 W
WBrithopus is an extinct genus of dinocephalian therapsids. It contains a single species, Brithopus priscus, known from fragmentary remains found in the Copper Sandstones near Isheevo, Russia.
 W
WKaibabvenator swiftae is a very large, extinct ctenacanthiform shark that lived in marine environments in what is now Arizona, during the Middle Permian Period. K. swiftae is known from large teeth up to 30 millimeters long found in the Kachina Microsite, of the lower Fossil Mountain Member, in the Kaibab Formation near Flagstaff, Arizona. The specific name honors researcher Sandra Swift for her paleontological contributions to Northern Arizona University.
 W
WNiaftasuchus is an extinct genus of therapsids. Only one species is recorded, Niaftasuchus zekkeli, from Nyafta, basin of the Mezen' River, Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. The family Niaftasuchidae was created by Ivankhenko in 1990, and initially attributed to the Tapinocephalia, essentially on the basis of the dentition; later it was regarded as Biarmosuchia, by share big orbits and fused vomers.
 W
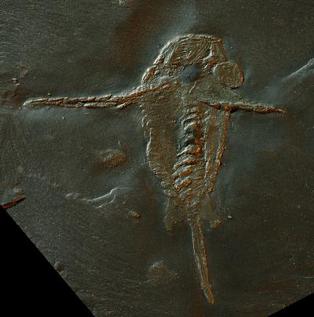
WSchinderhannes bartelsi is an anomalocarid known from one specimen from the lower Devonian Hunsrück Slates. Its discovery was astonishing because previously, anomalocaridids were known only from exceptionally well-preserved fossil beds (Lagerstätten) from the Cambrian, 100 million years earlier.
 W
WTribrachidium heraldicum is a tri-radially symmetric fossil animal that lived in the late Ediacaran (Vendian) seas. In life, it was hemispherical in form. T. heraldicum is the best known member of the extinct group Trilobozoa.
 W
WTrucidocynodon is an extinct genus of ecteniniid cynodonts from Upper Triassic of Brazil. It contains a single species, Trucidocynodon riograndensis. Fossils of Trucidocynodon were discovered in Santa Maria Formation outcrops in Paleorrota geopark Agudo. T. riograndensis was similar to Ecteninion lunensis from the Upper Triassic Ischigualasto formation of Argentina, but differed in several respects, including its larger size. It is known from a nearly complete holotype skeleton as well as a referred skull. The holotype skeleton had an estimated length of 1.2 meters, while the referred skull was 17% larger than that of the holotype. Trucidocynodon is considered one of the largest known carnivorous cynodonts from the Triassic, as well as one of the largest probainognathians in the entire Mesozoic.
 W
WYi is a genus of scansoriopterygid dinosaurs from the Late Jurassic of China. Its only species, Yi qi, is known from a single fossil specimen of an adult individual found in Middle or Late Jurassic Tiaojishan Formation of Hebei, China, approximately 159 million years ago. It was a small, possibly tree-dwelling (arboreal) animal. Like other scansoriopterygids, Yi possessed an unusual, elongated third finger, that appears to have helped to support a membranous gliding plane made of skin. The planes of Yi qi were also supported by a long, bony strut attached to the wrist. This modified wrist bone and membrane-based plane is unique among all known dinosaurs, and might have resulted in wings similar in appearance to those of bats.