 W
WIn chemistry, a colloid is a phase separated mixture in which one substance of microscopically dispersed insoluble or soluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Sometimes the dispersed substance alone is called the colloid; the term colloidal suspension refers unambiguously to the overall mixture. Unlike a solution, whose solute and solvent constitute only one phase, a colloid has a dispersed phase and a continuous phase that arise by phase separation. Typically, colloids do not completely settle or take a long time to settle completely into two separated layers.
 W
WCreationism is the religious belief that nature, and aspects such as the universe, Earth, life, and humans, originated with supernatural acts of divine creation. In its broadest sense, creationism includes a continuum of religious views, which vary in their acceptance or rejection of scientific explanations such as evolution that describe the origin and development of natural phenomena.
 W
WThe Great Chain of Being is a hierarchical structure of all matter and life, thought by medieval Christianity to have been decreed by God. The chain begins with God and descends through angels, humans, animals, and plants, to minerals.
 W
WCarl Wilhelm von Nägeli was a Swiss botanist. He studied cell division and pollination but became known as the man who discouraged Gregor Mendel from further work on genetics. He rejected natural selection as a mechanism of evolution, favouring orthogenesis driven by a supposed "inner perfecting principle".
 W
WLysenkoism was a political campaign led by Trofim Lysenko against genetics and science-based agriculture in the mid-20th century, rejecting natural selection in favour of Lamarckism and exaggerated claims for the benefits of vernalization and grafting. In time, the term has come to be identified as any deliberate distortion of scientific facts or theories for purposes that are deemed politically, religiously or socially desirable.
 W
WLev Semyonovich Berg, also known as Leo S. Berg was a leading Russian geographer, biologist and ichthyologist who served as President of the Soviet Geographical Society between 1940 and 1950.
 W
WThe Odic force is the name given in the mid-19th century to a hypothetical vital energy or life force by Baron Carl von Reichenbach. Von Reichenbach coined the name from that of the Norse god Odin in 1845. The study of Odic force is called odology.
 W
WOrthogenesis, also known as orthogenetic evolution, progressive evolution, evolutionary progress, or progressionism, is the biological hypothesis that organisms have an innate tendency to evolve in a definite direction towards some goal (teleology) due to some internal mechanism or "driving force". According to the theory, the largest-scale trends in evolution have an absolute goal such as increasing biological complexity. Prominent historical figures who have championed some form of evolutionary progress include Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, Pierre Teilhard de Chardin, and Henri Bergson.
 W
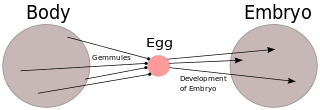
WPangenesis was Charles Darwin's hypothetical mechanism for heredity, in which he proposed that each part of the body continually emitted its own type of small organic particles called gemmules that aggregated in the gonads, contributing heritable information to the gametes. He presented this 'provisional hypothesis' in his 1868 work The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication, intending it to fill what he perceived as a major gap in evolutionary theory at the time. The etymology of the word comes from the Greek words pan and genesis ("birth") or genos ("origin"). Pangenesis mirrored ideas originally formulated by Hippocrates and other pre-Darwinian scientists, but built off of new concepts such as cell theory, explaining cell development as beginning with gemmules which were specified to be necessary for the occurrence of new growths in an organism, both in initial development and regeneration. It also accounted for regeneration and the Lamarckian concept of the inheritance of acquired characteristics, as a body part altered by the environment would produce altered gemmules. This made Pangenesis popular among the neo-Lamarckian school of evolutionary thought. This hypothesis was made effectively obsolete after the 1900 rediscovery among biologists of Gregor Mendel's theory of the particulate nature of inheritance.
 W
WIn the history of biology, preformationism is a formerly popular theory that organisms develop from miniature versions of themselves. Instead of assembly from parts, preformationists believed that the form of living things exist, in real terms, prior to their development. It suggests that all organisms were created at the same time, and that succeeding generations grow from homunculi, or animalcules, that have existed since the beginning of creation.
 W
WSpontaneous generation is a body of thought on the ordinary formation of living organisms without descent from similar organisms. The theory of spontaneous generation held that living creatures could arise from nonliving matter and that such processes were commonplace and regular. It was hypothesized that certain forms such as fleas could arise from inanimate matter such as dust, or that maggots could arise from dead flesh. A variant idea was that of equivocal generation, in which species such as tapeworms arose from unrelated living organisms, now understood to be their hosts. The idea of univocal generation, by contrast, refers to effectively exclusive reproduction from genetically related parent(s), generally of the same species.
 W
WTransmutation of species and transformism are 19th-century evolutionary ideas for the altering of one species into another that preceded Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection. The French Transformisme was a term used by Jean Baptiste Lamarck in 1809 for his theory, and other 19th century proponents of pre-Darwinian evolutionary ideas included Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, Robert Grant, and Robert Chambers, the anonymous author of the book Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation. Opposition in the scientific community to these early theories of evolution, led by influential scientists like the anatomists Georges Cuvier and Richard Owen and the geologist Charles Lyell, was intense. The debate over them was an important stage in the history of evolutionary thought and would influence the subsequent reaction to Darwin's theory.