 W
WAcetryptine (INN), also known as 5-acetyltryptamine (5-AT), is a drug described as an antihypertensive agent which was never marketed. Structurally, acetryptine is a substituted tryptamine, and is closely related to other substituted tryptamines like serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine). It was developed in the early 1960s. The binding of acetryptine to serotonin receptors does not seem to have been well-investigated, although it was assessed at the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptors and found to bind to them with high affinity. The drug may also act as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI); specifically, as an inhibitor of MAO-A.
 W
WAn adrenergic antagonist is a drug that inhibits the function of adrenergic receptors. There are five adrenergic receptors, which are divided into two groups. The first group of receptors are the beta (β) adrenergic receptors. There are β1, β2, and β3 receptors. The second group contains the alpha (α) adrenoreceptors. There are only α1 and α2 receptors. Adrenergic receptors are located near the heart, kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. There are also α-adreno receptors that are located on vascular smooth muscle.
 W
WAlfurolol is a beta blocker.
 W
WAjmalicine, also known as δ-yohimbine or raubasine, is an antihypertensive drug used in the treatment of high blood pressure. It has been marketed under numerous brand names including Card-Lamuran, Circolene, Cristanyl, Duxil, Duxor, Hydroxysarpon, Iskedyl, Isosarpan, Isquebral, Lamuran, Melanex, Raunatin, Saltucin Co, Salvalion, and Sarpan. It is an alkaloid found naturally in various plants such as Rauvolfia spp., Catharanthus roseus, and Mitragyna speciosa.
 W
WAlprenoxime is a beta blocker. It is a prodrug to alprenolol.
 W
WAncarolol is a beta blocker.
 W
WArnolol is a beta blocker.
 W
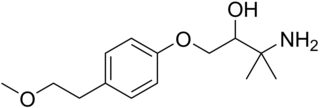
WAtiprosin (AY-28,228) is an antihypertensive agent which acts as a selective α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist. It also possesses some antihistamine activity, though it is some 15-fold weaker in this regard than as an alpha blocker. It was never marketed.
 W
WBietaserpine (INN), or 1-diaminoethylreserpine, is a derivative of reserpine used as an antihypertensive agent. Like reserpine, bietaserpine is a VMAT inhibitor.
 W
WBucindolol is a non-selective beta blocker with additional weak alpha-blocking properties and some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. It was under review by the FDA in the United States for the treatment of heart failure in 2009, but was rejected due to issues pertaining to integrity of data submitted.
 W
WButynamine is a tertiary aliphatic amine which has antihypertensive effects.
 W
WCiclafrine (INN) is a sympathomimetic phenethylamine and antihypertensive that was never marketed.
 W
WClonidine, sold as the brand name Catapres among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, drug withdrawal, menopausal flushing, diarrhea, spasticity and certain pain conditions. It is used by mouth, by injection, or as a skin patch. Onset of action is typically within an hour with the effects on blood pressure lasting for up to eight hours.
 W
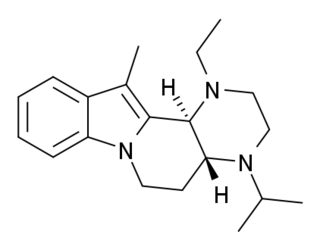
WCorynanthine, also known as rauhimbine, is an alkaloid found in the Rauvolfia and Pausinystalia genera of plants. It is one of the two diastereoisomers of yohimbine, the other being rauwolscine. It is also related to ajmalicine.
 W
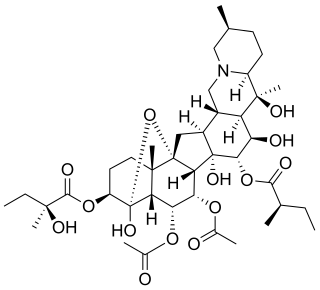
WCryptenamine (Unitensen) is a mixture of 10 hypotensive alkaloids extracted from Veratrum album. It is used in the treatment of hypertension.
 W
WDebrisoquine is a derivative of guanidine. It is an antihypertensive drug similar to guanethidine. Debrisoquine is frequently used for phenotyping the CYP2D6 enzyme, a drug-metabolizing enzyme.
 W
WDeserpidine (INN) is an antihypertensive drug related to reserpine which occurs naturally in Rauvolfia spp.
 W
WDihydralazine is a drug with antihypertensive properties. It belongs to the hydrazinophthalazine chemical class. It has very similar effects to hydralazine.
 W
WEndralazine is an antihypertensive of the hydrazinophthalazine chemical class. It is not approved for use in the United States.
 W
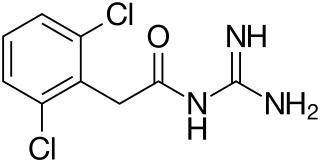
WGuanadrel is an antihypertensive agent. It is used in the form of its sulfate.
 W
WGuanfacine, sold under the brand name Tenex among others, is a medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and high blood pressure. It is a less preferred treatment for ADHD and for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth.
 W
WGuanoclor (INN), also known as guanochlor, is a sympatholytic drug. It is known to bind to non-adrenergic sites in pig kidney membranes.
 W
WHydracarbazine is a pyridazine that has found use as an antihypertensive agent.
 W
WHydralazine, sold under the brand name Apresoline among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. This includes high blood pressure in pregnancy and very high blood pressure resulting in symptoms. It has been found to be particularly useful in heart failure, together with isosorbide dinitrate, for treatment of people of African descent. It is given by mouth or by injection into a vein. Effects usually begin around 15 minutes and last up to six hours.
 W
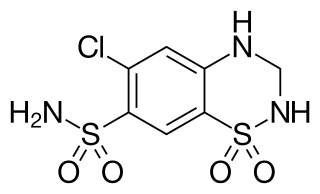
WHydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic medication often used to treat high blood pressure and swelling due to fluid build up. Other uses include treating diabetes insipidus and renal tubular acidosis and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with a high calcium level in the urine. For high blood pressure it is sometimes considered as a first-line treatment. HCTZ is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase effectiveness.
 W
WKetanserin (INN, USAN, BAN) (brand name Sufrexal; former developmental code name R41468) is a drug used clinically as an antihypertensive agent and in scientific research to study the serotonin system; specifically, the 5-HT2 receptor family. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1980.
 W
WLidanserin is a drug which acts as a combined 5-HT2A and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist. It was developed as an antihypertensive agent but was never marketed.
 W
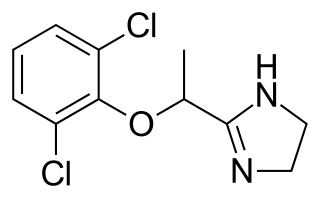
WLofexidine, sold under the brand name Lucemyra among others, is a medication historically used to treat high blood pressure, but more commonly used to help with the physical symptoms of opioid withdrawal. It is taken by mouth. It is an α2A adrenergic receptor agonist. It was approved for use by the Food and Drug Administration in the United States in 2018.
 W
WMethoserpidine is an antihypertensive drug related to reserpine.
 W
WMethyldopa, sold under the brand name Aldomet among others, is a medication used for high blood pressure. It is one of the preferred treatments for high blood pressure in pregnancy. For other types of high blood pressure including very high blood pressure resulting in symptoms other medications are typically preferred. It can be given by mouth or injection into a vein. Onset of effects is around 5 hours and they last about a day.
 W
WMetirosine is an antihypertensive drug. It inhibits the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase and, therefore, catecholamine synthesis, which, as a consequence, depletes the levels of the catecholamines dopamine, adrenaline and noradrenaline in the body.
 W
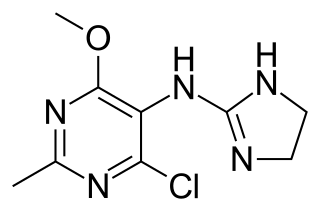
WMoxonidine (INN) is a new-generation alpha-2/imidazoline receptor agonist antihypertensive drug licensed for the treatment of mild to moderate essential hypertension. It may have a role when thiazides, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers are not appropriate or have failed to control blood pressure. In addition, it demonstrates favourable effects on parameters of the insulin resistance syndrome, apparently independent of blood pressure reduction. It is also a growth hormone releaser. It is manufactured by Solvay Pharmaceuticals under the brand name Physiotens & Moxon.
 W
WNaftopidil is a drug used in benign prostatic hypertrophy which acts as a selective α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist or alpha blocker.
 W
WPargyline (brand name Eutonyl) is an irreversible selective monoamine oxidase (MAO)-B inhibitor drug (IC50 for MAO-A is 0.01152 µmol/L and for MAO-B is 0.00820 µmol/L) It was brought to market in the US and the UK by Abbott in 1963 as an antihypertensive drug branded "Eutonyl". It was one of several MAO inhibitors introduced in the 1960s including nialamide, isocarboxazid, phenelzine, and tranylcypromine. By 2007 the drug was discontinued and as of 2014 there were no generic versions available in the US. In addition to its actions as an MAOI, pargyline has been found to bind with high affinity to the I2 imidazoline receptor (an allosteric site on the MAO enzyme).
 W
WPhentolamine, sold under the brand name Regitine among others, is a reversible nonselective α-adrenergic antagonist.
 W
WPildralazine (Atensil), also known as propyldazine or propildazine, is an antihypertensive and vasodilator.
 W
WPindolol, sold under the brand name Visken among others, is a nonselective beta blocker which is used in the treatment of hypertension. It is also an antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor, preferentially blocking inhibitory 5-HT1A autoreceptors, and has been researched as an add-on therapy to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in the treatment of depression.
 W
WPrazosin is a medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure, symptoms of an enlarged prostate, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It is a less preferred treatment of high blood pressure. Other uses may include heart failure and Raynaud syndrome. It is taken by mouth.
 W
WProgesterone (P4) is a medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is a progestogen and is used in combination with estrogens mainly in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low sex hormone levels in women. It is also used in women to support pregnancy and fertility and to treat gynecological disorders. Progesterone can be taken by mouth, in through the vagina, and by injection into muscle or fat, among other routes. A progesterone vaginal ring and progesterone intrauterine device used for birth control also exist in some areas of the world.
 W
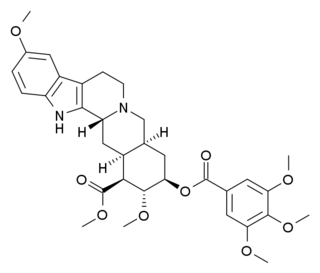
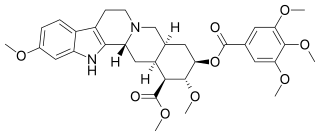
WRescinnamine, known by the brand names moderil, cinnasil, and anaprel, is an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor used as an antihypertensive drug.
 W
WReserpine is a drug that is used for the treatment of high blood pressure, usually in combination with a thiazide diuretic or vasodilator. Large clinical trials have shown that combined treatment with reserpine plus a thiazide diuretic reduces mortality of people with hypertension. Although the use of reserpine as a solo drug has declined since it was first approved by the FDA in 1955, a review recommends use of reserpine and a thiazide diuretic or vasodilator in patients who do not achieve adequate lowering of blood pressure with first-line drug treatment alone. The reserpine-hydrochlorothiazide combo pill was the 17th most commonly prescribed of the 43 combination antihypertensive pills available In 2012.
 W
WRilmenidine is a prescription medication for the treatment of hypertension. It is marketed under the brand names Albarel, Hyperium, Iterium and Tenaxum.
 W
WRostafuroxin is a digitoxigenin analog that has been shown to lower blood pressure in an animal model of hypertension. It modulates the effects of the enzyme Na+/K+-ATPase, which maintains sodium and potassium ion gradients across plasma membranes. Rostafuroxin is being studied in clinical trials for the treatment of essential hypertension.
 W
WSacubitril is an antihypertensive drug used in combination with valsartan. The combination drug sacubitril/valsartan, known during trials as LCZ696 and marketed under the brand name Entresto, is a treatment for heart failure. It was approved under the FDA's priority review process for use in heart failure on July 7, 2015.
 W
WSacubitrilat is the active metabolite of the antihypertensive drug sacubitril, which is used in the treatment of heart failure.
 W
WSyrosingopine is a drug, derived from reserpine. It is used to treat hypertension.
 W
WTiamenidine is an imidazoline compound that shares many of the pharmacological properties of clonidine. It acts as a centrally-acting α1 and α2 adrenergic receptor antagonist. In hypertensive volunteers, like clonidine, it significantly increased sinus node recovery time and lowered cardiac output. It was marketed by Sanofi-Aventis under the brand name Sundralen for the management of essential hypertension.
 W
WTolonidine is an antihypertensive.
 W
WXibenolol is a beta blocker.
 W
WXipranolol is a beta blocker.