 W
WIntellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability and formerly mental retardation (MR), is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significantly impaired intellectual and adaptive functioning. It is defined by an IQ under 70, in addition to deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors that affect everyday, general living.
 W
WAF4/FMR2 family member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AFF2 gene. Mutations in AFF2 are implicated in cases of breast cancer.
 W
WAlwadei Syndrome or Autosomal recessive mental retardation-61 (MRT61) is an autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by delayed psychomotor development, intellectual disability, and variable abnormal facial features. Severe patients may develop refractory seizures and have brain abnormalities, including hypoplasia of the corpus callosum. Alwadei Syndrome attributed to mutation in RUSC2 gene on chromosome 9p13.3.
 W
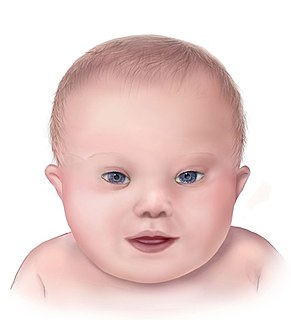
WCongenital hypothyroidism (CH) is thyroid hormone deficiency present at birth. If untreated for several months after birth, severe congenital hypothyroidism can lead to growth failure and permanent intellectual disability. Infants born with congenital hypothyroidism may show no effects, or may display mild effects that often go unrecognized as a problem. Significant deficiency may cause excessive sleeping, reduced interest in nursing, poor muscle tone, low or hoarse cry, infrequent bowel movements, significant jaundice, and low body temperature.
 W
WDown syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic facial features. The average IQ of a young adult with Down syndrome is 50, equivalent to the mental ability of an 8- or 9-year-old child, but this can vary widely.
 W
WFragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic disorder characterized by mild-to-moderate intellectual disability. The average IQ in males is under 55, while about two thirds of affected females are intellectually disabled. Physical features may include a long and narrow face, large ears, flexible fingers, and large testicles. About a third of those affected have features of autism such as problems with social interactions and delayed speech. Hyperactivity is common, and seizures occur in about 10%. Males are usually more affected than females.
 W
WIntellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability and formerly mental retardation (MR), is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significantly impaired intellectual and adaptive functioning. It is defined by an IQ under 70, in addition to deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors that affect everyday, general living.
 W
WAn idiot, in modern use, is a stupid or foolish person.
 W
WLead poisoning is a type of metal poisoning caused by lead in the body. The brain is the most sensitive. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, irritability, memory problems, infertility, and tingling in the hands and feet. It causes almost 10% of intellectual disability of otherwise unknown cause and can result in behavioral problems. Some of the effects are permanent. In severe cases anemia, seizures, coma, or death may occur.
 W
WLujan–Fryns syndrome (LFS) is an X-linked genetic disorder that causes mild to moderate intellectual disability and features described as Marfanoid habitus, referring to a group of physical characteristics similar to those found in Marfan syndrome. These features include a tall, thin stature and long, slender limbs. LFS is also associated with psychopathology and behavioral abnormalities, and it exhibits a number of malformations affecting the brain and heart. The disorder is inherited in an X-linked dominant manner, and is attributed to a missense mutation in the MED12 gene. There is currently no treatment or therapy for the underlying MED12 malfunction, and the exact cause of the disorder remains unclear.
 W
WMental age is a concept related to intelligence. It looks at how a specific individual, at a specific age, performs intellectually, compared to average intellectual performance for that individual's actual chronological age. The intellectual performance is based on performance in tests and live assessments by a psychologist. The score achieved by the individual is compared to the median average scores at various ages, and the mental age is derived such that the individual's score equates to the average score at age x.
 W
WMicrocephaly albinism digital anomalies syndrome is a very rare congenital genetic disease. The syndrome includes microcephaly, micrognathia, oculocutaneous albinism, hypoplasia of the distal phalanx of fingers, and agenesia of the distal end of the right big toe.
 W
WNoonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence in the syndrome is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia.
 W
WPhenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated, PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also result in a musty smell and lighter skin. A baby born to a mother who has poorly treated PKU may have heart problems, a small head, and low birth weight.
 W
WTetrahydrobiopterin deficiency (THBD, BH4D) is a rare metabolic disorder that increases the blood levels of phenylalanine. Phenylalanine is an amino acid obtained normally through the diet, but can be harmful if excess levels build up, causing intellectual disability and other serious health problems. In healthy individuals, it is metabolised (hydroxylated) into tyrosine, another amino acid, by phenylalanine hydroxylase. However, this enzyme requires tetrahydrobiopterin as a cofactor and thus its deficiency slows phenylalanine metabolism.
 W
WTuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a rare multisystem autosomal dominant genetic disease that causes non-cancerous tumours to grow in the brain and on other vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, liver, eyes, lungs and skin. A combination of symptoms may include seizures, intellectual disability, developmental delay, behavioral problems, skin abnormalities, lung disease, and kidney disease.