 W
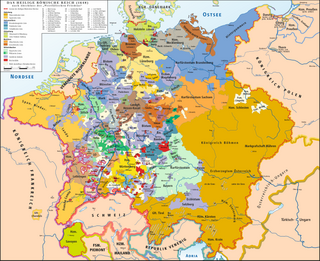
WThis list of states which were part of the Holy Roman Empire includes any territory ruled by an authority that had been granted imperial immediacy, as well as many other feudal entities such as lordships, sous-fiefs and allodial fiefs.
 W
WBrandenburg-Prussia is the historiographic denomination for the Early Modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohenzollern intermarried with the branch ruling the Duchy of Prussia, and secured succession upon the latter's extinction in the male line in 1618. Another consequence of the intermarriage was the incorporation of the lower Rhenish principalities of Cleves, Mark and Ravensberg after the Treaty of Xanten in 1614.
 W
WThe Dauphiné is a former province in southeastern France, whose area roughly corresponded to that of the present departments of Isère, Drôme, and Hautes-Alpes. The Dauphiné was originally the Dauphiné of Viennois.
 W
WThe Erblande of the House of Habsburg formed the Alpine heartland of the Habsburg Monarchy. They were the hereditary possessions of the Habsburgs within the Holy Roman Empire from before 1526. The Erblande were not all unified under the head of the dynasty prior to the 17th century. They were divided into several groupings: the Archduchy of Austria, Inner Austria, the County of Tyrol and Further Austria.
 W
WThe Marquisate of Finale was an Italian state in what is now Liguria, part of the former medieval Aleramici March. It was ruled for some six centuries by the Aleramici branch known as marquesses del Vasto and later Del Carretto, when Savona became a free commune. In 1598 the Marquisate was sold by its last marquis, Sforza Andrea to Philip II of Spain and in 1713 it was finally ceded to the Republic of Genoa, where it remained so until 1797, when it was invaded by Napoleon, ceasing its existence.
 W
WBreuberg is the name of a dynastic, franconian, noble family in Germany, descendants from the Lords of Lützelbach.
 W
WKoblenz, spelled Coblenz before 1926, is a German city on the banks of the Rhine and of the Moselle, a multi-nation tributary.
 W
WSankt Gerold is a municipality in the district of Bludenz in the Austrian state of Vorarlberg.
 W
WSalm is the name of several historic countships and principalities in present Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg and France.
 W
WThe Valle Mesolcina, also known as the Val Mesolcina or Misox (German), is an alpine valley of the Grisons, Switzerland, stretching from the San Bernardino Pass to Grono where it joins the Calanca Valley. It is the valley formed by the river Moesa.
 W
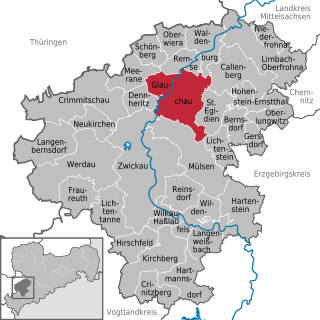
WGlauchau is a town in the German federal state of Saxony, on the right bank of the Mulde, 7 miles north of Zwickau and 17 miles west of Chemnitz by rail. It is part of the Zwickau district.
 W
WWaldenburg is a town in the district Zwickau in Saxony, Germany. The castle was owned by the House of Schönburg from 1378 until 1945. Neighborhood municipalities are Callenberg, the city of Glauchau and Limbach-Oberfrohna, Oberwiera and Remse as well as Göpfersdorf, Jückelberg and Ziegelheim.
 W
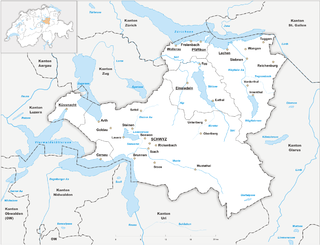
WThe canton of Schwyz is a canton in central Switzerland between the Alps in the south, Lake Lucerne to the west and Lake Zürich in the north, centered on and named after the town of Schwyz.
 W
WThe Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries; that is, what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord and Pas-de-Calais (Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy.
 W
WSilesia is a historical region of Central Europe mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately 40,000 km2 (15,400 sq mi), and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split into two main subregions, Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia has a diverse culture, including architecture, costumes, cuisine, traditions, and the Silesian language.
 W
WSolms-Rödelheim-Assenheim was a County of southern Hesse and eastern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The House of Solms had its origins at Solms, Hesse.
 W
WSolms is a town west of Wetzlar in the Lahn-Dill-Kreis, Hessen, Germany.
 W
WSolms-Hohensolms-Lich was at first a County and later Principality with Imperial immediacy in what is today the federal Land of Hessen, Germany.
 W
WSolms-Hohensolms-Lich was at first a County and later Principality with Imperial immediacy in what is today the federal Land of Hessen, Germany.
 W
WSolms-Rödelheim-Assenheim was a County of southern Hesse and eastern Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The House of Solms had its origins at Solms, Hesse.
 W
WBad Kreuznach is a town in the Bad Kreuznach district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a spa town most well known for its medieval bridge dating from around 1300, the Alte Nahebrücke, which is one of the few remaining bridges in the world with buildings on it.
 W
WSchwarzenberg is a German (Franconian) and Czech (Bohemian) aristocratic family, and it was one of the most prominent European noble houses. The Schwarzenbergs are members of the German nobility and Czech nobility and they held the rank of Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. The family belongs to the high nobility and traces its roots to the Lords of Seinsheim during the Middle Ages.
 W
WThe Manderscheid family was the most powerful family in the Eifel region of Germany for a considerable period of time in the 15th century. In 1457, Dietrich III von Manderscheid was made a Reichsgraf by the Emperor. When Dietrich died on 20 February 1498, he had appointed his sons Johann, Konrad and Wilhelm as new rulers — the family property had been distributed in 1488. Each of the sons founded a powerful lineage: Johann started the Manderscheid-Blankenheim-Gerolstein line, William the Manderscheid-Kail line, and Konrad (Cuno) the Manderscheid-Schleiden line. Augusta von Manderscheid-Blankenheim was the last countess. She was married to a member of the Bohemian nobility, the count of Sternberg.
 W
WSwedish Pomerania was a Dominion under the Swedish Crown from 1630 to 1815, situated on what is now the Baltic coast of Germany and Poland. Following the Polish War and the Thirty Years' War, Sweden held extensive control over the lands on the southern Baltic coast, including Pomerania and parts of Livonia and Prussia.
 W
WThe Old Swiss Confederacy was a loose confederation of independent small states within the Holy Roman Empire. It is the precursor of the modern state of Switzerland.
 W
WVogtland is a region spanning the German federal states of Bavaria, Saxony and Thuringia and north-western Bohemia in the Czech Republic. It overlaps with and is largely contained within Euregio Egrensis. The name alludes to the former leadership by the Vögte of Weida, Gera and Plauen.
 W
WThe County of Sargans was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1458 until the French Revolutionary War in 1798, Sargans became a condominium of the Old Swiss Confederacy, administered jointly by the cantons of Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Lucerne, Zürich, Glarus and Zug.