 W
WGermany is traditionally a country organized as a federal state. After the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the German-speaking territories of the empire became allied in the German Confederation (1815–1866), a league of states with some federalistic elements. After the war between Austria and Prussia of 1866, Prussia led the Northern states into a federal state called North German Confederation of 1867–1870. The Southern states joined the federal state in 1870/71, which was consequently renamed German Empire (1871–1918). The state continued as the Weimar Republic of 1919–1933.
 W
WThe Grand Duchy of Baden was a state in the southwest German Empire on the east bank of the Rhine. It existed between 1806 and 1918.
 W
WGay fascism is the idea that homosexuals were numerous and prominent as a group in the Nazi Party or the identification of Nazism with homosexuality more generally. It has been promoted by various individuals and groups both before and after World War II, especially by left-wing Germans during the Nazi era and the Christian right in the United States more recently. Historians regard the claim as having no merit.
 W
WGerman Autumn is a book published in 1947 collecting a series of journalistic essays by Swedish novelist Stig Dagerman. Written during the fall of 1946 while he was on assignment by the Swedish newspaper Expressen in Germany, it depicts life in the war-torn country in the immediate aftermath of World War II. It was not published in America until 2011. The 2010 Swedish edition has an introduction by Nobel Prize in Literature laureate Elfriede Jelinek. It was adapted into the 2008 French documentary film 1946, automne allemand that uses archival footage from post-war Germany to illustrate Dagerman's text.
 W
WThe German Confederation was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe, created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved in 1806.
 W
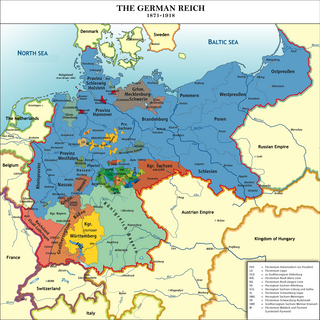
WThe German Empire or the Imperial State of Germany, also referred to as Imperial Germany or Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a republic.
 W
WHesse-Homburg was formed into a separate landgraviate in 1622 by the landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt; it was to be ruled by his son, although it did not become independent of Hesse-Darmstadt until 1668.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Saxony, lasting from 1806 to 1918, was an independent member of a number of historical confederacies in Napoleonic through post-Napoleonic Germany. The kingdom was formed from the Electorate of Saxony. From 1871 it was part of the German Empire. It became a free state in the era of Weimar Republic in 1918 after the end of World War I and the abdication of King Frederick Augustus III of Saxony. Its capital was the city of Dresden, and its modern successor state is the Free State of Saxony.
 W
WNazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich until 1943 and Greater German Reich in 1943–45, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country which they transformed into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", alluded to the Nazis' conceit that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which Hitler and the Nazis referred to as the Thousand Year Reich, ended in May 1945 after just 12 years, when the Allies defeated Germany, ending World War II in Europe.
 W
WThe North German Confederation was the German federal state which existed from July 1867 to December 1870. Although de jure a confederacy of equal states, the Confederation was de facto controlled and led by the largest and most powerful member, Prussia, which exercised its influence to bring about the formation of the German Empire. Some historians also use the name for the alliance of 22 German states formed on 18 August 1866. In 1870–1871, the south German states of Baden, Hesse-Darmstadt, Württemberg and Bavaria joined the country. On 1 January 1871, the country adopted a new constitution, which was written under the title of a new "German Confederation" but already gave it the name "German Empire" in the preamble and article 11.
 W
WPan-Germanism, also occasionally known as Pan-Germanicism, is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanists originally sought to unify all the German-speaking people – and possibly also Germanic-speaking peoples – in a single nation-state known as Großdeutschland.
 W
WSince April 2020, when Germany's Constitutional Court ruled that the pandemic lockdown – which had begun in March – did not allow authorities to impose blanket bans on rallies, several protests have been held in Germany against German governmental COVID-19 measures. These attracted a mix of people from varied backgrounds, including supporters of populist ideas who felt called to defend against what they saw as an arrogant central government; supporters of various conspiracy theories; and sometimes far right-wing groups. Anti-vaxxers generally also formed a major part of the protesters.
 W
WThe states of the German Confederation were those member states that from 20 June 1815 were part of the German Confederation, which lasted, with some changes in the member states, until 24 August 1866, under the presidency of the Austrian imperial House of Habsburg, which was represented by an Austrian presidential envoy to the Federal diet in Frankfurt.
 W
WThe Unification of Germany into the German Empire, a Prussia-dominated state with federal features, was officially proclaimed on 18 January 1871 in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles in France. The new state replaced the German Confederation, a decentralized association of the German duchies and states, and the preceding Holy Roman Empire which had become highly decentralized in its final centuries, with the new realm continuing the federalism and sovereignty of its member states on paper, but in practice applying Prussian centralization to all of the entities in the empire. Princes of the German states, excluding Austria-Hungary and its House of Habsburg-Lorraine, gathered at the ceremony to proclaim William I of Prussia and the House of Hohenzollern as German Emperor, following the French capitulation in the Franco-Prussian War.
 W
WThe Weimar Republic is a historical designation for the German federal state that existed from 1918 to 1933. The state was officially the German Reich, and was also referred to as the German Republic. The term "Weimar Republic" refers to the city of Weimar, where the republic's constituent assembly first took place. In English the country was usually simply called "Germany;" the term "Weimar Republic" did not become common in English until the 1930s.
 W
WDuring World War I, the German Empire was one of the Central Powers that lost the war. It began participation in the conflict after the declaration of war against Serbia by its ally, Austria-Hungary. German forces fought the Allies on both the eastern and western fronts, although German territory itself remained relatively safe from widespread invasion for most of the war, except for a brief period in 1914 when East Prussia was invaded. A tight blockade imposed by the Royal Navy caused severe food shortages in the cities, especially in the winter of 1916–17, known as the Turnip Winter. At the end of the war, Germany's defeat and widespread popular discontent triggered the German Revolution of 1918–19 which overthrew the monarchy and established the Weimar Republic.