 W
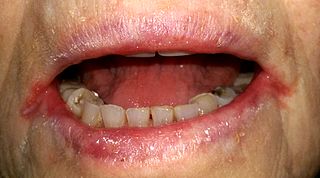
WActinic cheilitis is cheilitis caused by long term sunlight exposure. Essentially it is a burn, and a variant of actinic keratosis which occurs on the lip. It is a premalignant condition, as it can develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
 W
WAngular cheilitis (AC) is inflammation of one or both corners of the mouth. Often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting. It can also be itchy or painful. The condition can last for days to years. Angular cheilitis is a type of cheilitis.
 W
WCheilitis is inflammation of the lips.(1-2)
 W
WCleft lip and cleft palate, also known as orofacial cleft, is a group of conditions that includes cleft lip, cleft palate, and both together. A cleft lip contains an opening in the upper lip that may extend into the nose. The opening may be on one side, both sides, or in the middle. A cleft palate occurs when the roof of the mouth contains an opening into the nose. These disorders can result in feeding problems, speech problems, hearing problems, and frequent ear infections. Less than half the time the condition is associated with other disorders.
 W
WHerpes labialis, commonly known as cold sores, is a type of infection by the herpes simplex virus that affects primarily the lip. Symptoms typically include a burning pain followed by small blisters or sores. The first attack may also be accompanied by fever, sore throat, and enlarged lymph nodes. The rash usually heals within 10 days, but the virus remains dormant in the trigeminal ganglion. The virus may periodically reactivate to create another outbreak of sores in the mouth or lip.
 W
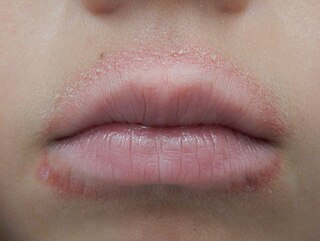
WLip licker's dermatitis, also called irritant contact cheilitis, is a type of skin inflammation around the lips due to saliva from repetitive lip licking. The resulting scaling, redness, chapping and crusting make a well-defined ring around the lips. The rash may extend as far as the tongue can reach and frequently spares the angle of the mouth.
 W
WPlasma cell gingivitis is a rare condition, appearing as generalized erythema (redness) and edema (swelling) of the attached gingiva, occasionally accompanied by cheilitis or glossitis. It is called plasma cell gingivitis where the gingiva (gums) are involved, plasma cell cheilitis, where the lips are involved, and other terms such as plasma cell orifacial mucositis, or plasma cell gingivostomatitis where several sites in the mouth are involved. On the lips, the condition appears as sharply outlined, infiltrated, dark red plaque with a lacquer-like glazing of the surface of the involved oral area.
 W
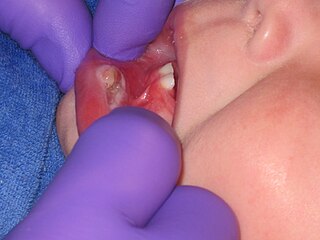
WRiga–Fede disease is a rare condition in infants characterized by ulceration on the ventral surface of the tongue or on the inner surface of the lower lip. It is caused by trauma to the soft tissue from erupted baby teeth.