central Edinburgh. The museum is part of National Museums Scotland. Admission is free.
 W
WThe Nor Loch, also known as the Nor' Loch and the North Loch, was a man-made loch formerly in Edinburgh, Scotland, in the area now occupied by Princes Street Gardens and Waverley station which lie between the Royal Mile and Princes Street.
 W
WOld College is a building of the University of Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located on South Bridge, and presently houses parts of the University's administration, the University of Edinburgh School of Law, and the Talbot Rice Gallery. Originally called the "New College", it was designed by Robert Adam to replace a number of older buildings.
 W
WThe Porteous Riots surrounded the activities of Captain John Porteous, Captain of the City Guard of Edinburgh, Scotland, who was lynched by a mob for his part in the killing of innocent civilians while ordering the men under his command to quell a disturbance during a public hanging in the Grassmarket, Edinburgh in April 1736. Although the rioters were generally supportive of the convicted smugglers, Porteous seems to have been a somewhat overbearing official, despised by the mob and the underclasses of Edinburgh society.
 W
WRamsay Garden is a block of sixteen private apartment buildings in the Castlehill area of Edinburgh, Scotland. They stand out for their red ashlar and white harled exteriors, and for their prominent position, most visible from Princes Street.
 W
WThe Royal Mile is a succession of streets forming the main thoroughfare of the Old Town of the city of Edinburgh in Scotland. The term was first used descriptively in W M Gilbert's Edinburgh in the Nineteenth Century (1901), "...with its Castle and Palace and the royal mile between", and was further popularised as the title of a guidebook, published in 1920.
 W
WThe Scottish Poetry Library was founded in 1984 by poet Tessa Ransford. It originally had two staff members, including Scottish poet, Tom Hubbard, and 300 books, but has since expanded to some 30,000 items of Scottish and international poetry. The library contains material in Scotland's three indigenous languages: Scottish Gaelic, Lowland Scots, and English.
 W
WThe Sermon on the Mound is the name given by the Scottish press to an address made by Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher to the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland on 21 May 1988. The name is a play on Jesus' Sermon on the Mount and on the artificial hill in Edinburgh called the Mound, on which the Church's Assembly Hall stands, and the fact that Thatcher was preaching to a church and nation that consistently rejected her ideology. She had been invited by the then Moderator of the General Assembly, Duncan Shaw.
 W
WSurgeons' Hall in Edinburgh, Scotland, is the headquarters of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh (RCSED). It houses the Surgeons' Hall Museum, and the library and archive of the RCSED. The present Surgeons' Hall was designed by William Henry Playfair and completed in 1832, and is a category A listed building.
 W
WThe Thistle Chapel, located in St Giles' Cathedral, Edinburgh, Scotland, is the chapel of the Order of the Thistle.
 W
WThe West Port is a street in Edinburgh's Old Town, Scotland, located just south of Edinburgh Castle. It runs from Main Point down to the south west corner of the Grassmarket. Its name derives from the fact it sloped up from the town gate named the West Port, which was the only westwards exit from the city when the city walls stood, allowing passage through the Flodden Wall. The port itself was demolished in 1786.