 W
WSenegal is a coastal West African nation located 14 degrees north of the equator and 14 degrees west of the Prime Meridian. The country's total area is 196,190 km2 of which 192,000 km2 is land and 4,190 km2 is water.
 W
WBambouk is a traditional name for the territory in eastern Senegal and western Mali, encompassing the Bambouk Mountains on its eastern edge, the valley of the Faleme River and the hilly country to the east of the river valley. It was a formally described district in French Sudan, but in 1895, the border between Sudan and Senegal was moved to the Faleme River, placing the western portion of the district within Senegal. The term is still used to designate the region, but there is no formal administrative area with that name.
 W
WBiffeche or Bifeche is an area of Senegal centred on the town of Savoigne, around 30 kilometres north-east of the major coastal city of Saint-Louis.
 W
WCap-Vert is a volcanic field in Senegal with a surface of 100 square kilometres (39 sq mi). The field covers the Cape Verde peninsula close to Dakar and was active until 600,000 years ago. It consists of a number of outcrops and two 100 metres (330 ft) high hills. The position of the dykes and lava flows has been influenced by local fault systems.
 W
WCasamance is the area of Senegal south of the Gambia including the Casamance River. It consists of the Lower Casamance and the Upper Casamance. The largest city of Casamance is Ziguinchor.
 W
WEnampore is a village in the Casamance region of Senegal. It lies about 23 kilometres from the Casamance's chief town Ziguinchor. It is noted for its impluvium houses, which are a distinctive feature of Jola architecture.
 W
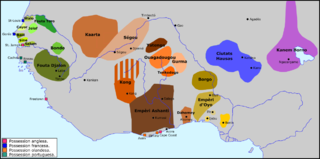
WFuladu or Fuladugu is a historic region in the Upper Casamance, in the south of Senegal, including certain areas in The Gambia near the border with Guinea. It corresponds roughly to the modern Kolda Department.
 W
WFuta Toro, often simply the Futa, is a semidesert region around the middle run of the Senegal River. This region is along the border of Senegal and Mauritania. It is well watered and fertile close to the river, but the interior parts of the region away from the river is porous, dry and infertile. This region is historically significant for the Islamic theocracies, Fulani states, jihad armies and migrants for Fouta Djallon that emerged from here.
 W
WGeological map of Senegal at 1/500 000
 W
WThe Grande Côte is a stretch of coastline in Senegal, running north from the Cap-Vert peninsula of Dakar to the border with Mauritania at St-Louis.
 W
WThe Iles de la Madeleine lie west of Dakar in Senegal. The islands are uninhabited. The main island is Sarpan, known for its Stone Age tool finds. The islands are also known for their birds, fish and plant life. The cliffs are steep, and had been carved by the sea over millions of years. It is one of the smallest national parks in the World.
 W
WThe Lompoul desert is a small desert located 145 km south of Saint-Louis, Senegal. It is characterized by orange sand dunes forming a landscape that is more akin to those of the Sahara and Mauritania than those of the surrounding area of Senegal, and is a popular tourist attraction of Senegal. The desert is named after the closest settlement, i.e., the village of Lompoul.
 W
WMorfil Island is an island lying between the River Senegal and the Doué River in northern Senegal. Morfil is an antiquated French term for raw ivory. It is separate from the mainland for almost 150 km.
 W
WSaloum Delta or Sine-Saloum Delta is a river delta in Senegal at the mouth of the Saloum River where it flows into the North Atlantic Ocean. The delta covers 180,000 hectares. It extends 72.5 kilometers along the coastline and 35 kilometers inland.
 W
WSudan is the geographic region to the south of the Sahara, stretching from Western to eastern Central Africa. The name derives from the Arabic bilād as-sūdān, or "the lands of the Blacks", referring to West Africa and northern Central Africa. The Arabic name was translated as Negroland on older English maps.