 W
WJohn James Audubon was an American ornithologist, naturalist, and painter. His combined interests in art and ornithology turned into a plan to make a complete pictoral record of all the bird species of North America. He was notable for his extensive studies documenting all types of American birds and for his detailed illustrations that depicted the birds in their natural habitats. His major work, a color-plate book entitled The Birds of America (1827–1839), is considered one of the finest ornithological works ever completed. Audubon is also known for having identified 25 new species. He is the namesake of the National Audubon Society and his name adorns a large number of towns, neighborhoods, and streets in every part of the United States. Dozens of scientific names first published by Audubon are currently in use by the scientific community.
 W
WJohn Bachman was an American Lutheran minister, social activist and naturalist who collaborated with John James Audubon to produce Viviparous Quadrupeds of North America and whose writings, particularly Unity of the Human Race, were influential in the development of the theory of evolution. He was married to the painter Maria Martin. Several species of animals are named in his honor.
 W
WVernon Orlando Bailey (1864–1942) was an American naturalist who specialized in mammalogy. He was employed by the Bureau of Biological Survey, United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). His contributions to the Bureau of Biological Survey numbered roughly 13,000 specimens including many new species. Bailey published 244 monographs and articles during his career with the USDA, and is best known for his biological surveys of Texas, New Mexico, North Dakota, and Oregon.
 W
WSpencer Fullerton Baird was an American naturalist, ornithologist, ichthyologist, herpetologist, and museum curator. Baird was the first curator to be named at the Smithsonian Institution. He would eventually serve as assistant Secretary of the Smithsonian from 1850 to 1878, and as Secretary from 1878 until 1887. He was dedicated to expanding the natural history collections of the Smithsonian which he increased from 6,000 specimens in 1850 to over 2 million by the time of his death. He published over 1,000 works during his lifetime.
 W
WCharles Fuller Baker was an American entomologist, botanist, agronomist and plant collector. He was the second dean of the University of the Philippines College of Agriculture, now the University of the Philippines Los Baños.
 W
WRollo Howard Beck was an American ornithologist, bird collector for museums, and explorer. Beck's petrel and three taxa of reptiles are named after him, including a subspecies of Galápagos tortoise, Chelonoidis nigra becki from Volcán Wolf. A recent paper by Fellers examines all the known taxa named for Beck. Beck was recognized for his extraordinary ability as a field worker by Robert Cushman Murphy as being "in a class by himself," and by University of California at Berkeley professor of zoology Frank Pitelka as "the field worker" of his generation.
 W
WCharles Harvey Bollman (1868–1889) was an American naturalist who published on fishes and myriapods, becoming known internationally for his work in a short career before dying at the age of 20, considered by David Starr Jordan one of the most brilliant and promising naturalists he had ever known.
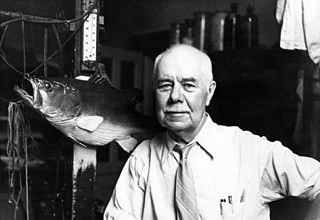 W
WHerbert Hutchinson Brimley was a self-trained zoologist and long-time director of the North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences. His brother, C.S. Brimley, was also a zoologist who worked at the same museum. Both Brimley brothers are buried at Historic Oakwood Cemetery in Raleigh.
 W
WJohn Cassin was an American ornithologist from Pennsylvania. He worked as curator and Vice President at the Philadelphia Academy of Natural Sciences and focused on the systemic classification of the Academy's extensive collection of birds. He was one of the founders of the Delaware County Institute of Science and published several books describing 194 new species of birds. Five species of North American birds are named in his honor.
 W
WCornelia Maria Clapp was an American zoologist and academic specializing in marine biology. She was born in Montague, Massachusetts, the first daughter and oldest child of two teachers, and was rated as one of the top zoologists in the United States in her lifetime.
 W
WLeila Gay Forbes Clark (1887-1964) was an entomologist and librarian at the Smithsonian Institution. She was the second woman to direct the Smithsonian's library. Prior to her work at the Smithsonian, she worked as a librarian at Wellesley College, Randolph-Macon Woman's College, and the US Department of Agriculture. She joined the Smithsonian in 1929 and spent the rest of her career there becoming director in 1942. During her tenure she oversaw the merger of the main Smithsonian Library with the U.S. National Museum Library which resulted in the centralized Smithsonian Libraries system currently in place.
 W
WJames Brackenridge Clemens was an American entomologist who specialized in Lepidoptera. He described many new species. His collection of microlepidoptera is in the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia.
 W
WJames Graham Cooper was an American surgeon and naturalist.
 W
WEdward Drinker Cope was an American paleontologist and comparative anatomist, as well as a noted herpetologist and ichthyologist. He was a founder of the Neo-Lamarckism school of thought. Born to a wealthy Quaker family, Cope distinguished himself as a child prodigy interested in science; he published his first scientific paper at the age of 19. Though his father tried to raise Cope as a gentleman farmer, he eventually acquiesced to his son's scientific aspirations. Cope married his cousin and had one child; the family moved from Philadelphia to Haddonfield, New Jersey, although Cope would maintain a residence and museum in Philadelphia in his later years.
 W
WElliott Ladd Coues was an American army surgeon, historian, ornithologist, and author.
 W
WJames Dwight Dana FRS FRSE was an American geologist, mineralogist, volcanologist, and zoologist. He made pioneering studies of mountain-building, volcanic activity, and the origin and structure of continents and oceans around the world.
 W
WHarrison Gray Dyar Jr. was an American entomologist.
 W
WWilliam Henry Edwards was an American businessman and entomologist. He was an industrial pioneer in the coalfields of West Virginia, opening some of the earliest mines in the southern part of the state. He was also a prominent naturalist specializing in the study of butterflies. He wrote The Butterflies of North America, a three-volume treatise that is highly regarded for its scholarship and the quality of its illustrations.
 W
WRosa Smith Eigenmann was an American ichthyologist, as well as a writer, editor, former curator at the California Academy of Sciences, and the first librarian of the San Diego Society of Natural History. She "is considered the first woman ichthyologist in the United States." Eigenmann was also the first woman to become president of Indiana University's chapter of Sigma Xi, an honorary science society. She authored twelve published papers of her own between 1880 and 1893, and collaborated with her husband, Carl H. Eigenmann, as "Eigenmann & Eigenmann" on twenty-five additional works between 1888 and 1893. Together, they are credited with describing about 150 species of fishes.
 W
WWalter Faxon was an American ornithologist and carcinologist. He was born at Jamaica Plain, Massachusetts, where he grew up. He received three degrees from Harvard University. One of his greater ornithological achievements was demonstration that Brewster's warbler is a hybrid.
 W
WCharles Henry Fernald was an American entomologist, geologist, and zoologist, who is credited as the first college professor of economic entomology. Fernald grew up at Fernald Point in Mount Desert, Maine, and went on to prepare for college at Maine Wesleyan Seminary before joining the navy in 1862. After receiving a master's degree from Bowdoin College he went on to serve as principal of several academies in Maine. Throughout his career he would document and describe several species of microlepidoptera and in 1886 became the first full-time professor and chair of the natural sciences at what is now the University of Massachusetts Amherst. Fernald Hall and the Fernald Entomological Society at the same institution, are named for him and his son, Henry Torsey Fernald, who would later hold the same position as his father. His wife, Maria Elizabeth Fernald, was a noted entomologist in her own right.
 W
WAlbert Kenrick Fisher was an American ornithologist, known for his 1893 book The Hawks and Owls of the United States in Their Relation to Agriculture.
 W
WSamuel Walton Garman, or "Garmann" as he sometimes styled himself, was a naturalist/zoologist from Pennsylvania. He became noted as an ichthyologist and herpetologist.
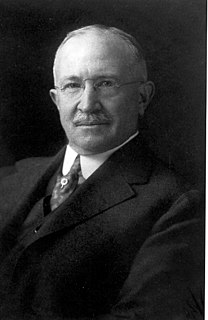 W
WCharles Henry Gilbert was a pioneer ichthyologist and fishery biologist of particular significance to natural history of the western United States. He collected and studied fishes from Central America north to Alaska and described many new species. Later he became an expert on Pacific salmon and was a noted conservationist of the Pacific Northwest. He is considered by many as the intellectual founder of American fisheries biology. He was one of the 22 "pioneer professors" of Stanford University.
 W
WCharles Frédéric Girard was a French biologist specializing in ichthyology and herpetology.
 W
WRichard Harlan was an American naturalist, zoologist, herpetologist, physicist, and paleontologist. He was the author of Fauna Americana, published in 1825, and American Herpetology.
 W
WEdmund Heller was an American zoologist. He was President of the Association of Zoos & Aquariums for two terms, from 1935-1936 and 1937-1938.
 W
WLewis Ezra Hicks was an American geologist and zoologist.
 W
WJohn Edwards Holbrook was an American zoologist, herpetologist, physician, and naturalist, born in Beaufort, South Carolina, the son of Silas Holbrook, a teacher, and Mary Edwards. Although Holbrook's memoir, written by his medical partner, and his tombstone both give the date 1794 for his birth, this is incorrect. Holbrook received his A.B. degree from Brown University in 1815, and his M.D. from the University of Pennsylvania in 1818. In 1827, he married Harriott Pinckney Rutledge (1802–1863), granddaughter of John Rutledge and a member of the Middleton-Rutledge-Pinckney family.
 W
WJoseph Bassett Holder (1824–1888) was an American zoologist and physician.
 W
WRev William Jacob Holland FRSE LLD was the eighth Chancellor of the University of Pittsburgh (1891–1901) and Director of the Carnegie Museums of Pittsburgh. He was an accomplished zoologist and paleontologist, as well as an ordained Presbyterian minister.
 W
WDavid Starr Jordan was the founding president of Stanford University. He was an ichthyologist during his research tenure. Prior to Stanford, he was president of Indiana University. He was also a eugenicist whose published views expressed a fear of "race-degeneration" and asserted that cattle and human beings are "governed by the same laws of selection." Starr was also an antimilitarist who initially opposed U.S. involvement in World War I.
 W
WErnest Everett Just was a pioneering African-American biologist, academic and science writer. Just's primary legacy is his recognition of the fundamental role of the cell surface in the development of organisms. In his work within marine biology, cytology and parthenogenesis, he advocated the study of whole cells under normal conditions, rather than simply breaking them apart in a laboratory setting.
 W
WJohn Krider was an American gunsmith and ornithologist who operated a sporting goods store on the northeast corner of Second St. and Walnut St. in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, for much of the 19th century. On the second floor of Krider's shop was a taxidermy shop, where hundreds of bird specimens were prepared over multiple decades.
 W
WEdward Laurens Mark was an American zoologist, Hersey Professor of Anatomy and Director of the Zoological Laboratory of the Museum of Comparative Zoology (MCZ) at Harvard University. In his landmark cytological monograph published in 1881, Mark also conceived the parenthetical referencing for citation, also known as Harvard referencing.
 W
WOthniel Charles Marsh was professor of Paleontology in Yale College and President of the National Academy of Sciences. He was one of the preeminent scientists in the field of paleontology. Among his legacies are the discovery or description of dozens of new species and theories on the origins of birds.
 W
WTheodore Luqueer Mead was an American naturalist, entomologist and horticulturist. As an entomologist he discovered more than 20 new species of North American butterflies and introduced the Florissant Fossil Beds in Colorado to the wider scientific world. As a horticulturist, he is best known for his pioneering work on the growing and cross-breeding of orchids, and the creation of new forms of caladium, bromeliad, crinum, amaryllis and hemerocallis (daylily). In addition he introduced many new semi-tropical plants, particularly palm varieties, into North America. Recently a comprehensive historical biography of his life and times has been published.
 W
WEdgar Alexander Mearns was a notable American ornithologist and field naturalist.
 W
WClinton Hart Merriam was an American zoologist, mammalogist, ornithologist, entomologist, ecologist, ethnographer, geographer, and naturalist.
 W
WManly Miles was an American zoologist and agriculturalist.
 W
WThomas Harrison Montgomery Jr. was an American zoologist who made important contributions to cell biology–especially in chromosomes and their roles in sex determination–as well as the biology of birds and several groups invertebrates, naming many species of ribbon worms, rotifers, and spiders. He studied in Berlin before becoming a researcher and professor at the University of Pennsylvania, where he primarily worked until his death at the age of 39. In his short career he published 80 scientific papers and two books.
 W
WJohn Howard Moore was an American zoologist, philosopher, educator and socialist. He advocated for the ethical consideration and treatment of animals and authored several articles, books, essays and pamphlets on ethics, vegetarianism, humanitarianism and education. He is best known for his work The Universal Kinship (1906), which advocated for a secular sentiocentric philosophy he called the doctrine of "Universal Kinship", based on the shared evolutionary kinship between all sentient beings.
 W
WIda Shepard Oldroyd (1856–1940) was an American conchologist and Curator of Geology at Stanford University for over 20 years, who curated what was for a time the second largest collection of mollusk shells in the world. Oldroyd and her husband, Tom Shaw Oldroyd, amassed one of the largest private shell collections in California. Ida was recognized as an active and early pioneer of conchology in the western United States. She was a charter member of the American Malacological Union, which she served as vice-president in 1934 and as honorary president from 1935 to 1940.
 W
WSophonisba Angusciola (Peale) Sellers, known by the nickname "Sopy", was an early American ornithologist and artist. She was also a noted quilt-maker and a surviving example of her work is preserved in the Philadelphia Museum of Art. She is recognized as the first woman in America to collect and prepare bird specimens for scientific study.
 W
WConstantine Samuel Rafinesque-Schmaltz was a French 19th-century polymath born near Constantinople in the Ottoman Empire and self-educated in France. He traveled as a young man in the United States, ultimately settling in Ohio in 1815, where he made notable contributions to botany, zoology, and the study of prehistoric earthworks in North America. He also contributed to the study of ancient Mesoamerican linguistics, in addition to work he had already completed in Europe.
 W
WMary Jane Rathbun was an American zoologist who specialized in crustaceans. She worked at the Smithsonian Institution, often unaided, from 1884 until her death. She described more than a thousand new species and subspecies and many higher taxa.
 W
WRichard Rathbun was an American biologist and administrator at the Smithsonian Institution.
 W
WElmer Samuel Riggs was an American paleontologist known for his work with the Field Museum of Natural History in Chicago, Illinois.
 W
WJohn Adam Ryder, was an American zoologist and embryologist. He worked for the United States Fish Commission from 1880 to 1886 and Professor of Comparative Embryology at the University of Pennsylvania from 1886 to 1895.
 W
WThomas Say was an American entomologist, conchologist, and herpetologist. His definitive studies of insects and shells, numerous contributions to scientific journals, and scientific expeditions to Florida, Georgia, the Rocky Mountains, Mexico, and elsewhere made him an internationally known naturalist. Say has been called the father of American descriptive entomology and American conchology. He served as librarian for the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, curator at the American Philosophical Society, and professor of natural history at the University of Pennsylvania.
 W
WJennie Maria Arms Sheldon was an American entomologist, educator, historian, author, and museum curator. She worked closely with zoologist Alpheus Hyatt at the Boston Society of Natural History, and she was the curator of the Memorial Hall Museum in Deerfield, Massachusetts, for a quarter of a century.
 W
WAlthea Rosina Sherman was born in Farmersburg Township, Clayton County, Iowa. She was an illustrator, educator, self-taught ornithologist and writer who commissioned the building of the Chimney Swifts' Tower which allowed her to be the first to study and demonstrate the life cycle of chimney swifts. Her career in ornithology also lead to her publishing more than 70 articles in scientific and ornithological journals and lead to her election as a member of the American Ornithologists' Union and inclusion in the Who's Who of Women in Science. Additionally, her work as an illustrator, particularly of the American goldfinch, inspired the Iowa Legislature to adopt the American goldfinch as the State bird.
 W
WLeonhard Hess Stejneger was a Norwegian-born American ornithologist, herpetologist and zoologist. Stejneger specialized in vertebrate natural history studies. He gained his greatest reputation with reptiles and amphibians.
 W
WCharles Wardell Stiles was an American parasitologist born in Spring Valley, New York. He was notable for working on a campaign against hookworm infestation in the American South, where it had been found to cause high rates of anemia, a debilitating disease.
 W
WWilliam Stimpson was a noted American scientist. He was interested particularly in marine biology. Stimpson became an important early contributor to the work of the Smithsonian Institution and later, director of the Chicago Academy of Sciences.
 W
WCharles Henry Turner was an American zoologist, educator, and comparative psychologist, known for his studies on the behavior of insects, particularly bees and ants. Born in Cincinnati, Ohio, Turner was the first African American to receive a graduate degree at the University of Cincinnati and most likely the first African American to earn a PhD from the University of Chicago. He spent most of his career as a high school teacher in Sumner High School in St. Louis.
 W
WEdward Payson Van Duzee was an American entomologist noted for his work on Hemiptera. As of 1885, he was a librarian at Grosvenor Library of Buffalo New York for 28 years, and then relocated to California in 1912 where he took a position at Scripps Institute in La Jolla. The same year, Van Duzee became a fellow at the Entomological Society of America. Due to his fellowship, Van Duzee was appointed as an instructor of entomology at the University of California, Berkeley, from 1914–16, after which he was served as curator of the entomology collection at the California Academy of Sciences from 1916 to 1940. At the time of his death, he had approximately 165 publications in addition to his noted Catalogue of the Hemiptera where he established 46 new genera and 906 species or subspecies.
 W
WCharles Otis Whitman was an American zoologist, who was influential to the founding of classical ethology. A dedicated educator who preferred to teach a few research students at a time, he made major contributions in the areas of evolution and embryology of worms, comparative anatomy, heredity, and animal behaviour. He was known as the "Father of Zoology" in Japan.