 W
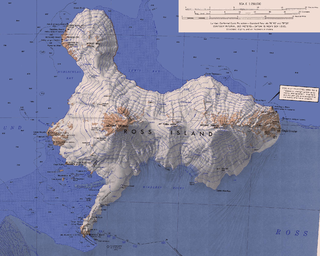
WAurora Glacier is a large glacier draining that part of Ross Island between Mount Erebus and Mount Terra Nova, and flowing south into McMurdo Ice Shelf. It was named by A.J. Heine in 1963 after the Aurora, the ship of the Ross Sea Party of the British expedition under Ernest Shackleton, 1914–17.
 W
WBarne Glacier is a steep glacier in Antarctica which descends from the western slopes of Mount Erebus and terminates on the west side of Ross Island, between Cape Barne and Cape Evans where it forms a steep ice cliff. It was discovered by the Discovery Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott, and named by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09, under Ernest Shackleton, after nearby Cape Barne, which itself is named after Michael Barne of Sotterley, Suffolk who was the second lieutenant during the Discovery Expedition.
 W
WMount Bird is a 1,765 m (5,791 ft) high shield volcano standing about 7 miles (11 km) south of Cape Bird, the northern extremity of Ross Island. It was mapped by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott, and apparently named by them after Cape Bird. Endeavour Piedmont Glacier lies on its slopes.
 W
WCape Evans is a rocky cape on the west side of Ross Island, Antarctica, forming the north side of the entrance to Erebus Bay.
 W
WCastle Rock is a bold rock crag, 415 metres (1,360 ft) high, standing 3 miles (5 km) northeast of Hut Point on the central ridge of Hut Point Peninsula, Ross Island. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott, who so named it because of its shape.
 W
WCaughley Beach is the northernmost beach on the ice-free coast south-west of Cape Bird, Ross Island, Antarctica. It was mapped by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1958–59, and named for Graeme Caughley, biologist with the party that visited Cape Bird. New College Valley, Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.116, lies above the beach.
 W
WCinder Hill is a prominent dissected volcano, 305 metres (1,000 ft) high, consisting of layers of red basalt scoria and cinders and abundant olivine nodules, standing between Harrison Stream and Wilson Stream on the ice-free lower west slopes of Mount Bird, Ross Island. It was mapped and descriptively named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1958–59.
 W
WEndeavour Piedmont Glacier is a piedmont glacier, 6 nautical miles long and 2 nautical miles wide, between the southwest part of Mount Bird and Micou Point, Ross Island. In association with the names of expedition ships grouped on this island, it was named after HMNZS Endeavour, a tanker/supply ship which for at least 10 seasons, 1962–63 to 1971–72, transported bulk petroleum products and cargo to Scott Base and McMurdo Station on Ross Island.
 W
WErebus Bay is a bay about 24 kilometres (13 nmi) wide between Cape Evans and Hut Point Peninsula, on the west side of Ross Island. The bay was explored by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott. It was named by Scott's second expedition, the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, which built its headquarters on Cape Evans; the feature is surmounted by Mount Erebus.
 W
WErebus Glacier is a glacier draining the lower southern slopes of Mount Erebus, Ross Island, Antarctica. It flows west to Erebus Bay where it forms the floating Erebus Glacier Tongue. It was named in association with Mount Erebus by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott.
 W
WHut Point Peninsula is a long, narrow peninsula from 3 to 5 km wide and 24 km (15 mi) long, projecting south-west from the slopes of Mount Erebus on Ross Island, Antarctica. McMurdo Station (US) and Scott Base (NZ) are Antarctic research stations located on the Hut Point Peninsula.
 W
WLewis Bay is a bay indenting the north coast of Ross Island, Antarctica, between Mount Bird and Cape Tennyson.
 W
WMcDonald Beach is an extensive beach lying west of Inclusion Hill and 6 nautical miles (11 km) southwest of Cape Bird on Ross Island, Antarctica. It was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1958–59, after Captain Edwin A. McDonald, then Deputy Commander, US Naval Support Force, Antarctica, who provided extensive transport and other facilities to the NZGSAE in support of the survey of the Cape Bird area.
 W
WThe McMurdo Ice Shelf is the portion of the Ross Ice Shelf bounded by McMurdo Sound and Ross Island on the north and Minna Bluff on the south. Studies show this feature has characteristics quite distinct from the Ross Ice Shelf and merits individual naming. A.J. Heine, who made investigations in 1962–63, suggested the name for the ice shelf bounded by Ross Island, Brown Peninsula, Black Island and White Island. The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names has extended the application of this name to include the contiguous ice shelf southward to Minna Bluff.
 W
WPony Lake is a small lake immediately north of Flagstaff Point at Cape Royds, Ross Island. Named by British Antarctic Expedition (1907–09), who built their winter hut adjacent to this lake, because they had their ponies tethered nearby.
 W
WRocky Point is a 40 m high headland between Horseshoe Bay and Maumee Bight, about 4 km north of Cape Royds on Ross Island, Antarctica.
 W
WSherve Peak is a peak rising to 2200 m in the west part of Guardrail Ridge in Kyle Hills, Ross Island. It was named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) (2000) after John Sherve, facilities maintenance supervisor/construction coordinator at McMurdo Station, 1988–94; ASA resident manager at McMurdo Station, winter 1994; National Science Foundation (NSF) McMurdo Station manager, December 1997-Nov. 1998.
 W
WStarr Lake is a small meltwater lake which is a source of water for McMurdo Station on Ross Island. The lake is situated in the area of constant snow cover on Hut Point Peninsula, approximately 0.5 nautical miles (0.93 km) north of the station and midway between First Crater and Crater Hill. The name Starr Lake came into general use at McMurdo Station for this feature in the early 1970s. It is named after James W. Starr, steelworker, U.S. Navy, who was closely associated with the development of the lake as a source of station water.
 W
WMount Terra Nova is a snow-covered inactive volcanic mountain, 2,130 m (6,990 ft), between Mount Erebus and Mount Terror on Ross Island. It was first mapped by the Discovery expedition in 1901–04, and named for Terra Nova, the relief ship for this expedition and the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13.
 W
WTerrace Lake is a descriptive name for a small, elongate lake which lies in a valley with moraine from the Barne Glacier, about 0.5 nautical miles (0.9 km) east of Cape Barne on Ross Island. The name appears on the maps of the British Antarctic Expedition (1910–13), but may have been applied earlier by the British Antarctic Expedition (1907–09).