 W
WArenberg, also spelled as Aremberg or Ahremberg, is a former county, principality and finally duchy that was located in what is now Germany. The Dukes of Arenberg remain a prominent Belgian noble family.
 W
WThe Bitburg controversy concerned a ceremonial visit by Ronald Reagan, the incumbent President of the United States, to a German military cemetery in Bitburg, West Germany in May 1985. The visit was intended to commemorate the 40th anniversary of the end of World War II in Europe but aroused considerable criticism in the United States and around the world when it became known that 49 of the 2,000 German soldiers buried at the site had been members of the Waffen-SS, the military arm of Nazi Germany's Schutzstaffel (SS). The entire SS was judged to be a criminal organisation at the Nuremberg trials. The fact that Reagan had not been scheduled to visit former concentration camps compounded the controversy and a trip to Bergen-Belsen concentration camp was later added to his itinerary.
 W
WThe Battle of the Bulge, also known as the Ardennes Counteroffensive, was a major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II, and took place from 16 December 1944 to 25 January 1945. It was launched through the densely forested Ardennes region in Belgium and Luxembourg towards the end of the war in Europe. The offensive was intended to stop Allied use of the Belgian port of Antwerp and to split the Allied lines, allowing the Germans to encircle and destroy four Allied armies and force the Western Allies to negotiate a peace treaty in the Axis powers' favor.
 W
WThe County of Virneburg was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire in the region of the Eifel in present-day Rhineland-Palatinate.
 W
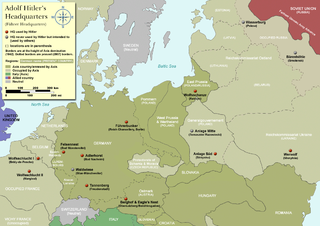
WAt the start of the Western European campaign of 1940, the Felsennest was the codename for one of Hitler's Führer Headquarters near Bad Münstereifel, Germany. It was much more cramped than Adolf Hitler's other field bunkers, having only four rooms. Hitler was at the Felsennest in the autumn of 1939, because there were plans to invade France and the Low Countries. He was there again on May 10, 1940 when the invasion took place.
 W
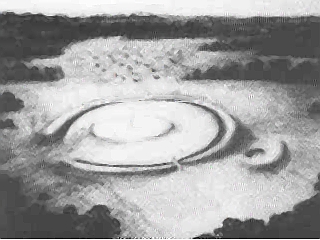
WThe Goloring is an ancient earthworks monument located near Koblenz, Germany. It was created in the Bronze Age era, which dates back to the Urnfield culture. During this time a widespread solar cult is believed to have existed in Central Europe.
 W
WThe Herkelstein is a hill, 434.5 m, in the northeastern part of the der Eifel, in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It forms the highest point of the Eschweiler Ridge and lies in the North Eifel Nature Park. Geologically the region is part of the Limestone Eifel, the Herkelstein itself - like the rock formations of the Kakus Caves - is made of Devonian Limestone. It lies between the villages of Weiler am Berge and Holzheim (Mechernich). From the top there is a good long-distance view over the Cologne Bay.
 W
WThe Battle of Hürtgen Forest was a series of fierce battles fought from 19 September to 16 December 1944, between American and German forces on the Western Front during World War II, in the Hürtgen Forest, a 140 km2 (54 sq mi) area about 5 km (3.1 mi) east of the Belgian–German border. It was the longest battle on German ground during World War II and is the longest single battle the U.S. Army has ever fought.
 W
WOrdensburg Vogelsang is a former Nazi estate placed at the former military training area in Eifel National Park in North Rhine-Westphalia. The landmarked and completely preserved estate was used by the National Socialists between 1936 and 1939 as an educational centre for future leaders. Since 1 January 2006 the area has been open to visitors. It is one of the largest architectural relics of National Socialism. The gross area of the landmarked buildings is 50,000 m2.
 W
WThe Peasants' War was a peasant revolt in 1798 against the French occupiers of the Southern Netherlands, a region which now includes Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Germany. The French had annexed the region in 1795 and control of the region was officially ceded to the French after the Treaty of Campo Formio in 1797. The revolt is considered part of the French Revolutionary Wars.
 W
WPrüm Abbey is a former Benedictine abbey in Prüm, now in the diocese of Trier (Germany), founded by the Frankish widow Bertrada the elder and her son Charibert, Count of Laon, on 23 June 720. The first abbot was Angloardus.
 W
WOn 15 July 1949 an ammunition depot on the hill of Kalvarienberg in the Eifel mountains exploded. The cause of the explosion, in which the town was heavily damaged and 12 people killed, was never discovered. The crater, which is still visible today, is one of the largest man-made explosion craters in existence. A cross on the Kalvarienberg commemorates the victims of the disaster.
 W
WRoer [ʁo.ɛʁ] was a department of the French First Republic and later First French Empire in present-day Germany and the Netherlands. It was named after the river Roer (Rur), which flows through the department. It was formed in 1795, when the Southern Netherlands and the left bank of the Rhine were occupied by the French. The department was formed from the duchies of Jülich and Cleves, the part of the Archbishopric of Cologne left of the Rhine, the Free City of Aachen, the Prussian part of the duchy of Guelders and some smaller territories. In 1805 the city of Wesel was added to the department. The capital was Aix-la-Chapelle (Aachen).
 W
WSarre was a department in the First French Republic and First French Empire. Its territory is now part of Germany and Belgium. Named after the river Saar, it was created in 1798 in the aftermath of the Treaty of Campo Formio of 18 October 1797 which ceded the left bank of the Rhine to France.
 W
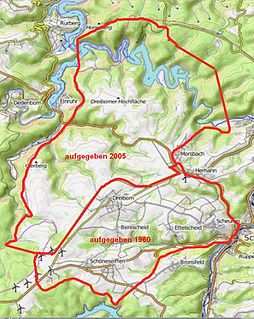
WVogelsang Military Training Area lay in the German North Eifel hills between the villages of Simmerath, Heimbach and Schleiden in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It was established in 1946 and handed back at the end of 2005, and consisted of the grounds of the former Nazi leadership training centre in the fort of Vogelsang on the Erpenscheid hill plus additional terrain including the so-called Dreiborn Plateau. In the north and east it was bounded by the Urft Reservoir. The training area had an area of around 45 km2 and since 1 January 2006 has been fully incorporated into the Eifel National Park. Until 1950 the training area was run by the British armed forces and thereafter until 31 December 2005 by the Belgian military.