 W
WHermann Martin Asmuss was a Baltic German paleozoologist and professor at the Imperial University of Dorpat.
 W
WAugust Assmann (1819-1898) was a German entomologist who specialised in fossil insects of Lepidoptera and Hemiptera.
 W
WEmil Bessels was a German zoologist, entomologist, physician, and Arctic researcher who is best known his controversial role in the attempted but ill-fated Polaris expedition to the North Pole in 1871. Circumstantial evidence strongly points to Bessels as the most likely suspect in the death of the expedition's commander, American explorer Charles Francis Hall, via arsenic poisoning.
 W
WJohann Wilhelm Theodor Ludwig von Blandowski, known as William Blandowski, was a German explorer, soldier, zoologist and mining engineer of Polish roots, he is most famous for his exploration of the Murray and Darling Rivers in Australia.
 W
WJohann Friedrich von Brandt was a German-Russian naturalist, who worked mostly in Russia.
 W
WChristian Casimir Brittinger was a German botanist, entomologist and ornithologist.
 W
WAlexander Georg von Bunge was a Russian botanist. He is best remembered for scientific expeditions into Asia and especially Siberia.
 W
WKarl Hermann Konrad Burmeister was a German Argentine zoologist, entomologist, herpetologist, and botanist. He was born in Stralsund and died in Buenos Aires. A brief biography, with particular reference to his work on phasmids was published by Bragg in 2007.
 W
WFriedrich Otto Büttner was a German entomologist who specialised in Lepidoptera. He wrote the original description of Stenoptilia pneumonanthes in Die Pommerschen, insbesondere die Stettiner Microlepidoptern. Entomologische Zeitung 41: 383-473. Stettin. (1880).Friedrich Büttner was a Member of the Stettin Entomological Society. By profession he was a teacher.
 W
WHugo Theodor Christoph was a German and Russian entomologist.
 W
WGustav Adolf Carl Closs also as Closs, A., Closs, A.G., Closz, Adolf Gustav was a German painter, illustrator and heraldist and an entomologist.
 W
WMaria Johanna Dahl, née Grosset was a Ukrainian-born German zoologist, arachnologist, and carcinologist. Along with her husband, Friedrich Dahl, she was a co-author and editor of the zoological series Die Tierwelt Deutschlands, published between 1925 and 1968.
 W
WGeorg Dieck was a German entomologist and botanist.
 W
WKoncordie Amalie Dietrich was a German naturalist who was best known for her pioneering work in Australia from 1863 to 1872, collecting specimens for the Museum Godeffroy in Hamburg.
 W
WFriedrich Karl Wilhelm Dönitz or Doenitz was a German physician, anatomist, zoologist, and entomologist. He described numerous species of insects, ticks and worked for thirteen years in Japan where he was a professor of anatomy while also serving as the first forensic physician there.
 W
WMax Wilhelm Karl Draudt was a German entomologist, who specialised in Lepidoptera.
 W
WChristian Gottfried Ehrenberg, German naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist, was one of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. Ehrenberg was an evangelist.
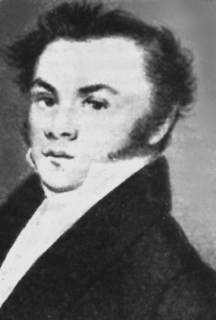 W
WKarl Eduard von Eichwald was a Baltic German geologist, physician, and naturalist, who worked in Russia.
 W
WEugenius Johann Christoph Esper was a German zoologist and naturalist. Born in Wunsiedel in Bavaria, he was professor of zoology at Erlangen university.
 W
WJohann Gotthelf Fischer von Waldheim was a German and Russian anatomist, entomologist and paleontologist.
 W
WChristian Friedrich Freyer was a German entomologist mainly interested in Lepidoptera.
 W
WHans Fruhstorfer was a German explorer, insect trader and entomologist who specialised in Lepidoptera. He collected and described new species of exotic butterflies, especially in Adalbert Seitz's Macrolepidoptera of the World. He is best known for his work on the butterflies of Java.
 W
WPaul Bernhard Gerhard was a German entomologist who specialised in Lepidoptera.
 W
WCarl Eduard Adolph Gerstaecker was a German zoologist and entomologist.
 W
WJohann Friedrich Gmelin was a German naturalist, botanist, entomologist, herpetologist, and malacologist.
 W
WJuan Cristóbal Gundlach, born Johannes Christoph Gundlach was a Cuban naturalist and taxonomist.
 W
WAlbert Karl Ludwig Gotthilf Günther FRS, also Albert Charles Lewis Gotthilf Günther, was a German-born British zoologist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist. Günther is ranked the second-most productive reptile taxonomist with more than 340 reptile species described.
 W
WFriedrich Gustav Jakob Henle was a German physician, pathologist, and anatomist. He is credited with the discovery of the loop of Henle in the kidney. His essay, "On Miasma and Contagia," was an early argument for the germ theory of disease. He was an important figure in the development of modern medicine.
 W
WJohann Friedrich Wilhelm Herbst was a German naturalist and entomologist from Petershagen, Minden-Ravensberg. He served as a chaplain in the Prussian army. His marriage in Berlin, 1770, with Euphrosyne Luise Sophie (1742–1805), daughter of the Prussian Hofrat Libert Waldschmidt seems to have been childless.
 W
WDr Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer was a German entomologist and physician. He was born, and died, in Regensburg. Herrich-Schäffer studied and collected particularly butterflies and moths (Lepidoptera). He was chairman of the Regensburg Botanical Society from 1861 to 1871, and was awarded an honorary citizenship of Regensburg in 1871.
 W
WMartin Theodor von Heuglin, was a German explorer and ornithologist.
 W
WErnst Hofmann was a German entomologist who specialised in Lepidoptera. He is not to be confused with Ottmar Hofmann also was an entomologist specialising in Lepidoptera.
 W
WJacob Hübner was a German entomologist. He was the author of Sammlung Europäischer Schmetterlinge (1796–1805), a founding work of entomology.
 W
WHeinrich Ernst Karl Jordan was a German-British entomologist.
 W
WJohann Jakob von Kaup was a German naturalist. A proponent of natural philosophy, he believed in an innate mathematical order in nature and he attempted biological classifications based on the Quinarian system. Kaup is also known for having coined popular prehistoric taxa like Pterosauria and Machairodus.
 W
WJulius von Kennel was a German zoologist and entomologist born in Schwegenheim.
 W
WTheodor Franz Wilhelm Kirsch was a German entomologist who specialised in Coleoptera.
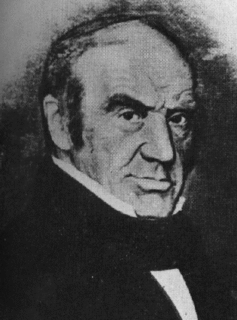 W
WCarl Ludwig Koch was a German entomologist and arachnologist. He was responsible for classifying a great number of spiders, including the Brazilian whiteknee tarantula and common house spider. He was born in Kusel, Germany, and died in Nuremberg, Germany.
 W
WKarl Matthias Friedrich Magnus Kraepelin was a German naturalist who specialised in the study of scorpions, centipedes, spiders and solfugids, and was noted for his monograph Scorpiones und Pedipalpi (Berlin) in 1899, which was an exhaustive survey of the taxonomy of the Order Scorpiones. From 1889–1914 he was Director of the Naturhistorisches Museum Hamburg, which was destroyed during World War II, and worked on myriapods from 1901–1916.
 W
WHeinrich Kuhl was a German naturalist and zoologist.
 W
WMartin Hinrich Carl Lichtenstein was a German physician, explorer, botanist and zoologist.
 W
WJohann Heinrich Friedrich Link was a German naturalist and botanist. The standard author abbreviation Link is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.
 W
WPaul Matschie was a German zoologist.
 W
WJohannes Peter Müller was a German physiologist, comparative anatomist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist, known not only for his discoveries but also for his ability to synthesize knowledge. The paramesonephric duct was named in his honor.
 W
WLorenz Oken was a German naturalist, botanist, biologist, and ornithologist. Oken was born Lorenz Okenfuss in Bohlsbach, Ortenau, Baden, and studied natural history and medicine at the universities of Freiburg and Würzburg. He went on to the University of Göttingen, where he became a Privatdozent, and shortened his name to Oken. As Lorenz Oken, he published a small work entitled Grundriss der Naturphilosophie, der Theorie der Sinne, mit der darauf gegründeten Classification der Thiere (1802). This was the first of a series of works which established him as a leader of the movement of "Naturphilosophie" in Germany.
 W
WPeter Simon Pallas FRS FRSE was a Prussian zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia (1767–1810).
 W
WJosef Anton Maximilian Perty was a German naturalist and entomologist. He was a professor of zoology and comparative anatomy at the University of Bern. His first name is sometimes spelled as "Joseph".
 W
WWilhelm Karl Hartwich Peters was a German naturalist and explorer.
 W
WEduard Friedrich Poeppig was a German botanist, zoologist and explorer.
 W
WJulius Theodor Christian Ratzeburg was a German zoologist, botanist, entomologist, and forester.
 W
WHeinrich Gottlieb Ludwig Reichenbach was a German botanist and ornithologist. It was he who first requested Leopold Blaschka to make a set of glass marine invertebrate models for scientific education and museum showcasing, the successful commission giving rise to the creation of the Blaschkas' Glass sea creatures and, subsequently and indirectly, the more famous Glass Flowers.
 W
WWilhelm Peter Eduard Simon Rüppell was a German naturalist and explorer. Rüppell is occasionally transliterated to "Rueppell" for the English alphabet.
 W
WHermann Schlegel was a German ornithologist, herpetologist and ichthyologist.
 W
WJohann Gottlob Theaenus Schneider was a German classicist and naturalist.
 W
WJohann Christian Daniel von Schreber, often styled J.C.D. von Schreber, was a German naturalist.
 W
WJohann Baptist Ritter von Spix was a German biologist. From his expedition to Brazil he brought to Germany a large variety of specimens of plants, insects, mammals, birds, amphibians and fish. They constitute an important basis for today's National Zoological Collection in Munich. Numerous examples of his ethnographic collections, such as dance masks and the like, are now part of the collection of the Museum of Ethnography in Munich.
 W
WJohann Andreas Wagner was a German palaeontologist, zoologist and archaeologist who wrote several important works on palaeontology.
 W
WPrince Alexander Philipp Maximilian zu Wied-Neuwied was a German explorer, ethnologist and naturalist. He led a pioneering expedition to southeast Brazil between 1815–1817, from which the album Reise nach Brasilien, which first revealed to Europe real images of Brazilian Indians, was the ultimate result. It was translated into several languages and recognized as one of the greatest contributions to the knowledge of Brazil at the beginning of the nineteenth century. In 1832 he embarked on another expedition, this time to United States, together with the Swiss painter Karl Bodmer.
 W
WPhilipp Christoph Zeller was a German entomologist.
 W
WKarl Alfred Ritter von Zittel was a German palaeontologist best known for his Handbuch der Palaeontologie (1876-1880).