 W
WThe cerebrum or telencephalon is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex, as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric left and right cerebral hemispheres.
 W
WThe anterior commissure is a white matter tract connecting the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres across the midline, and placed in front of the columns of the fornix. The great majority of fibers connecting the two hemispheres travel through the corpus callosum, which is over 10 times larger than the anterior commissure, and other routes of communication pass through the hippocampal commissure or, indirectly, via subcortical connections. Nevertheless, the anterior commissure is a significant pathway that can be clearly distinguished in the brains of all mammals.
 W
WThe archicortex, or archipallium, is the phylogenetically oldest region of the brain's cerebral cortex. It is often considered contiguous with the olfactory cortex, but its extent varies among species. In older species, such as fish, the archipallium makes up most of the cerebrum. Amphibians develop an archipallium and paleopallium.
 W
WBroca's area, or the Broca area, is a region in the frontal lobe of the dominant hemisphere, usually the left, of the brain with functions linked to speech production.
 W
WA Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells.
 W
WCerebral edema is excess accumulation of fluid (edema) in the intracellular or extracellular spaces of the brain. This typically causes impaired nerve function, increased pressure within the skull, and can eventually lead to direct compression of brain tissue and blood vessels. Symptoms vary based on the location and extent of edema and generally include headaches, nausea, vomiting, seizures, drowsiness, visual disturbances, dizziness, and in severe cases, coma and death.
 W
WThe vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter, the cerebral cortex, that is supported by an inner layer of white matter. In eutherian (placental) mammals, the hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum, a very large bundle of nerve fibers. Smaller commissures, including the anterior commissure, the posterior commissure and the fornix, also join the hemispheres and these are also present in other vertebrates. These commissures transfer information between the two hemispheres to coordinate localized functions.
 W
WThe cerebral peduncles are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem. They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the front of the pons and contain the large ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) nerve tracts that run to and from the cerebrum from the pons. Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the cerebral cortex, the spinal cord and the cerebellum. The cerebral peduncle, by most classifications, is everything in the midbrain except the tectum. The region includes the tegmentum, crus cerebri and pretectum. By this definition, the cerebral peduncles are also known as the basis pedunculi, while the large ventral bundle of efferent fibers is referred to as the cerebral crus or the pes pedunculi.
 W
WIn neuroanatomy, the cingulum is a nerve tract – a collection of axons – projecting from the cingulate gyrus to the entorhinal cortex in the brain, allowing for communication between components of the limbic system. It forms the white matter core of the cingulate gyrus, following it from the subcallosal gyrus of the frontal lobe beneath the rostrum of corpus callosum to the parahippocampal gyrus and uncus of the temporal lobe.
 W
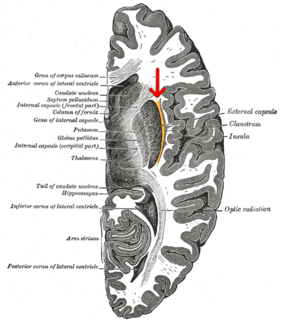
WThe claustrum is a thin, bilateral structure, a collection of neurons and supporting glial cells, that connects to cortical and subcortical regions of the brain. It is located between the insula laterally and the putamen medially, separated by the extreme and external capsules respectively. The blood supply to the claustrum is fulfilled via the middle cerebral artery. It is considered to be the most densely connected structure in the brain, allowing for integration of various cortical inputs into one experience rather than singular events. The claustrum is difficult to study given the limited number of individuals with claustral lesions and the poor resolution of neuroimaging.
 W
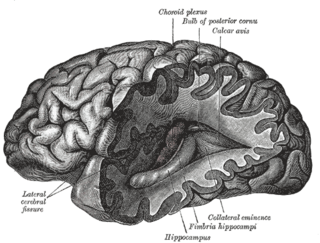
WThe collateral eminence is an elongated swelling lying lateral to and parallel with the hippocampus. It corresponds with the medial part of the collateral fissure, and its size depends on the depth and direction of this fissure. It is continuous behind with a flattened triangular area, the trigone of the lateral ventricle, situated between the posterior and inferior cornua. It is not always present.
 W
WThe collateral fissure is on the tentorial surface of the hemisphere and extends from near the occipital pole to within a short distance of the temporal pole.
 W
WThe colour centre is a region in the brain primarily responsible for visual perception and cortical processing of colour signals received by the eye, which ultimately results in colour vision. The colour centre in humans is thought to be located in the ventral occipital lobe as part of the visual system, in addition to other areas responsible for recognizing and processing specific visual stimuli, such as faces, words, and objects. Many functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies in both humans and macaque monkeys have shown colour stimuli to activate multiple areas in the brain, including the fusiform gyrus and the lingual gyrus. These areas, as well as others identified as having a role in colour vision processing, are collectively labelled visual area 4 (V4). The exact mechanisms, location, and function of V4 are still being investigated.
 W
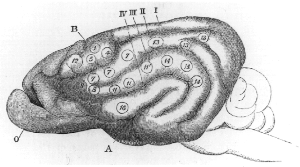
WA cortical homunculus is a distorted representation of the human body, based on a neurological "map" of the areas and proportions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor functions, or sensory functions, for different parts of the body. The word homunculus is Latin for "little man", and was a term used in alchemy and folklore long before scientific literature began using it. A cortical homunculus, or "cortex man", illustrates the concept of a representation of the body lying within the brain. Nerve fibres—conducting somatosensory information from all over the body—terminate in various areas of the parietal lobe in the cerebral cortex, forming a representational map of the body.
 W
WCortical remapping, also referred to as cortical reorganization, is the process by which an existing cortical map is affected by a stimulus resulting in the creating of a 'new' cortical map. Every part of the body is connected to a corresponding area in the brain which creates a cortical map. When something happens to disrupt the cortical maps such as an amputation or a change in neuronal characteristics, the map is no longer relevant. The part of the brain that is in charge of the amputated limb or neuronal change will be dominated by adjacent cortical regions that are still receiving input, thus creating a remapped area. Remapping can occur in the sensory or motor system. The mechanism for each system may be quite different. Cortical remapping in the somatosensory system happens when there has been a decrease in sensory input to the brain due to deafferentation or amputation, as well as a sensory input increase to an area of the brain. Motor system remapping receives more limited feedback that can be difficult to interpret.
 W
WThe external capsule is a series of white matter fiber tracts in the brain. These fibers run between the most lateral segment of the lentiform nucleus and the claustrum.
 W
WThe extreme capsule is a series of nerve tracts between the claustrum and the insular cortex. It is also described as a thin capsule of white matter as association fibres. The extreme capsule is separated from the external capsule by the claustrum, and the extreme capsule separates the claustrum from the insular cortex, and all these lie lateral to the corpus striatum components.
 W
WIn the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three primary brain vesicles during the early development of the nervous system. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions.
 W
WThe fornix is a C-shaped bundle of nerve fibers in the brain that acts as the major output tract of the hippocampus. The fornix also carries some afferent fibers to the hippocampus from structures in the diencephalon and basal forebrain. The fornix is part of the limbic system. While its exact function and importance in the physiology of the brain are still not entirely clear, it has been demonstrated in humans that surgical transection – the cutting of the fornix along its body – can cause memory loss. There is some debate over what type of memory is affected by this damage, but it has been found to most closely correlate with recall memory rather than recognition memory. This means that damage to the fornix can cause difficulty in recalling long-term information such as details of past events, but it has little effect on the ability to recognize objects or familiar situations.
 W
WThe frenulum veli, or frenulum of superior medullary velum, also known as the frenulum veli medullaris superioris, cerebellar frenulum, or frenulum cerebelli is a slightly raised white band passing from the inferior end of the medial longitudinal fissure, through the groove between the quadrigeminal bodies, and down to the superior medullary velum.
 W
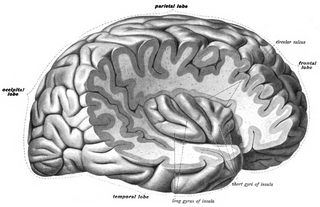
WThe frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each hemisphere. It is separated from the parietal lobe by a groove between tissues called the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by a deeper groove called the lateral sulcus. The most anterior rounded part of the frontal lobe is known as the frontal pole, one of the three poles of the cerebrum.
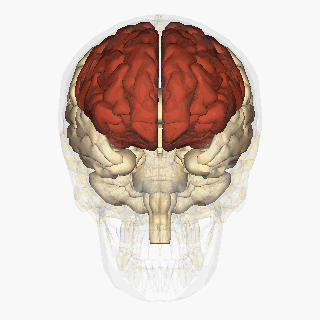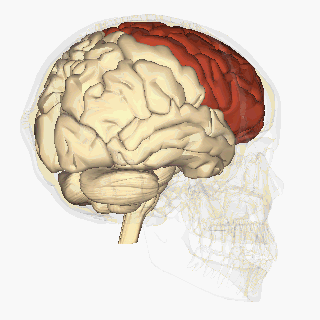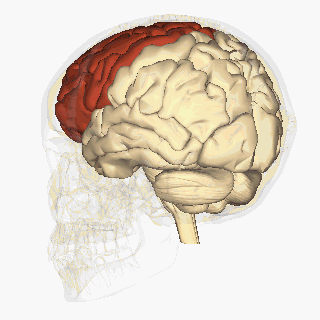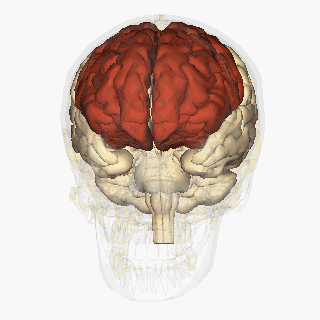 W
WFronto-cerebellar dissociation is the disconnection and independent function of frontal and cerebellar regions of the brain. It is characterized by inhibited communication between the two regions, and is notably observed in cases of ADHD, schizophrenia, alcohol abuse, and heroin abuse. The frontal and cerebellar regions make distinctive contributions to cognitive performance, with the left-frontal activations being responsible for selecting a response to a stimulus, while the right-cerebellar activation is responsible for the search for a given response to a stimulus. Left-frontal activation increases when there are many appropriate responses to a stimulus, and right-cerebellar activation increases when there is a single appropriate response to a stimulus. A person with dissociated frontal and cerebellar regions may have difficulties with selecting a response to a stimuli, or difficulties with response initiation. Fronto-cerebellar dissociation can often result in either the frontal lobe or the cerebellum becoming more active in place of the less active region as a compensatory effect.
 W
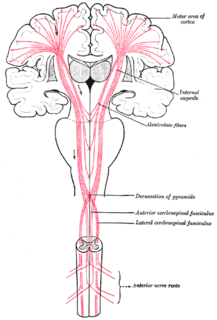
WThe geniculate fibers are the fibers in the region of the genu of the internal capsule; they originate in the motor part of the cerebral cortex, and, after passing downward through the base of the cerebral peduncle with the cerebrospinal fibers, undergo decussation and end in the motor nuclei of the cranial nerves of the opposite side.
 W
WIn neuroanatomy, a gyrus is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci. Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals.
 W
WA hypercomplex cell is a type of visual processing neuron in the mammalian cerebral cortex. Initially discovered by David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel in 1965, hypercomplex cells are defined by the property of end-stopping, which is a decrease in firing strength with increasingly larger stimuli. The sensitivity to stimulus length is accompanied by selectivity for the specific orientation, motion, and direction of stimuli. For example, a hypercomplex cell may only respond to a line at 45˚ that travels upward. Elongating the line would result in a proportionately weaker response. Ultimately, hypercomplex cells can provide a means for the brain to visually perceive corners and curves in the environment by identifying the ends of a given stimulus.
 W
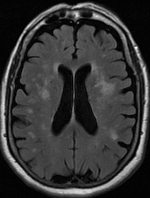
WLeukoaraiosis is a particular abnormal change in appearance of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It is often seen in aged individuals, but sometimes in young adults. On MRI, leukoaraiosis changes appear as white matter hyperintensities (WMHs). On CT scans, leukoaraiosis appears as hypodense periventricular white-matter lesions.
 W
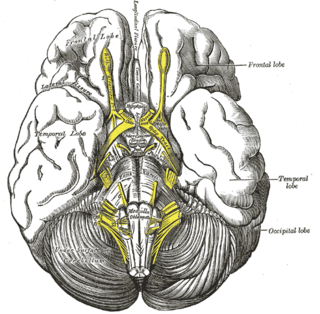
WThe interpeduncular fossa is a somewhat rhomboid-shaped area of the base of the brain, limited in front by the optic chiasma, behind by the antero-superior surface of the pons, antero-laterally by the converging optic tracts, and postero-laterally by the diverging cerebral peduncles.
 W
WThe spinothalamic tract is a sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.
 W
WThe lateralization of brain function is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. The medial longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. Although the macrostructure of the two hemispheres appears to be almost identical, different composition of neuronal networks allows for specialized function that is different in each hemisphere.
 W
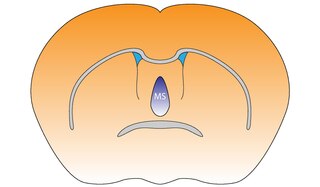
WThe medial septal nucleus (MS) is one of the septal nuclei. Neurons in this nucleus give rise to the bulk of efferents from the septal nuclei. A major projection from the medial septal nucleus terminates in the hippocampal formation.
 W
WThe longitudinal fissure is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continuation of the dura mater called the falx cerebri. The inner surfaces of the two hemispheres are convoluted by gyri and sulci just as is the outer surface of the brain.
 W
WThe occipital gyri (OcG) are three gyri in parallel, along the lateral portion of the occipital lobe, also referred to as a composite structure in the brain. The gyri are the superior occipital gyrus, the middle occipital gyrus, and the inferior occipital gyrus, and these are also known as the occipital face area. The superior and inferior occipital sulci separates the three occipital gyri.
 W
WThe occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1. Human V1 is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the occipital pole. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the Stria of Gennari. Visually driven regions outside V1 are called extrastriate cortex. There are many extrastriate regions, and these are specialized for different visual tasks, such as visuospatial processing, color differentiation, and motion perception. The name derives from the overlying occipital bone, which is named from the Latin ob, behind, and caput, the head. Bilateral lesions of the occipital lobe can lead to cortical blindness.
 W
WThe olfactory bulb is a neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) and the hippocampus where it plays a role in emotion, memory and learning. The bulb is divided into two distinct structures: the main olfactory bulb and the accessory olfactory bulb. The main olfactory bulb connects to the amygdala via the piriform cortex of the primary olfactory cortex and directly projects from the main olfactory bulb to specific amygdala areas. The accessory olfactory bulb resides on the dorsal-posterior region of the main olfactory bulb and forms a parallel pathway. Destruction of the olfactory bulb results in ipsilateral anosmia, while irritative lesions of the uncus can result in olfactory and gustatory hallucinations.
 W
WIn human brain anatomy, an operculum, may refer to the frontal, temporal, or parietal operculum, which together cover the insula as the opercula of insula. It can also refer to the occipital operculum, part of the occipital lobe.
 W
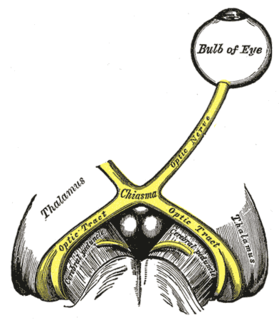
WThe optic chiasm, or optic chiasma, is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, although in cyclostomes, it is located within the brain.
 W
WThe optic tract is a part of the visual system in the brain. It is a continuation of the optic nerve that relays information from the optic chiasm to the ipsilateral lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus.
 W
WThe inferior or orbital surface of the frontal lobe is concave, and rests on the orbital plate of the frontal bone. It is divided into four orbital gyri by a well-marked H-shaped orbital sulcus. These are named, from their position, the medial, anterior, lateral, and posterior, orbital gyri. The medial orbital gyrus presents a well-marked antero-posterior sulcus, the olfactory sulcus, for the olfactory tract; the portion medial to this is named the straight gyrus, and is continuous with the superior frontal gyrus on the medial surface.
 W
WPacchionian foramen means:incisurae tentorii a thick opening in the center of the diaphragm of sella through which the infundibulum passes
 W
WIn anatomy of animals, the paleocortex, or paleopallium, is a region within the telencephalon in the vertebrate brain. This type of cortical tissue consists of three cortical laminae. In comparison, the neocortex has six layers and the archicortex has three or four layers. Because the number of laminae that compose a type of cortical tissue seems to be directly proportional to both the information-processing capabilities of that tissue and its phylogenetic age, paleocortex is thought to be an intermediate between the archicortex and the neocortex in both aspects.
 W
WIn neuroanatomy, pallium refers to the layers of grey and white matter that cover the upper surface of the cerebrum in vertebrates. The non-pallial part of the telencephalon builds the subpallium. In basal vertebrates the pallium is a relatively simple three-layered structure, encompassing 3–4 histogenetically distinct domains, plus the olfactory bulb.
 W
WThe paracentral sulcus is a sulcus of the brain. It forms the paracentral lobule's anterior border. It is part of the cingulate sulcus.
 W
WThe parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
 W
WThe postcentral sulcus of the parietal lobe lies parallel to, and behind, the central sulcus in the human brain.
 W
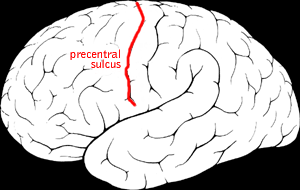
WThe precentral sulcus is a part of the human brain that lies parallel to, and in front of, the central sulcus.
 W
WAbout 5 centimetres (2.0 in) in front of the occipital pole of the human brain, on the infero-lateral border is an indentation or notch, named the preoccipital notch. It is considered a landmark because the occipital lobe is located just behind the line that connects that notch with the parietoccipital sulcus.
 W
WThe septal area is an area in the lower, posterior part of the medial surface of the frontal lobe, and refers to the nearby septum pellucidum.
 W
WThe septum pellucidum is a thin, triangular, vertical double membrane separating the anterior horns of the left and right lateral ventricles of the brain. It runs as a sheet from the corpus callosum down to the fornix.
 W
WThe insular cortex is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus within each hemisphere of the mammalian brain.
 W
WThe stria terminalis is a structure in the brain consisting of a band of fibers running along the lateral margin of the ventricular surface of the thalamus. Serving as a major output pathway of the amygdala, the stria terminalis runs from its centromedial division to the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus.
 W
WThe striatum, or corpus striatum, is a nucleus in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia.
 W
WThe subcallosal area is a small triangular field on the medial surface of the hemisphere in front of the subcallosal gyrus, from which it is separated by the posterior parolfactory sulcus; it is continuous below with the olfactory trigone, and above and in front with the cingulate gyrus; it is limited anteriorly by the anterior parolfactory sulcus.
 W
WThe temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
 W
WUlegyria is a diagnosis used to describe a specific type of cortical scarring in the deep regions of the sulcus that leads to distortion of the gyri. Ulegyria is identified by its characteristic "mushroom-shaped" gyri, in which scarring causes shrinkage and atrophy in the deep sulcal regions while the surface gyri are spared. This condition is most often caused by hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in the perinatal period. The effects of ulegyria can range in severity, although it is most commonly associated with cerebral palsy, mental retardation and epilepsy. N.C. Bresler was the first to view ulegyria in 1899 and described this abnormal morphology in the brain as “mushroom-gyri." Although ulegyria was first identified in 1899, there is still limited information known or reported about the condition.