 W
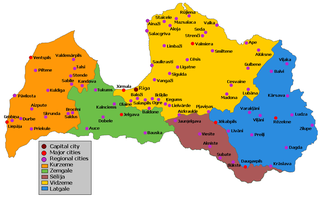
WCultural regions of Latvia are several areas within Latvia formally recognised as distinct from the rest of the country. While some of these regions are seen purely as culturally distinct, others have historically been parts of different countries and have been used to divide the country for administrative and other purposes. The Constitution of Latvia recognises four distinct regions: Kurzeme, Zemgale, Latgale and Vidzeme.
 W
WBandava - and old Curonian land which existed in the territory of the Latvia during the late Iron Age until it was conquered and divided in 1253 by Bishopric of Courland and Livonian Order.
 W
WCourland is one of the historical and cultural regions in western Latvia. The largest city is Liepāja, the third largest city in Latvia. The regions of Semigallia and Selonia are sometimes considered as part of Courland as they were formerly held by the same duke.
 W
WThe Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was a duchy in the Baltic region, in what was then known as Livonia, that existed from 1561 to 1569 as a nominally vassal state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently made part of the Crown of the Polish Kingdom from 1569 to 1726 and incorporated into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1726. On 28 March 1795, it was annexed by the Russian Empire in the Third Partition of Poland.
 W
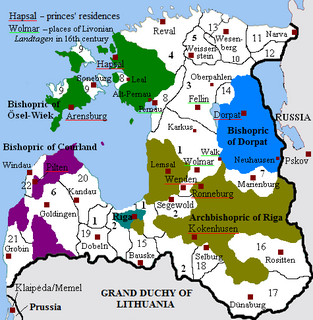
WThe Bishopric of Courland was the second smallest (4500 km2) ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation founded in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade. During the Livonian War in 1559 the bishopric became a possession of Denmark, and in 1585 sold by Denmark to Poland–Lithuania.
 W
WThe principality of Jersika was an early medieval Latgalian principality in eastern modern-day Latvia and one of the largest early states in Latvia before the German conquests. The capital of Jersika was located on a hill fort 165 km (103 mi) southeast of Riga.
 W
WThe Principality of Koknese was a small vassal state of the Principality of Polotsk on the right bank of the Daugava River in ancient Livonia during the Middle Ages.
 W
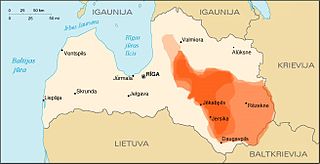
WLatgale is one of the four historical and cultural regions of Latvia recognised in the Constitution of the Republic of Latvia. It is the easternmost region and is north of the Daugava River. While most of Latvia is historically Lutheran, Latgale is predominantly Roman Catholic: 65.3% according to a 2011 survey. There is also a strong Eastern Orthodox minority (23.8%), of which 13.8% are Russian Orthodox Christians and 10.0% are Old Believers.
 W
WLivonia is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.
 W
WMõtsa Pūol or Metsepole was an ancient Livonian county inhabited by the Finnic Livonians, on the east coast of the Gulf of Riga, at the northwest of what is now the Vidzeme region of Latvia. Metsepole was bordered by the ancient Estonian Sakala County to the north, Latgalian Tālava to the east and Livonian county of Turaida to the south.
 W
WPiemare was one of the main Curonian kihelkonds with an administrative center in Esestua (Seeburg) before the 13th century. It was located between Bandava, Duvzare and the Baltic sea on the territory of present Liepāja district in Latvia. For the first time the territory was mentioned in the memorandum between Lammechinus, king of Esestua and Baudouin of Aulne Abbey, cistercian monk, vicelegate of Pope Gregory IX on 28 December 1230. Toponyms were named in partition agreement between the Bishop of Courland and the Livonian Order in 1253. The territory included the following settlements : Vārtaja, Tadaiķi, Ūsaiķi, Ilga, Līpa, Gavieze, Vārve, Padone, Peke, Okte, Ģelži, Lindale, Troista, Ievade, Dzēre, Boja, Droga, Krote, Apriķi, Ilmede, Diždupļi, Mazdupļi, Grobiņa, Neres, Stroķi, Tāši, Aistere, Vērgale, Rīva, Medze, Līva, Razge, Perkone, Dunalka, Prūši, Karkele, Dzintere, Saliena and Saka.
 W
WThe Russian Partition constituted the former territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that were annexed by the Russian Empire in the course of late-18th-century Partitions of Poland. The Russian acquisition encompassed the largest share of Poland's population, living on 463,200 km2 of land constituting the eastern and central territory of the previous commonwealth. The first partitioning led by imperial Russia took place in 1772; the next one in 1793, and the final one in 1795, resulting in Poland's elimination for the next 123 years.
 W
WSelonia, also known as Augšzeme, is a cultural region of Latvia encompassing the eastern part of the historical region of Semigallia as well as a portion of northeastern Lithuania. Its main city and cultural center is Jēkabpils. The Selonian language has become extinct, though some of the inhabitants still speak a Latgalian dialect.
 W
WTālava was a Latgalian country in the northern Vidzeme and northern Latgale region of today's Latvia. It was bordered by the Latgalian Principality of Jersika to the south, the Livonian counties of Metsepole and Idumeja to the west, the Estonian counties of Sakala and Ugandi to the north and the Russian Novgorod Republic to the east.
 W
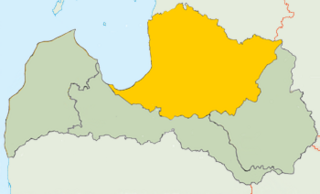
WVidzeme is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia. The capital of Latvia, Riga, is situated in the southwestern part of the region. Population: around 1.3 million (year?). Literally meaning "the Middle Land", it is situated in north-central Latvia north of the Daugava River. Sometimes in German, it is also known as Livland, the German form from Latin Livonia, though it comprises only a small part of Medieval Livonia and about half of Swedish Livonia.