 W
WThe Republic of Acre or the Independent State of Acre were the names of a series of separatist governments in then Bolivia's Acre region between 1899 and 1903. The region was eventually annexed by Brazil in 1903 and is now the State of Acre.
 W
WAmazonas Province was one of the provinces of the Empire of Brazil. It was created in 1850 from territory of Grão-Pará Province.
 W
WThe Argentine Confederation was the last predecessor state of modern Argentina; its name is still one of the official names of the country according to the Argentine Constitution, Article 35. It was the name of the country from 1831 to 1852, when the provinces were organized as a confederation without a head of state. The governor of Buenos Aires Province managed foreign relations during this time. Under his rule, the Argentine Confederation resisted attacks by Brazil, Bolivia, Uruguay, France and the UK, as well as other Argentine factions during the Argentine Civil Wars.
 W
WThe State of Buenos Aires was a secessionist republic resulting from the overthrow of the Argentine Confederation government in the Province of Buenos Aires on September 11, 1852. The State of Buenos Aires was never recognized by the Confederation or by foreign nations; it remained, however, nominally independent under its own government and constitution. Buenos Aires rejoined the Argentine Confederation after the former's victory at the Battle of Pavón in 1861.
 W
WDutch colonisation of the Guianas—the coastal region between the Orinoco and Amazon rivers in South America—began in the late 16th century. The Dutch originally claimed all of Guiana but—following attempts to sell it first to Bavaria and then to Hanau and the loss of sections to Portugal, Britain, and France—the section actually settled and controlled by the Netherlands became known as Dutch Guiana.
 W
WThe Free and Independent State of Cundinamarca was a rebel state in colonial Colombia, replacing the Spanish colonial Viceroyalty of New Granada from 1810 to 1815. It was part of the Foolish Fatherland period at the beginning of the Spanish American wars of independence. Its capital was Bogotá, the former capital of the Viceroyalty of New Granada.
 W
WGran Colombia is the historiographical designation for the state, then known simply as Colombia, that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to 1831. The state included the territories of present-day Colombia, Ecuador, Panama and Venezuela, and parts of northern Peru and northwestern Brazil. The term Gran Colombia is used historiographically to distinguish it from the current Republic of Colombia, which is also the official name of the former state.
 W
WThe Republic of Independent Guiana commonly referred to by the name of the capital Counani, was a short-lived independent state in South America.
 W
WThe Juliana Republic was declared in the imperial Brazilian province of Santa Catarina on July 24, 1839, and lasted only until November 15, 1839. The Republic was declared in an extension of the Ragamuffin War in the neighboring province of Rio Grande do Sul, where the Riograndense Republic had been declared.
 W
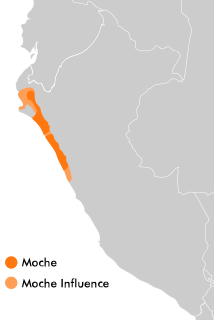
WThe Moche civilization flourished in northern Peru with its capital near present-day Moche, Trujillo, Peru from about 100 to 700 AD during the Regional Development Epoch. While this issue is the subject of some debate, many scholars contend that the Moche were not politically organized as a monolithic empire or state. Rather, they were likely a group of autonomous polities that shared a common culture, as seen in the rich iconography and monumental architecture that survives today.
 W
WThe Republic of North Peru was one of the three constituent Republics of the short-lived Peru–Bolivian Confederation of 1836–1839.
 W
WThe Peru–Bolivian Confederation was a short-lived state that existed in South America between 1836 and 1839. The country was a loose confederation between the states of Peru, divided into the Republic of North Peru and the Republic of South Peru, and Bolivia, with the capital located in Tacna. The Peru–Bolivian Confederation's formation was personally influenced by Marshal Andrés de Santa Cruz, the President of Bolivia, who served as the first and only head of state under the title "Supreme Protector".
 W
WThe Protectorate of Peru was a protectorate created in 1821 in modern Peru after its declaration of independence. It existed for a year and 17 days, under the rule of José de San Martín and Argentina.
 W
WThe Riograndense Republic, often called the Piratini Republic, was a de facto state that seceded from the Empire of Brazil roughly coinciding with the present state of Rio Grande do Sul. It was proclaimed on 11 September 1836, by General Antônio de Sousa Neto, as a direct consequence of the victory obtained by Gaúcho oligarchic forces at the Battle of Seival (1836), during the Farroupilha Revolution (1835–1845). It had a constitution adopted in 1843 and was recognised only by Britain, France, and Uruguay.
 W
WThe Sapa Inca, Sapan Inka or Sapa Inka, also known as Apu ("divinity"), Inka Qhapaq, or simply Sapa, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Cuzco and later, the Emperor of the Inca Empire (Tawantinsuyu) and the Neo-Inca State. While the origins of the position are mythical and originate from the legendary foundation of the city of Cusco, it seems to have come into being historically around 1100 CE. Although the Inca believed the Sapa to be the son of Inti and often referred to him as Intip Churin or ‘Son of the Sun,’ the position eventually became hereditary, with son succeeding father. The principal wife of the Inca was known as the Coya or Qoya. The Sapa Inca was at the top of the social hierarchy, and played a dominant role in the political and spiritual realm.
 W
WThe Republic of Tucumán was a short-lived state centered on the town of San Miguel de Tucumán in today's Argentina that was formed after the collapse of central authority in 1820, and that broke up the next year. The "Republic" remained a political unit within the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata.
 W
WThe United Provinces of New Granada was a country in South America from 1811 to 1816, a period known in Colombian history as the Patria Boba. It was formed from areas of the New Kingdom of Granada, roughly corresponding to the territory of modern-day Colombia. The government was a federation with a parliamentary system, consisting of a weak executive and strong congress. The country was reconquered by Spain in 1816.
 W
WThe United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, earlier known as the United Provinces of South America, a union of provinces in the Río de la Plata region of South America, emerged from the May Revolution in 1810 and the Argentine War of Independence of 1810–1818. It comprised most of the former Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata dependencies and had Buenos Aires as its capital.
 W
WThe Viceroyalty of New Granada was the name given on 27 May 1717, to the jurisdiction of the Spanish Empire in northern South America, corresponding to modern Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela. Created in 1717 by king Felipe V, inside of a new territorial control policy, it was suspended in 1723 due to financial problems and was restored in 1739 until the independence movement suspended it again in 1810. The territory corresponding to Panama was incorporated later in 1739, and the provinces of Venezuela were separated from the Viceroyalty and assigned to the Captaincy General of Venezuela in 1777. In addition to these core areas, the territory of the Viceroyalty of New Granada included Guyana, southwestern Suriname, parts of northwestern Brazil, and northern Peru.