 W
WThe 1886 eruption of Mount Tarawera occurred in the early hours of 10 June 1886 in the North Island near Rotorua then extended to Waimangu, New Zealand. It is the deadliest eruption in New Zealand since the arrival of Europeans. Around 120 people were killed, and many settlements were destroyed or buried.
 W
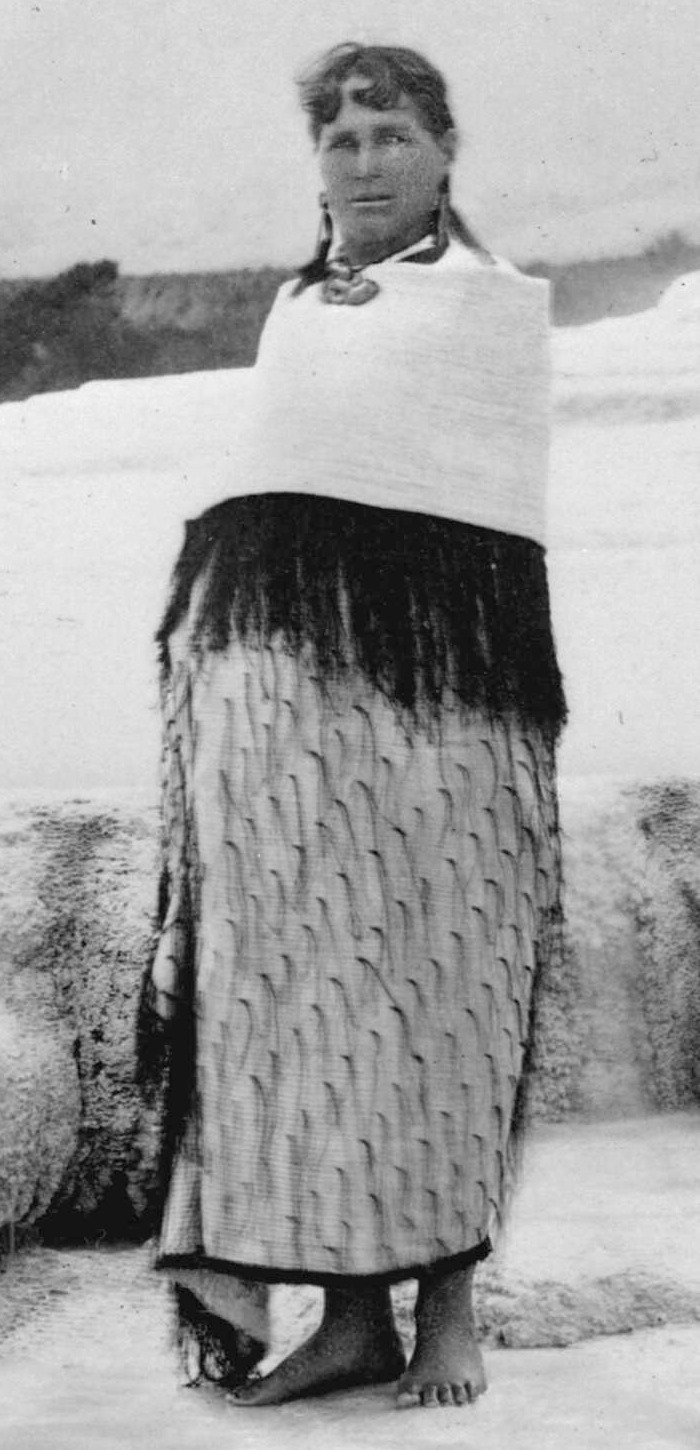
WSophia Hinerangi was a New Zealand tourist guide and temperance leader. Of Māori descent, she identified with the Ngāti Ruanui iwi.
 W
WMount Tarawera is a volcano on the North Island of New Zealand. Located 24 kilometres southeast of Rotorua, it consists of a series of rhyolitic lava domes that were fissured down the middle by an explosive basaltic eruption in 1886. This eruption was one of New Zealand's largest historical eruptions, and killed an estimated 120 people. The fissures run for about 17 kilometres northeast-southwest.
 W
WThe Pink Terrace, or Te Otukapuarangi in Māori, and the White Terrace, also known as Te Tarata, were natural wonders of New Zealand. They were reportedly the largest silica sinter deposits on earth. Until recently, they were lost and thought destroyed in the 1886 eruption of Mount Tarawera, while new hydrothermal features formed to the south-west i.e. Waimangu Volcanic Rift Valley.
 W
WLake Rotomahana is an 800-hectare (2,000-acre) lake in northern New Zealand, located 20 kilometres to the south-east of Rotorua. It is immediately south-west of the dormant volcano Mount Tarawera, and its geography was substantially altered by a major 1886 eruption of Mount Tarawera. Along with the mountain, it lies within the Okataina caldera.
 W
WLake Tarawera is the largest of a series of lakes which surround the volcano Mount Tarawera in the North Island of New Zealand. Like the mountain, it lies within the Okataina caldera. It is located 18 kilometres (11 mi) to the east of Rotorua, and beneath the peaks of the Tarawera massif i.e. Wahanga, Ruawahia, Tarawera and Koa. The lake's surface area is 39 square kilometres (15 sq mi).
 W
WTe Wairoa was a village, now a ghost town that is also known as the Buried Village, close to the shore of Lake Tarawera in New Zealand's North Island. It was a Māori and European settlement founded in 1848 by the Revd Seymour Mills Spencer where visitors would stay on their way to visit the Pink and White Terraces. The village was destroyed by the eruption of the volcano Mount Tarawera on June 10, 1886. 120 people died in the eruption, many of them in other villages closer to the volcano. The site of one of these villages (Kokotaia) was instrumental in the recent rediscovery of the Pink and White Terrace locations.
 W
WThe Waimangu Volcanic Rift Valley is the hydrothermal system created on 10 June 1886 by the volcanic eruption of Mount Tarawera, on the North Island of New Zealand. It encompasses Lake Rotomahana, the site of the Pink and White Terraces, as well as the location of the Waimangu Geyser, which was active from 1900 to 1904. The area has been increasingly accessible as a tourist attraction and contains Frying Pan Lake, which is the largest hot spring in the world, and the steaming and usually pale blue Inferno Crater Lake, the largest geyser-like feature in the world although the geyser itself cannot be seen since it plays at the bottom of the lake.
 W
WAlfred Patchett Warbrick was a New Zealand boatbuilder, rugby player and tourist guide. Of Māori descent, he identified with the Ngāti Rangitihi and Te Arawa iwi.